8 Powerful Mind Mapping Techniques to Use in 2025
Unlock your creativity and boost productivity with these 8 powerful mind mapping techniques. Learn how to brainstorm, plan, and organize your ideas effectively.
In a world saturated with information, capturing, connecting, and developing ideas is a critical skill for success. Traditional linear note-taking often fails to mirror our brain's natural, associative way of thinking, leading to fragmented understanding and missed connections. This is where the power of mind mapping techniques comes in, transforming complex information into a visual, memorable, and highly organized format.
But not all mind maps are created equal. To truly enhance productivity and clarity, you need to match the method to the mission. Different goals, from strategic planning to academic research, require different visual approaches. This guide moves beyond the basics to explore eight distinct mind mapping techniques. We'll cover everything from Tony Buzan's classic radiant thinking to specialized methods like argument mapping and collaborative digital strategies.
You will learn the specific 'how' and 'why' behind each technique, complete with actionable insights and practical tips. We'll show you how to leverage these methods to elevate your brainstorming, streamline project planning with tools like Zemith, and solve complex problems more effectively. Get ready to move beyond simple bubbles and branches and harness the full power of structured visual thinking to bring your most innovative ideas to life.
1. Tony Buzan's Radiant Thinking Mind Maps
The original and most foundational of all mind mapping techniques is Tony Buzan's Radiant Thinking model. Developed in the 1970s, this method is designed to mirror the brain's natural, non-linear thought processes. It starts with a central idea, represented by an image, and expands outward through organically flowing, curved branches. Each branch represents a key thought or theme, which then spiders into smaller, associated sub-topics.
This technique moves away from traditional, linear note-taking, instead favoring a structure that mimics neural networks. The use of colors, images, and single keywords on each line helps to stimulate both the logical and creative sides of the brain, leading to enhanced memory recall and more profound insights.
Why This Technique is Foundational
Buzan’s method isn't just a diagramming tool; it's a comprehensive thinking system. Its organic nature makes it incredibly versatile, adopted by major organizations like Boeing for complex aircraft design and Range Rover for innovative product development. It taps into the brain's capacity for association, making it one of the most effective mind mapping techniques for brainstorming, studying, and strategic planning. The visual hierarchy and colorful connections make complex information easier to digest and remember.
How to Implement Radiant Thinking
Follow these actionable steps to create an authentic Buzan-style mind map:
- Start with a Central Image: Begin in the center of a blank page with a powerful image that encapsulates your main topic. This visual anchor engages your brain more effectively than a simple word.
- Use Thick, Curved Main Branches: Draw thick, organic branches radiating from the central image. Assign one key theme or category to each, using a different color to help visually separate your main ideas.
- One Word Per Line: Attach your words to lines that connect and flow from the branches. Strictly limit yourself to one keyword or a very short phrase per line. This forces precision and encourages more connections.
- Incorporate Visuals: Add small drawings, icons, and symbols throughout your map. These personal visual cues create stronger mental associations and significantly boost memory retention.
Key Insight: For teams looking to operationalize Radiant Thinking, a digital platform is invaluable. The Zemith Whiteboard provides a flexible canvas to implement these principles collaboratively. You can drag-and-drop images for your central idea, use digital pens for organic branches, and allow multiple users to contribute colors and keywords in real-time, turning a classic technique into a modern, actionable workflow.
2. Digital/Software-Based Mind Mapping
The evolution of mind mapping into the digital age has given rise to powerful software-based techniques. This modern approach uses specialized applications to create, edit, and share mind maps electronically, moving beyond the physical limitations of pen and paper. It leverages technology to integrate multimedia, facilitate real-time collaboration, and offer advanced formatting options, making it ideal for dynamic, distributed teams and complex projects.
Digital mind mapping techniques allow for a fluid and easily editable structure. Unlike a hand-drawn map, you can effortlessly rearrange nodes, expand or collapse branches, and link to external resources like documents, websites, and videos. This transforms the mind map from a static diagram into an interactive knowledge hub.

Why This Technique is Essential
Digital mind mapping excels in professional and academic environments where collaboration, speed, and integration are paramount. Companies like Microsoft use tools such as MindMeister for cross-team project management, while Siemens employs XMind for high-level strategic planning sessions. The ability to instantly share, comment on, and co-edit a map from anywhere in the world makes it a cornerstone of modern workflow. This method is perfect for remote teams, detailed project planning, and creating dynamic presentations.
How to Implement Digital Mind Mapping
Follow these actionable steps to leverage software for your mind mapping needs:
- Choose the Right Software: Select a tool that aligns with your goals. Consider platforms like Zemith that integrate mapping with other productivity tools, like document editors and AI assistants, to create a seamless workflow from idea to execution.
- Learn Keyboard Shortcuts: The primary advantage of digital mapping is speed. Mastering keyboard shortcuts for adding nodes, creating branches, and formatting text will dramatically accelerate your workflow.
- Use Templates Strategically: Many tools offer pre-built templates for common tasks like project plans or meeting agendas. Use them as a starting point, but always customize them to fit your specific context and creative style.
- Leverage Integrations: Connect your mind mapping software with other tools in your tech stack, like project management apps or cloud storage. This creates a seamless flow of information and keeps your projects synchronized.
Key Insight: For teams aiming to push the boundaries of productivity, integrating AI can further enhance digital mind mapping. AI can help automate brainstorming, summarize research, and suggest connections you might have missed. Platforms like Zemith are at the forefront, combining a flexible mapping canvas with AI-driven insights to streamline complex tasks. Discover more about the impact of AI tools on research and how they can augment your digital mapping efforts.
3. Concept Mapping
While many mind mapping techniques prioritize organic brainstorming, Concept Mapping offers a more structured, hierarchical approach to representing knowledge. Developed by Joseph Novak in the 1970s, this method focuses on clarifying the specific relationships between ideas. It moves beyond simple association by using labeled connecting lines, or "linking words," to form propositions: two or more concepts connected by words to create a meaningful statement.
Unlike the radial structure of many mind maps, a concept map is typically hierarchical, flowing from the most general concepts at the top to more specific, detailed ones at the bottom. This makes it an exceptional tool for organizing existing knowledge, studying complex subjects, and identifying gaps in understanding. Its logical framework is designed to represent propositional knowledge clearly and concisely.
This infographic illustrates the core components of a concept map, showing how a focus question guides the arrangement of general and specific concepts, with cross-links revealing deeper connections.
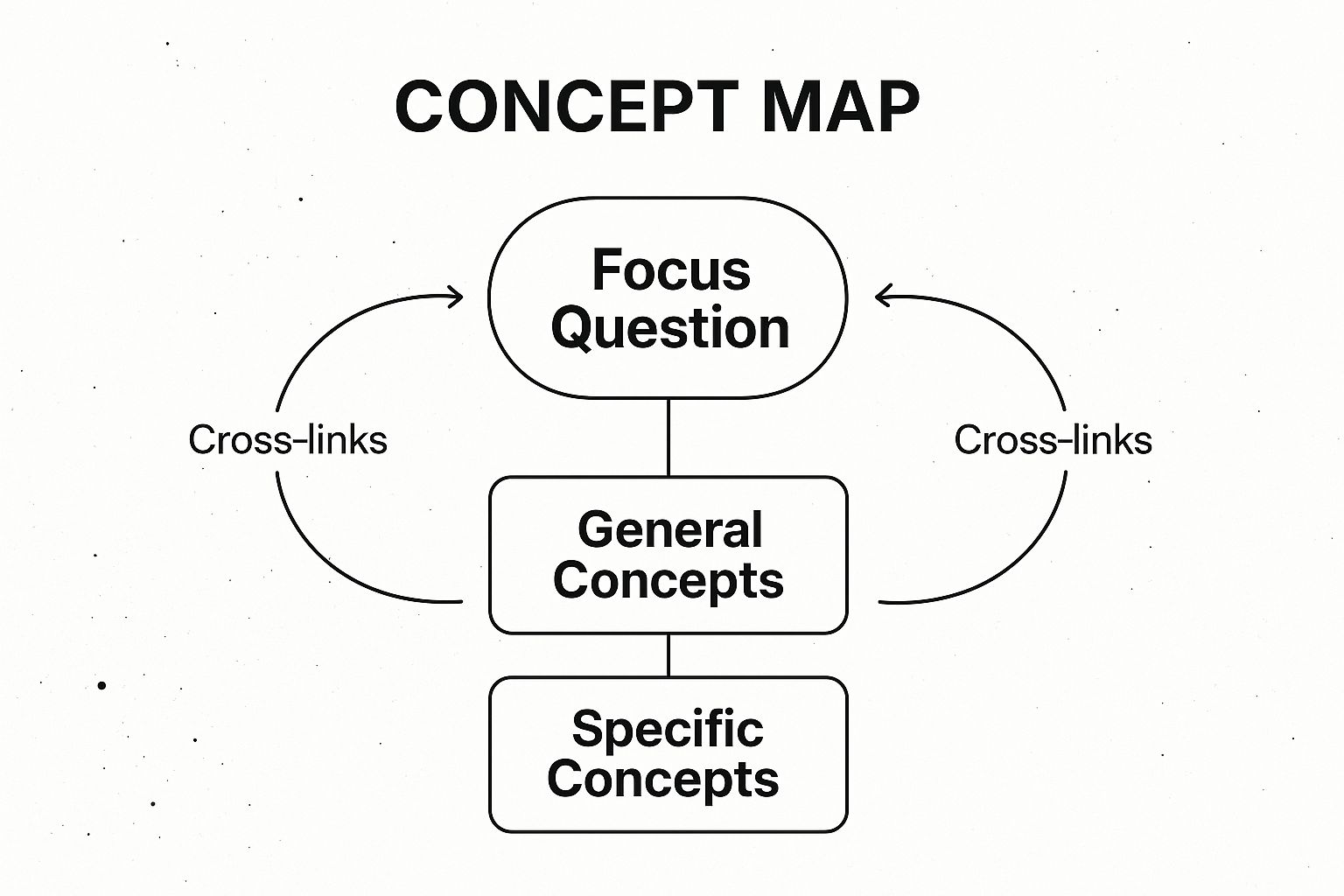
The visualization highlights how a clear hierarchy and explicit cross-links create a powerful and structured representation of knowledge.
Why This Technique is Foundational
Concept mapping is a cornerstone of meaningful learning and knowledge management. Its structured nature forces you to think critically about how ideas are related, not just that they are connected. Esteemed organizations like NASA rely on concept maps to navigate complex systems, and medical schools use them to teach intricate topics like anatomy and physiology. It provides a clear, logical snapshot of a knowledge domain, making it ideal for instructional design, knowledge transfer, and systems analysis.
How to Implement Concept Mapping
Follow these actionable steps to build a powerful concept map:
- Start with a Focus Question: Begin with a clear, specific question you want to answer. For example, "What are the key factors that influence consumer purchasing decisions?" This question provides the context for your map.
- Identify and Rank Key Concepts: Brainstorm a list of concepts related to your question. Arrange them in a hierarchy, placing the most general, inclusive concepts at the top and the more specific ones underneath.
- Connect Concepts with Linking Words: Draw lines between related concepts and add a short phrase or verb on the line to define the relationship (e.g., "leads to," "is composed of," "causes"). This creates meaningful propositions.
- Look for Cross-Links: Identify and draw connections between concepts in different branches of your map. These cross-links often reveal novel insights and a deeper, more integrated understanding of the topic.
Key Insight: To make concept maps truly actionable for a team, they must be part of a larger knowledge system. A platform like Zemith allows teams to collaboratively build concept maps on its Whiteboard, then link each concept to detailed notes, research documents, or action items within the same workspace. This transforms a static diagram into a dynamic, searchable, and executable knowledge model for the entire organization.
4. Flow-Based Mind Mapping
Unlike the radial structure of traditional mind maps, Flow-Based Mind Mapping is a dynamic approach focused on visualizing processes, sequences, and systems. It uses arrows, directional indicators, and a linear or cyclical layout to map the natural flow of thoughts, actions, or information. This technique excels at breaking down complex workflows and understanding cause-and-effect relationships.
This method shifts the focus from simple association to logical progression. It's less about brainstorming all possible ideas and more about organizing existing concepts into a coherent, actionable sequence. This makes it one of the most practical mind mapping techniques for planning projects, optimizing systems, and documenting procedures.

Why This Technique is Foundational
Flow-Based Mind Mapping is the backbone of process improvement and systems thinking. Its power lies in making abstract processes tangible and easy to analyze. For example, Toyota uses it to refine its legendary lean manufacturing processes, while Amazon employs it for supply chain optimization. In software development, teams use it for mapping user journeys to identify pain points and opportunities for a better experience. It turns a complex series of steps into a clear, visual story.
How to Implement Flow-Based Mind Mapping
Follow these actionable steps to create a clear and effective flow map:
- Define Start and End Points: Clearly identify the beginning and end of the process you are mapping. This provides a solid framework and focus for your diagram.
- Use Arrows and Directional Cues: The core of this technique is showing direction. Use clear, unambiguous arrows to connect steps and indicate the flow of the process from one stage to the next.
- Incorporate Decision Diamonds: When a process involves a choice or a conditional step, use a diamond shape. Draw branches from the diamond for each possible outcome (e.g., "Yes/No" or "Approved/Rejected").
- Color-Code Different Paths: Use distinct colors to differentiate between various process streams, user types, or parallel tasks. This adds a layer of visual clarity, making the map easier to interpret at a glance.
Key Insight: To get the most value from a flow map, it must be a living document, not a static artifact. Using an integrated platform like Zemith, teams can build flow maps on the Whiteboard, then use the AI Document Assistant to automatically generate standard operating procedures (SOPs) or project plans directly from the map's structure. This closes the gap between process design and execution, turning visual plans into actionable workflows.
5. Collaborative Mind Mapping
Collaborative mind mapping elevates the individual brainstorming process into a dynamic, team-based activity. This technique leverages collective intelligence by allowing multiple participants to simultaneously contribute to a shared mind map. By bringing diverse perspectives together, teams can generate more comprehensive, innovative, and well-rounded solutions than any single individual could alone. It's a powerful method for group brainstorming, strategic planning, and problem-solving.
This approach transforms mind mapping from a personal thinking tool into a powerful communication and alignment framework. Popularized by design thinking practitioners at institutions like Stanford's d.school and innovation consultancies such as IDEO, it fosters a shared understanding and ownership of ideas. Whether conducted in-person with a large whiteboard or virtually using digital platforms, it ensures all voices are heard and visualized in real-time.
Why This Technique is Effective
Collaborative mind mapping breaks down silos and encourages cross-pollination of ideas. It's used by agile teams at Google for product brainstorming and consulting firms like Deloitte for mapping out complex client strategies. The visual nature of the map makes it easy for teams to see connections between different ideas, identify gaps, and build upon each other's contributions. This synergy often leads to breakthrough insights that wouldn't surface in a linear discussion.
How to Implement Collaborative Mind Mapping
Follow these actionable steps for a successful collaborative session:
- Establish Clear Ground Rules: Before starting, agree on a facilitator and set protocols. Define the central topic clearly and ensure everyone understands the objective of the session.
- Use Timed Sessions: Break the mapping process into timed intervals (e.g., 10-15 minutes) to maintain energy and focus. This encourages rapid idea generation without getting bogged down in analysis.
- Structure Contributions: To ensure all voices are heard, use a platform like Zemith that allows for features like anonymous contributions or color-coded inputs per participant, which can help democratize the session.
- Assign a Facilitator: A skilled facilitator is crucial to guide the conversation, prevent single individuals from dominating, and ensure the map remains organized and focused on the core topic.
Key Insight: For teams looking to enhance their collective intelligence, these mind mapping techniques are invaluable when running a virtual brainstorming session. Digital tools like Zemith are built to facilitate this process, offering features like real-time cursors, structured templates, and easy sharing to streamline team collaboration. Using such platforms can significantly improve workflow efficiency for remote and hybrid teams.
6. Argument Mapping
Argument Mapping is a highly structured and specialized mind mapping technique designed to visually deconstruct logical reasoning. Unlike brainstorming-focused maps, this method focuses exclusively on the logical relationships between claims, evidence, and conclusions. It uses a clear, box-and-line structure with specific conventions to represent premises, co-premises, objections, and the final conclusion.
This technique is less about free-flowing creativity and more about rigorous critical thinking. It forces the user to break down an argument into its core components and evaluate the strength and validity of each part. Popularized by critical thinking educators like Tim van Gelder, argument mapping is a powerful tool for analyzing complex debates, constructing persuasive essays, or making evidence-based decisions.
Why This Technique is Foundational
Argument mapping excels where other mind mapping techniques may fall short: providing logical clarity. Its systematic approach is invaluable in fields that demand precision and evidence. For instance, law schools use it for case analysis, and policy analysts employ it to evaluate legislative proposals. By laying out the entire logical structure, it exposes weak points, unstated assumptions, and gaps in reasoning that might otherwise go unnoticed in a block of text.
How to Implement Argument Mapping
Follow these actionable steps to construct a clear and logical argument map:
- Start with the Conclusion: Identify the main claim or conclusion of the argument and place it at the very top of your map. This is the central point everything else will support or challenge.
- Identify the Premises: Below the conclusion, add the key reasons (premises) that directly support it. Connect them to the conclusion with lines, indicating a relationship of support.
- Distinguish Evidence from Opinion: For each premise, add supporting evidence, data, or facts. Use a different shape or color to clearly separate verifiable evidence from subjective opinions or assumptions.
- Incorporate Counter-Arguments: Actively seek out and map objections, counter-arguments, or rebuttals. Connect these to the specific premises they challenge, often using a different color (like red) to signify opposition.
Key Insight: An argument map becomes truly powerful when it's connected to its sources. On a platform like Zemith, teams can build an argument map on the Whiteboard and attach source documents, data snippets, and citations directly to each premise and piece of evidence. This transforms a static analysis into a dynamic, verifiable, and highly persuasive tool for deep, collaborative thinking and decision-making.
7. Systems Mind Mapping
Systems Mind Mapping transcends basic brainstorming by integrating the principles of systems thinking into a visual framework. This advanced technique isn't just about connecting ideas; it's about visualizing the intricate web of relationships, feedback loops, and emergent properties within a complex system. It shifts the focus from isolated components to the underlying structure that drives behavior.
Developed from the work of pioneers like Peter Senge and Donella Meadows, this approach is designed to uncover hidden dynamics and leverage points for change. Instead of a simple tree structure, a systems map visualizes stocks (accumulations like inventory or morale), flows (rates of change), and feedback loops (reinforcing or balancing cycles). This makes it one of the most powerful mind mapping techniques for deep analysis.
Why This Technique is Foundational
Systems Mind Mapping is a diagnostic tool for understanding complexity. It's used by leading institutions like MIT for organizational learning and by corporations like Shell for strategic scenario planning. By mapping the entire system, teams can identify root causes of persistent problems rather than just treating symptoms. It reveals how different parts of a system influence one another, often in non-obvious ways.
This method is invaluable for organizational analysis, process improvement, and strategic foresight. It helps teams see the bigger picture, anticipate the unintended consequences of decisions, and identify the most effective places to intervene for lasting improvement.
How to Implement Systems Mind Mapping
Follow these actionable steps to create a map that reveals systemic insights:
- Define System Boundaries: Clearly determine what is inside and outside the scope of your system. What are the key elements you need to analyze?
- Identify Stocks and Flows: Start by mapping the primary stocks (e.g., "Customer Satisfaction," "Product Inventory") and the flows that increase or decrease them (e.g., "New Customer Signups," "Product Sales"). Use different shapes or icons to distinguish between them.
- Map Feedback Loops: Look for connections that form circles. A reinforcing loop amplifies change (e.g., more happy customers lead to more referrals, leading to more happy customers). A balancing loop seeks stability (e.g., low inventory triggers a reorder process to restore inventory levels).
- Identify Leverage Points: Analyze the map to find points where a small change could have a significant impact on the entire system. These are your key intervention opportunities.
Key Insight: For organizations aiming to codify and share deep systemic knowledge, integrating these maps into a central repository is crucial. You can learn more about how to structure these insights by exploring effective knowledge management systems. A platform like Zemith allows teams to build, share, and iterate on these complex systems maps, turning abstract insights into a shared, actionable understanding of the organization.
8. Speed Mind Mapping
Speed Mind Mapping is a high-octane, time-constrained approach designed for rapid idea generation and immediate problem-solving. This technique prioritizes quantity over quality in its initial phase, using strict time limits to bypass the brain's natural filter. The core principle is to capture a deluge of thoughts quickly, preventing over-analysis and encouraging spontaneous, instinctual connections.
This method is less about creating a perfectly organized diagram and more about generating a raw, unfiltered snapshot of your thoughts under pressure. By forcing continuous movement and rapid association, it’s one of the most effective mind mapping techniques for breaking through creative blocks, making fast decisions, and kickstarting complex projects when momentum is critical.
Why This Technique is Effective
The power of Speed Mind Mapping lies in its ability to circumvent perfectionism and self-censorship. Innovation workshops and agile development teams rely on this method to fuel brainstorming sessions and rapid prototyping. For instance, an advertising agency might use it to generate dozens of campaign slogans in minutes, or a startup accelerator could employ it to quickly map out potential product features. It’s an invaluable tool for any scenario where quick thinking is paramount.
How to Implement Speed Mind Mapping
Follow these actionable steps to leverage speed for maximum creative output:
- Set a Visible Timer: Define a strict time limit, typically between 5 to 15 minutes, and keep the timer visible. The pressure is a key component of the technique.
- Use an AI Prompt: Kickstart your session by asking an AI tool like Zemith's Chat to generate initial seed ideas related to your topic. This can help overcome the "blank page" problem instantly.
- Focus on Quantity: Aim to fill the page with as many branches and keywords as possible within the allotted time. The objective is to generate a high volume of raw ideas to refine later.
- Refine with AI: After the timed session, use an AI assistant to automatically cluster, categorize, and even summarize the chaotic output of your speed map, instantly turning raw ideas into a structured foundation.
Key Insight: For teams operating in fast-paced environments, a digital tool can amplify the benefits of this technique. Platforms like Zemith offer a frictionless canvas where multiple users can simultaneously "dump" ideas onto a shared map in real-time. Afterward, the integrated AI can help organize the brainstormed chaos, making it perfect for remote design sprints or emergency planning sessions where every second counts.
Mind Mapping Techniques Comparison
| Mind Mapping Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tony Buzan's Radiant Thinking Mind Maps | Medium to High: Artistic skills and time needed | Moderate: Colors, images, drawing tools | Enhanced memory, creative & non-linear thinking | Education, creative planning, personal brain-storming | Engages both brain hemispheres, flexible & creative |
| Digital/Software-Based Mind Mapping | Medium: Software learning curve, subscription costs | High: Devices, internet, software licenses | Professional, collaborative maps with multimedia | Team projects, remote collaboration, professional use | Real-time collaboration, easy editing, integration |
| Concept Mapping | High: Requires subject mastery and careful design | Moderate: Analytical tools or software | Deep comprehension, knowledge gaps identification | Education, complex subject analysis, assessment | Explicit relationships, deep learning, assessment tool |
| Flow-Based Mind Mapping | Medium to High: Understanding processes required | Moderate: Visual tools, software may help | Clear process visualization, bottleneck identification | Workflow planning, project management, process improvement | Shows cause/effect, process flows, decision support |
| Collaborative Mind Mapping | Medium: Needs facilitation and coordination | High: Digital platforms or in-person setup | Diverse ideas, team alignment, consensus building | Team brainstorming, strategy sessions, workshops | Harnesses collective knowledge, promotes engagement |
| Argument Mapping | High: Logical principles & formal notation | Moderate: Specialized software or templates | Improved critical thinking & logical analysis | Debate prep, research, policy evaluation | Clarifies arguments, finds fallacies, enhances logic |
| Systems Mind Mapping | High: Systems thinking expertise required | Moderate to High: Visual and analytical tools | Reveals system behavior, root cause identification | Organizational analysis, strategy, complex problem-solving | Holistic view, identifies leverage points, strategic |
| Speed Mind Mapping | Low: Time-limited, fast execution | Low: Minimal tools, pen and paper sufficient | Rapid idea generation, breaks mental blocks | Brainstorming, quick decisions, problem-solving | Prevents overthinking, encourages spontaneity |
From Mind Map to Masterpiece with Zemith
We have journeyed through a diverse landscape of powerful mind mapping techniques, from the foundational principles of Tony Buzan’s Radiant Thinking to the specialized structures of Argument and Systems Mapping. Each method offers a unique lens through which to view complex information, break down challenges, and ignite creative solutions. You now have a versatile toolkit to tackle any project, whether you're brainstorming a new software feature, outlining a research paper, or planning a complex marketing campaign.
The core takeaway is that mind mapping is not a monolithic practice. It is a flexible, adaptable discipline that evolves with your needs. The true power isn’t just in knowing these techniques; it's in knowing when to apply them. Speed Mapping is your ally against a tight deadline, while Collaborative Mapping is essential for team alignment. Understanding this strategic application is the first step toward mastery.
Bridging the Gap from Idea to Impact
The ultimate goal of any mind map is to produce a tangible outcome: a finished report, a functional piece of code, a launched product, or a compelling presentation. This is often where the process breaks down. Ideas get trapped in static diagrams, forcing you to switch between multiple applications for research, writing, and collaboration, which fragments your focus and kills momentum.
This is precisely the gap that an integrated workspace like Zemith is designed to fill. Imagine starting your next project not with a blank page, but with a dynamic canvas. You could begin by using a flow-based mind map on Zemith’s Whiteboard to outline a user journey, then seamlessly pull in market research and data using the integrated multi-model AI. Your insights can be instantly organized and expanded upon in the Smart Notepad, which helps structure your thoughts into coherent sections.
Your Actionable Path Forward
To truly integrate these mind mapping techniques into your workflow, you need a system that supports, rather than hinders, your creative process. Here is how you can transform your approach:
- Select a Technique: For your next project, consciously choose one of the mapping styles we discussed. Are you trying to understand a complex system? Try Systems Mapping. Are you building a persuasive argument? Use Argument Mapping.
- Use an Integrated Platform: Instead of a standalone tool, use a unified hub like Zemith. This allows you to embed your mind map directly into your project workspace, keeping it connected to your research, drafts, and team discussions.
- Transform, Don't Transcribe: Leverage AI-powered tools to turn your map's nodes into actionable content. With Zemith's Document Assistant, a branch from your mind map can become the foundation for a detailed project brief, a block of code, or a section of a report, eliminating redundant manual work.
By adopting this integrated approach, your mind maps cease to be simple diagrams. They become living blueprints that guide your entire project lifecycle, from initial spark to final masterpiece. You're no longer just visualizing ideas; you are building them in an environment designed for peak productivity and creativity.
Ready to stop juggling tools and start building your best ideas? Discover how Zemith integrates powerful mind mapping capabilities with an all-in-one AI workspace to supercharge your entire creative and productive workflow. Transform your mind maps into tangible results by visiting Zemith and start your journey today.
Explore Zemith Features
Introducing Zemith
The best tools in one place, so you can quickly leverage the best tools for your needs.
All in One AI Platform
Go beyond AI Chat, with Search, Notes, Image Generation, and more.
Cost Savings
Access latest AI models and tools at a fraction of the cost.
Get Sh*t Done
Speed up your work with productivity, work and creative assistants.
Constant Updates
Receive constant updates with new features and improvements to enhance your experience.
Features
Selection of Leading AI Models
Access multiple advanced AI models in one place - featuring Gemini-2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, GPT 5, and more to tackle any tasks

Speed run your documents
Upload documents to your Zemith library and transform them with AI-powered chat, podcast generation, summaries, and more
Transform Your Writing Process
Elevate your notes and documents with AI-powered assistance that helps you write faster, better, and with less effort
Unleash Your Visual Creativity
Transform ideas into stunning visuals with powerful AI image generation and editing tools that bring your creative vision to life

Accelerate Your Development Workflow
Boost productivity with an AI coding companion that helps you write, debug, and optimize code across multiple programming languages
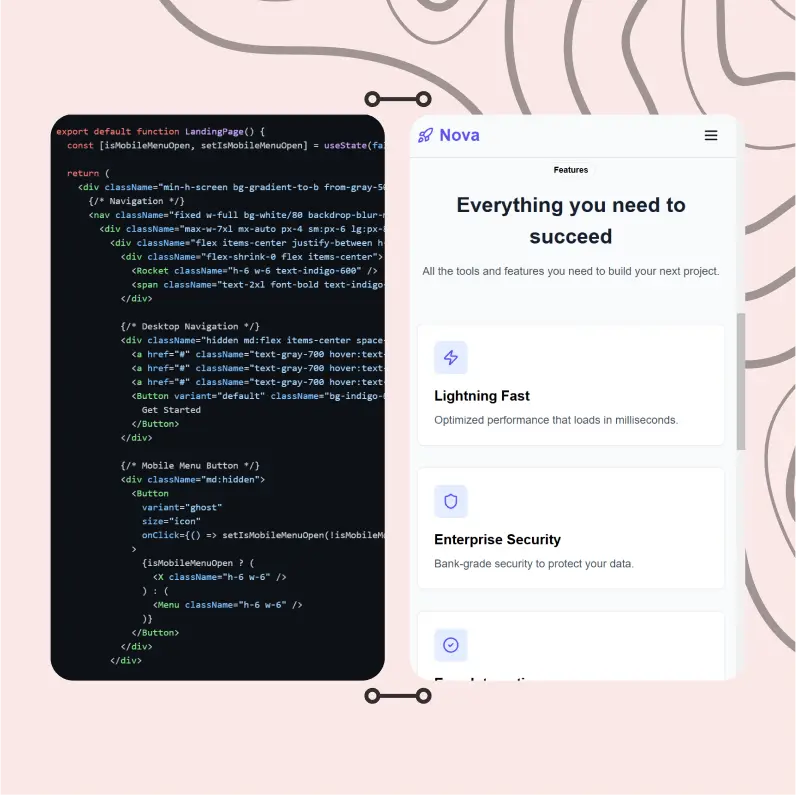
Powerful Tools for Everyday Excellence
Streamline your workflow with our collection of specialized AI tools designed to solve common challenges and boost your productivity

Live Mode for Real Time Conversations
Speak naturally, share your screen and chat in realtime with AI
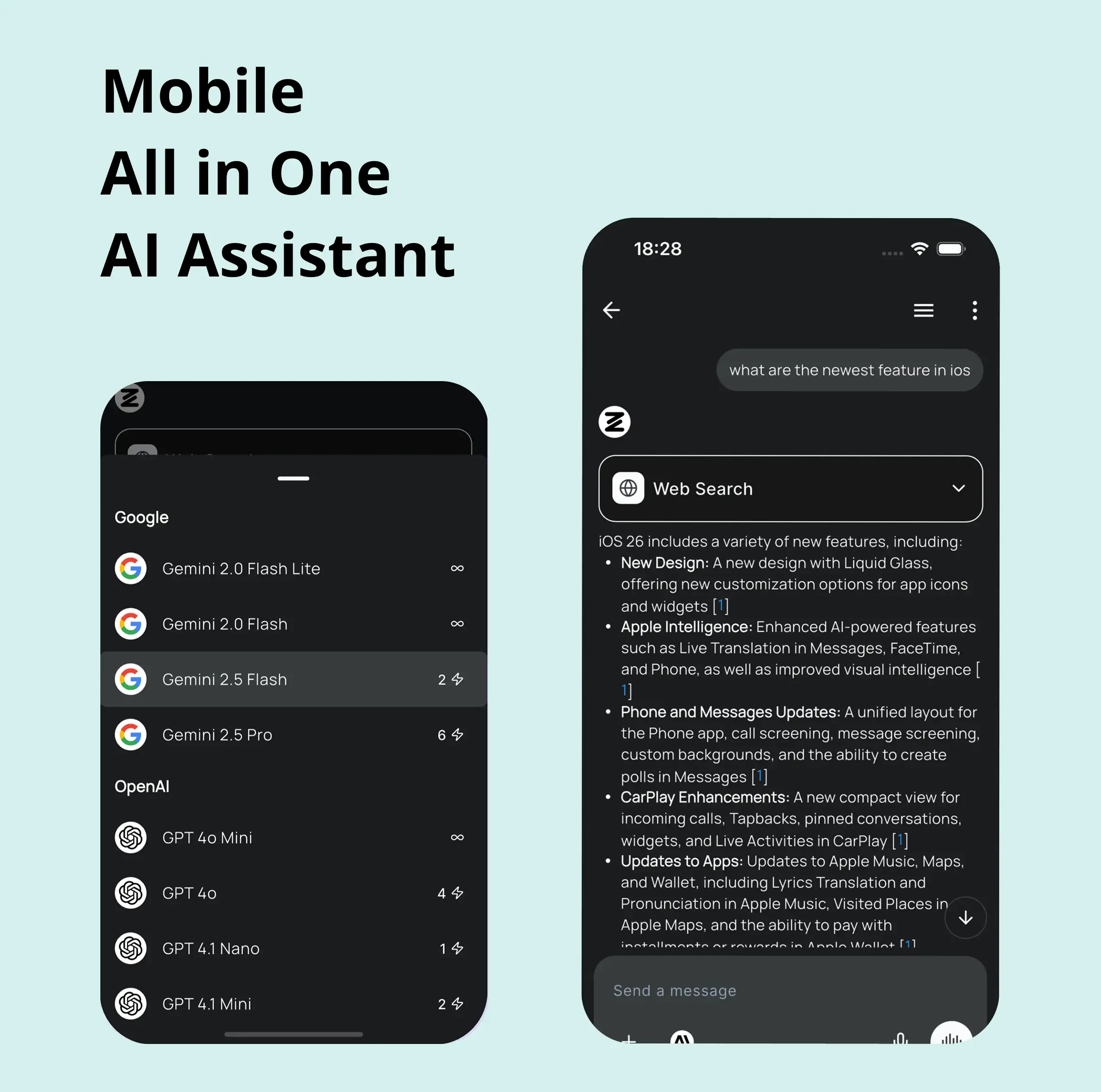
AI in your pocket
Experience the full power of Zemith AI platform wherever you go. Chat with AI, generate content, and boost your productivity from your mobile device.
Deeply Integrated with Top AI Models
Beyond basic AI chat - deeply integrated tools and productivity-focused OS for maximum efficiency
Straightforward, affordable pricing
Save hours of work and research
Affordable plan for power users
Plus
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
Professional
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
What Our Users Say
Great Tool after 2 months usage
simplyzubair
I love the way multiple tools they integrated in one platform. So far it is going in right dorection adding more tools.
Best in Kind!
barefootmedicine
This is another game-change. have used software that kind of offers similar features, but the quality of the data I'm getting back and the sheer speed of the responses is outstanding. I use this app ...
simply awesome
MarianZ
I just tried it - didnt wanna stay with it, because there is so much like that out there. But it convinced me, because: - the discord-channel is very response and fast - the number of models are quite...
A Surprisingly Comprehensive and Engaging Experience
bruno.battocletti
Zemith is not just another app; it's a surprisingly comprehensive platform that feels like a toolbox filled with unexpected delights. From the moment you launch it, you're greeted with a clean and int...
Great for Document Analysis
yerch82
Just works. Simple to use and great for working with documents and make summaries. Money well spend in my opinion.
Great AI site with lots of features and accessible llm's
sumore
what I find most useful in this site is the organization of the features. it's better that all the other site I have so far and even better than chatgpt themselves.
Excellent Tool
AlphaLeaf
Zemith claims to be an all-in-one platform, and after using it, I can confirm that it lives up to that claim. It not only has all the necessary functions, but the UI is also well-designed and very eas...
A well-rounded platform with solid LLMs, extra functionality
SlothMachine
Hey team Zemith! First off: I don't often write these reviews. I should do better, especially with tools that really put their heart and soul into their platform.
This is the best tool I've ever used. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is very fast.
reu0691
This is the best AI tool I've used so far. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is incredibly fast. Just looking at the changelogs, you can see how consistently the developers have ...
