7 Ways to Study Smarter Not Harder in 2025
Unlock your potential with these 7 powerful techniques. Learn how to study smarter not harder to boost retention, understanding, and overall productivity.
In a world of information overload, the old adage of 'the more hours you put in, the better the results' is collapsing under its own weight. The real key to academic and professional success isn't about endless nights hunched over textbooks; it's about efficiency and effectiveness. This guide is your roadmap to study smarter not harder. We will explore seven science-backed techniques that transform how you learn, helping you retain more information in less time and with less stress.
Forget burnout and embrace strategic learning. These methods are designed for deep understanding, not just rote memorization. To truly embrace this new era of effective learning, it's crucial to understand how to improve your focus and attention. As we dive into these powerful strategies, we'll also highlight how modern AI tools, like the integrated suite found on Zemith, can amplify these techniques. Tools like Zemith's AI-powered note-taking and flashcard generator help automate tedious tasks and create a personalized, powerful learning environment. Get ready to revolutionize your study habits and unlock your true potential.
1. The Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique is a powerful time management method designed to help you study smarter, not harder, by breaking down your study sessions into focused, manageable intervals. Developed by Francesco Cirillo in the late 1980s, this system leverages intense focus and scheduled breaks to maximize mental agility and prevent the burnout that often comes with long, unstructured study periods. It's a simple yet profoundly effective way to conquer procrastination and improve concentration.
The process is straightforward: you work in 25-minute sprints called "pomodoros," followed by a short 5-minute break. After completing four consecutive pomodoros, you reward yourself with a longer, more restorative break of 15-30 minutes. This cycle trains your brain to maintain high levels of focus for short periods, making daunting tasks like exam preparation or complex research feel much more approachable.

How to Implement the Pomodoro Technique
To get started, you only need a timer and a clear task list. The key is strict adherence to the work-break cycle. During a 25-minute pomodoro, your only job is to focus on the pre-selected task, with zero distractions allowed. This means putting your phone on silent, closing irrelevant browser tabs, and signaling to others that you are in a deep work session.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Plan Your Pomodoros: Before starting, decide exactly which tasks you will tackle. For example, dedicate one pomodoro to reading a chapter, another to summarizing notes, and a third to solving practice problems.
- Use a Dedicated Timer: A physical timer or a specialized app can help you stay honest. The ticking sound of a physical timer can be a psychological cue to remain on task.
- Make Breaks Restful: Your 5-minute breaks should be a true mental reset. Avoid checking your phone or email. Instead, stand up, stretch, grab a glass of water, or simply look out a window. This allows your brain to consolidate information and prepare for the next sprint.
- Track Your Progress with Zemith: Keep a log of how many pomodoros you complete each day. Platforms like Zemith integrate task management with your notes, allowing you to track time spent on specific topics, providing a sense of accomplishment and valuable data on your productivity patterns.
The Pomodoro Technique is incredibly versatile, adopted by software developers and writers alike. By mastering this technique, especially when integrated with a knowledge management tool, you can transform your study habits, enabling you to learn more effectively in less time.
2. Active Recall
Active Recall is a highly effective learning technique that shifts your focus from passively consuming information to actively retrieving it from your memory. Instead of re-reading a textbook chapter or reviewing your notes, you challenge your brain to pull out the information on its own. This process of retrieval is a mental workout that significantly strengthens the neural pathways associated with that memory, making it far more durable and easier to access in the future. This method is a cornerstone of how to study smarter, not harder.
The core principle is simple: testing is a tool for learning, not just for assessment. Each time you force yourself to remember a concept, formula, or definition without looking at the source material, you are signaling to your brain that this information is important and should be retained. This effortful process leads to deeper, more meaningful learning than the false sense of familiarity gained from passive review. It's the difference between recognizing a face in a crowd and being able to sketch it from memory.

How to Implement Active Recall
To integrate Active Recall into your study routine, you need to transform your study materials into self-testing opportunities. This means turning passive review sessions into active practice sessions. Instead of reading a chapter, your goal becomes answering questions about it from memory. A medical student might use flashcards to recall anatomical terms, while a history student creates quizzes from their notes.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Instantly Generate Flashcards with Zemith: Don't just put a term on one side and a definition on the other. With Zemith's AI flashcard generator, you can automatically create question-based cards directly from your notes, forcing you to think deeply. For example, it can turn a note on "Photosynthesis" into a question like "What are the inputs and outputs of photosynthesis?"
- Use the Blank Sheet Method: After studying a topic, take out a blank piece of paper and write down everything you can remember about it. Then, compare your sheet to your notes to identify knowledge gaps.
- Explain Concepts Aloud: Try to teach the concept to an imaginary student or a study partner. This forces you to articulate your thoughts clearly and reveals where your understanding is weak.
- Turn Notes into Questions: Go through your notes and rephrase key points as questions in the margin. Later, you can cover the notes and use these questions to quiz yourself.
While active recall is a powerful technique, exploring broader active learning strategies can further enhance your study methods. Using a platform like Zemith that centralizes note-taking and AI-powered quizzing can streamline the entire active recall process.
3. Spaced Repetition
Spaced Repetition is a powerful learning technique that helps you study smarter, not harder, by interrupting the natural process of forgetting. Based on the "forgetting curve" research by Hermann Ebbinghaus, this method involves reviewing information at systematically increasing intervals. Instead of cramming, you strategically revisit material just before you are about to forget it, which dramatically improves long-term memory retention and makes learning more efficient.
The core principle is simple: each time you successfully recall a piece of information, the interval before the next review gets longer. For example, a concept you review today might be scheduled for review again in three days, then a week, then two weeks, and so on. This active recall process strengthens neural pathways, moving knowledge from your fragile short-term memory into robust, long-term storage.
The following infographic illustrates the initial review cycle in a typical Spaced Repetition schedule, showing how reviews become less frequent over time as memory strengthens.
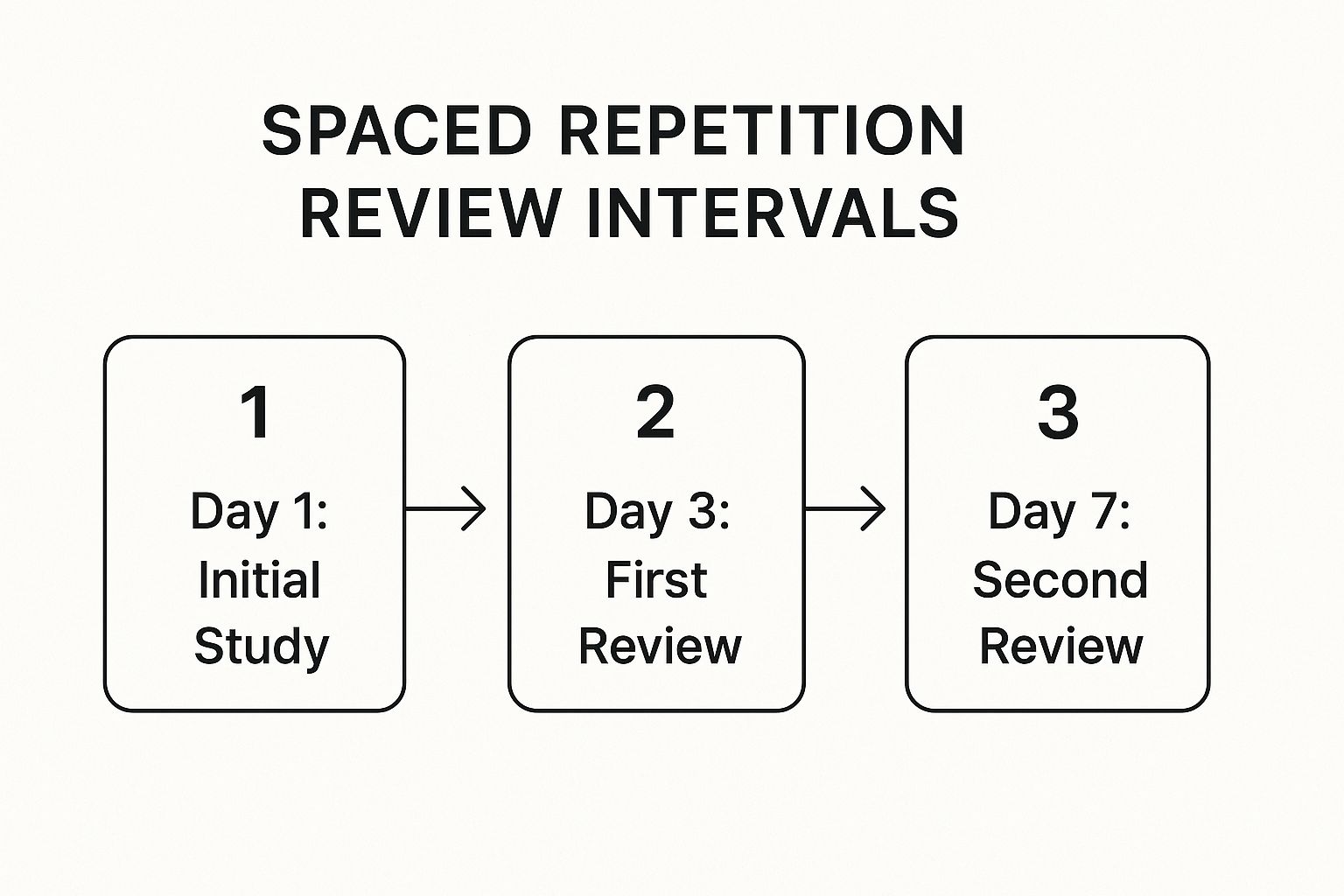
This process demonstrates how the initial heavy lifting of memorization transitions into lighter, periodic maintenance, cementing knowledge for the long term.
How to Implement Spaced Repetition
The most effective way to implement Spaced Repetition is with dedicated flashcard software that automates the scheduling process. These tools use algorithms to determine the optimal time for you to review each piece of information based on your previous performance. Your primary task is to create the study materials and commit to consistent daily reviews.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Use Integrated Software like Zemith: Platforms like Zemith are built to integrate Spaced Repetition directly with your notes. This eliminates the need for separate apps and ensures that the information you capture is automatically scheduled for review, saving you time and effort.
- Create Simple, Atomic Cards: Each flashcard should test only one piece of information. For example, instead of a card asking "Describe photosynthesis," create separate cards for "What is the primary pigment in photosynthesis?" and "What are the outputs of the light-dependent reactions?"
- Make It a Daily Habit: Consistency is crucial. Set aside a specific time each day for your reviews. This routine ensures you never fall behind on your scheduled cards, which is key to making the system work.
- Enhance Cards with Cues: Incorporate images, mnemonics, or personal examples into your flashcards. These visual and associative cues create stronger memory links, making information easier to recall.
Spaced Repetition is a foundational technique for anyone who needs to master a large body of information. By leveraging a tool like Zemith that combines note-taking with automated Spaced Repetition, you can build a comprehensive learning system and ensure the knowledge you gain today is still accessible weeks, months, and even years from now.
4. The Feynman Technique
The Feynman Technique is a mental model for learning that forces you to understand a concept so deeply that you can explain it in the simplest terms. Named after Nobel laureate physicist Richard Feynman, this method is a cornerstone for anyone looking to study smarter, not harder, by transforming passive memorization into active, durable knowledge. It's built on the idea that if you can't explain something simply, you don't truly understand it. This forces you to identify and fill the gaps in your own comprehension.
The technique involves a four-step process: choose a concept, attempt to teach it to a beginner, identify the areas where you struggle, and then review and simplify your explanation. This iterative cycle deconstructs complex information into its core components. By doing so, you build a solid foundation of understanding rather than just a superficial familiarity with the topic.
How to Implement the Feynman Technique
To begin, all you need is a piece of paper, a pen, and a concept you wish to master. The goal is to move beyond jargon and complex terminology to articulate the idea using plain language. This process reveals precisely where your knowledge is weak, allowing you to target your study efforts effectively.
For instance, a biology student might try explaining photosynthesis using only everyday words and simple analogies, as if teaching a ten-year-old. Similarly, an engineering student could break down thermodynamics using examples like a boiling kettle or a refrigerator.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Use Zemith for AI-Powered Simplification: Start by taking notes on a topic. Then, use Zemith's AI to "Explain Like I'm 5." This instantly gives you a simplified version to use as a baseline for your own explanation, helping you identify complex jargon and find simpler language.
- Lean on Analogies: Use real-world analogies and metaphors to connect abstract concepts to familiar experiences. This makes the information more relatable and easier to grasp for both you and your imaginary student.
- Explain to a Real Person: If possible, practice explaining the topic to a friend or family member who has no background in the subject. Their questions will quickly highlight areas where your explanation is unclear or incomplete.
- Focus on the 'Why': Don't just explain what something is; focus on why it works the way it does and how its components interact. This promotes a deeper, more conceptual understanding.
The Feynman Technique is exceptionally powerful for complex subjects and is a critical skill for tasks like academic writing. To apply this method to your academic work, you can find more strategies in our guide to research paper writing tips on zemith.com. By consistently applying this technique, you can ensure you are truly learning and not just memorizing.
5. Mind Mapping
Mind Mapping is a dynamic visual learning technique that helps you study smarter, not harder, by organizing information in a way that mirrors how your brain naturally works. Popularized by author Tony Buzan, this method arranges concepts in a hierarchical, radial structure that resembles a tree or web. It allows you to break down complex topics into digestible pieces, fostering creativity and making it easier to see the connections between different ideas.
Starting with a central topic, you extend main branches for major subtopics and then add smaller branches for supporting details. This process engages both the logical and creative sides of your brain, which enhances memory retention and deepens your understanding. Instead of linear, text-heavy notes, you create a vibrant, memorable diagram that simplifies complex information and boosts recall.

How to Implement Mind Mapping
To create a mind map, you begin with a blank page or a digital canvas, placing your main subject in the center. From there, you draw branches outward for each key theme or sub-category. For example, a history student could place "World War II" at the center, with main branches for "Causes," "Major Battles," and "Consequences," and smaller branches detailing specific events or figures for each.
The goal is to capture thoughts and information rapidly without being constrained by a rigid structure. It's an ideal method for brainstorming essays, summarizing lecture content, or planning complex projects.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Start with a Central Image: Use a powerful image or a clear keyword in the center to represent your main topic. This visual anchor makes the subject more memorable.
- Use Color and Keywords: Assign different colors to different themes or branches to create visual separation. Stick to single keywords or very short phrases instead of long sentences to keep the map clean and focused.
- Embrace Curves and Symbols: Draw curved, organic lines instead of straight ones, as they are more visually engaging. Add small icons, symbols, and images to reinforce ideas and improve memory recall.
- Leverage Integrated Digital Tools: While pen and paper are great, tools like Zemith integrate mind mapping directly with your notes and flashcards. You can create a mind map to brainstorm, then convert key nodes into flashcards for active recall with a single click, creating a seamless learning workflow.
By mastering mind mapping within a connected ecosystem like Zemith, you can transform how you process and retain information, making your study sessions far more effective and efficient.
6. Interleaving
Interleaving is a sophisticated learning strategy that helps you study smarter, not harder, by mixing different but related topics or skills within a single study session. Instead of practicing one concept repeatedly before moving to the next (known as "blocked practice"), interleaving forces your brain to constantly switch gears. This method enhances your ability to differentiate between concepts and choose the correct solution, leading to deeper, more durable learning.
The core idea is that this mental scrambling makes learning feel harder initially but results in significantly better long-term retention. By alternating between different types of problems, such as algebra and geometry, you train your brain not just to execute a procedure but to recognize which procedure to use in the first place. This skill is crucial for real-world problem-solving and exam performance where questions are mixed up.
How to Implement Interleaving
To begin using interleaving, you need to shift from studying in blocks to creating a mixed practice schedule. Instead of dedicating an entire evening to one subject, you will intentionally jump between several related ones. This process prevents your brain from going on autopilot and promotes more active, engaged thinking.
For example, a language learner might cycle through vocabulary flashcards, a grammar exercise, and a short listening comprehension task all within one hour. Each switch forces a mental reset and retrieval of different knowledge sets, strengthening the neural pathways for each skill.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Organize Your Mix with Zemith: Before you start, identify three to four related topics. Use Zemith's tagging or nested folder system to group related notes (e.g., algebra, geometry, trigonometry). This makes it easy to pull up different topics and switch between them seamlessly during your study session.
- Keep Switches Frequent: Initially, try switching topics every 15-20 minutes. This prevents you from getting too comfortable with one problem type and forces your brain to stay agile.
- Focus on Related Concepts: Interleaving works best when the topics share underlying principles but require different strategies. Mixing wildly unrelated subjects, like history and calculus, is less effective than mixing different types of math problems.
- Combine with Spaced Repetition: For maximum impact, pair interleaving with spaced repetition. Reviewing your mixed-topic sessions at increasing intervals will solidify your understanding and combat the forgetting curve.
Interleaving is a powerful technique embraced in fields from sports psychology to music education. By using a tool like Zemith to organize your study materials, you can easily implement this advanced strategy and build a more flexible and robust understanding of any subject.
7. Elaborative Interrogation
Elaborative interrogation is a powerful cognitive strategy that helps you study smarter, not harder, by transforming passive learning into an active process of inquiry. Instead of simply memorizing facts, this technique involves asking "why" and "how" questions to generate deep, meaningful explanations for what you are learning. It forces you to connect new information with existing knowledge, building a robust and interconnected mental framework.
The core principle is to challenge every new piece of information you encounter. By questioning the underlying reasons and mechanisms, you move beyond surface-level understanding to grasp the core concepts. This method is particularly effective because it mimics how experts think, constantly probing for deeper connections and causal relationships. It forces your brain to work harder at the moment of learning, which significantly strengthens long-term retention.
How to Implement Elaborative Interrogation
To begin, you simply need to cultivate a habit of curiosity. As you read a textbook, watch a lecture, or review your notes, pause frequently to ask questions about the material. The goal is to construct a logical explanation in your own words, rather than just rereading or highlighting the text. This active construction process is what makes the learning stick.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Ask AI "Why" with Zemith: As you take notes, use Zemith's AI chat to ask "Why is this true?" or "How does this concept relate to [another topic]?" The AI can generate explanations and highlight connections you might have missed, sparking deeper inquiry and helping you build a more robust mental model.
- Connect New to Old: Actively try to link new facts to concepts you already understand. Ask, "How does this new information relate to what I learned last week?"
- Generate Multiple Explanations: Don't settle for the first reason that comes to mind. Challenge yourself to think of several possible explanations for a phenomenon, then evaluate which one is most plausible.
- Verify Your Reasoning: After creating your own explanation, check it against reliable sources like your textbook or academic journals. This step corrects misunderstandings and reinforces the correct information.
This technique is a cornerstone of critical thinking. By embedding elaborative interrogation into your study routine, especially with an AI assistant like the one in Zemith to act as a Socratic partner, you can master complex topics more effectively and achieve deep, lasting comprehension.
7-Method Study Techniques Comparison
| Technique | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pomodoro Technique | Low - simple timer-based routine | Minimal - timer or app | Improved focus, reduced fatigue, higher productivity | Task-based learning, consistent study schedules | Boosts concentration, easy to start |
| Active Recall | Medium - needs practice and materials | Moderate - flashcards, apps like Anki | Strong long-term retention, better exam performance | Any subject, exam prep, identifying knowledge gaps | Enhances memory retention, efficient study |
| Spaced Repetition | Medium - requires setup and discipline | Moderate - software (Anki, Memrise) | Maximized retention with less total study time | Memorization of large factual datasets | Optimal scheduling, prevents cramming |
| Feynman Technique | Medium to high - time intensive | Low - pen and paper or digital notes | Deep understanding and mastery of concepts | Complex topics, teaching, conceptual learning | Builds comprehension and communication skills |
| Mind Mapping | Medium - artistic or digital tools | Low to moderate - paper, pens, or apps | Improved creativity, concept connections, memory aid | Brainstorming, organizing complex information | Visual and verbal integration, enhances recall |
| Interleaving | Medium - requires careful planning | Minimal - varied study materials | Better discrimination and flexible problem-solving | Mixed topics study, skills practice | Enhances transfer of learning, reduces overconfidence |
| Elaborative Interrogation | Medium - requires active questioning | Low - pen and paper or digital notes | Deeper understanding and critical thinking | Understanding causal and mechanistic relationships | Promotes critical thinking, stronger memory |
Integrate and Amplify: Your Path to Supercharged Learning
Navigating the landscape of advanced learning requires more than sheer effort; it demands a strategic, integrated approach. Throughout this article, we've dissected powerful techniques designed to help you study smarter not harder. We explored the disciplined focus of the Pomodoro Technique, the memory-forging power of Active Recall, and the long-term retention benefits of Spaced Repetition.
We also uncovered methods for deep comprehension. The Feynman Technique taught us to simplify complexity, Mind Mapping showed us how to visualize connections, Interleaving demonstrated the value of varied practice, and Elaborative Interrogation pushed us to ask "why" to build stronger neural pathways. Each strategy is a potent tool on its own, but their true potential is unlocked when you weave them together into a personalized learning system.
From Individual Tactics to an Integrated System
The goal is not to randomly apply these methods but to build a cohesive workflow. True mastery in how to study smarter not harder comes from synergy. Imagine this workflow, powered by Zemith:
- You use the Pomodoro Technique to dedicate a focused 25-minute block to a new topic, tracking your time within Zemith.
- During this time, you apply the Feynman Technique, writing a simplified explanation of the concept in your notes and using Zemith's AI to help simplify it further.
- Next, you create a Mind Map in Zemith to visually connect this new concept to other components of the system you already understand.
- From your simplified notes, you instantly generate Active Recall flashcards with Zemith's AI.
- Finally, Zemith automatically schedules these flashcards using a built-in Spaced Repetition system to ensure the knowledge moves from short-term to long-term memory.
This integrated process transforms passive reading into an active, multi-faceted learning experience. The key is to move beyond simply knowing about these techniques and start consciously combining them, which a unified platform makes effortless.
Your Action Plan for Smarter Studying
Embarking on this journey doesn't require a complete overhaul of your current habits overnight. The most sustainable path is one of gradual integration. Start by selecting one or two techniques that seem most applicable to your immediate goals.
Your Next Step: Choose one technique to implement this week. Will it be using Pomodoros to manage your study sessions? Or applying the Feynman Technique to that one complex topic you've been avoiding? Commit to one small change.
The profound benefit of adopting these strategies extends far beyond passing an exam or completing a project. It’s about building a sustainable framework for lifelong learning, enabling you to acquire new skills faster, retain information longer, and solve complex problems with greater clarity and confidence. By mastering how you learn, you equip yourself to thrive in a world where continuous adaptation is not just an advantage, but a necessity.
Ready to stop juggling apps and start building your integrated learning system? Zemith centralizes your knowledge and supercharges your study sessions with AI-powered tools like instant flashcard generation and smart summaries, making it effortless to apply these techniques. Transform your learning workflow and unlock your full potential by visiting Zemith today.
Explore Zemith Features
Introducing Zemith
The best tools in one place, so you can quickly leverage the best tools for your needs.
All in One AI Platform
Go beyond AI Chat, with Search, Notes, Image Generation, and more.
Cost Savings
Access latest AI models and tools at a fraction of the cost.
Get Sh*t Done
Speed up your work with productivity, work and creative assistants.
Constant Updates
Receive constant updates with new features and improvements to enhance your experience.
Features
Selection of Leading AI Models
Access multiple advanced AI models in one place - featuring Gemini-2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, GPT 5, and more to tackle any tasks

Speed run your documents
Upload documents to your Zemith library and transform them with AI-powered chat, podcast generation, summaries, and more
Transform Your Writing Process
Elevate your notes and documents with AI-powered assistance that helps you write faster, better, and with less effort
Unleash Your Visual Creativity
Transform ideas into stunning visuals with powerful AI image generation and editing tools that bring your creative vision to life

Accelerate Your Development Workflow
Boost productivity with an AI coding companion that helps you write, debug, and optimize code across multiple programming languages
Powerful Tools for Everyday Excellence
Streamline your workflow with our collection of specialized AI tools designed to solve common challenges and boost your productivity

Live Mode for Real Time Conversations
Speak naturally, share your screen and chat in realtime with AI
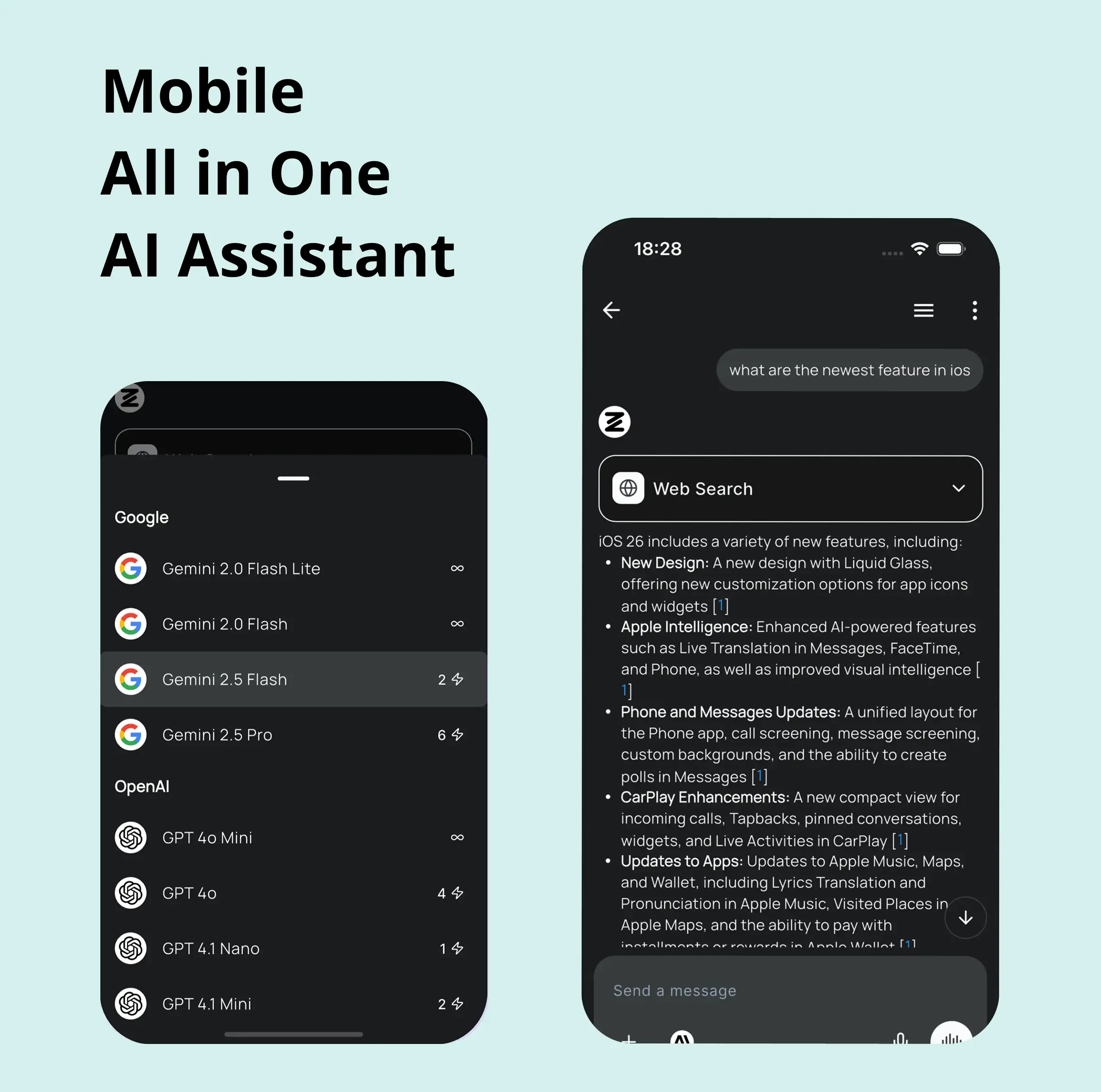
AI in your pocket
Experience the full power of Zemith AI platform wherever you go. Chat with AI, generate content, and boost your productivity from your mobile device.
Deeply Integrated with Top AI Models
Beyond basic AI chat - deeply integrated tools and productivity-focused OS for maximum efficiency
Straightforward, affordable pricing
Save hours of work and research
Affordable plan for power users
Plus
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
Professional
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
What Our Users Say
Great Tool after 2 months usage
simplyzubair
I love the way multiple tools they integrated in one platform. So far it is going in right dorection adding more tools.
Best in Kind!
barefootmedicine
This is another game-change. have used software that kind of offers similar features, but the quality of the data I'm getting back and the sheer speed of the responses is outstanding. I use this app ...
simply awesome
MarianZ
I just tried it - didnt wanna stay with it, because there is so much like that out there. But it convinced me, because: - the discord-channel is very response and fast - the number of models are quite...
A Surprisingly Comprehensive and Engaging Experience
bruno.battocletti
Zemith is not just another app; it's a surprisingly comprehensive platform that feels like a toolbox filled with unexpected delights. From the moment you launch it, you're greeted with a clean and int...
Great for Document Analysis
yerch82
Just works. Simple to use and great for working with documents and make summaries. Money well spend in my opinion.
Great AI site with lots of features and accessible llm's
sumore
what I find most useful in this site is the organization of the features. it's better that all the other site I have so far and even better than chatgpt themselves.
Excellent Tool
AlphaLeaf
Zemith claims to be an all-in-one platform, and after using it, I can confirm that it lives up to that claim. It not only has all the necessary functions, but the UI is also well-designed and very eas...
A well-rounded platform with solid LLMs, extra functionality
SlothMachine
Hey team Zemith! First off: I don't often write these reviews. I should do better, especially with tools that really put their heart and soul into their platform.
This is the best tool I've ever used. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is very fast.
reu0691
This is the best AI tool I've used so far. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is incredibly fast. Just looking at the changelogs, you can see how consistently the developers have ...
