10 Project Management Best Practices for 2025 Success
Discover 10 actionable project management best practices to boost efficiency and drive success. Learn key strategies for planning, risk, and team alignment.
In today's fast-paced environment, mastering project management isn't just an advantage—it's a fundamental requirement for success. Sticking to outdated or informal methods often leads to missed deadlines, significant budget overruns, and frustrated, inefficient teams. To truly excel and deliver consistent results, you need a modern, actionable framework built on proven principles. This guide outlines 10 critical project management best practices designed to bring clarity, predictability, and efficiency to your workflow.
Each principle covered is a crucial building block for creating more streamlined and successful project outcomes. We will move beyond generic advice to provide concrete implementation steps and real-world examples. We'll explore how integrating these strategies, especially when supported by a unified workspace like Zemith, can transform your entire process from initial scoping to final review. This approach turns potential project chaos into a well-oiled machine, ensuring every initiative is set up for success from day one. For a comprehensive guide on optimizing project success, explore these additional resources on Project Management Best Practices. This article serves as your blueprint for turning good projects into great ones.
1. Define Clear Project Scope and Objectives
Establishing a crystal-clear project scope and defining measurable objectives is the cornerstone of effective project management. This foundational step involves creating a detailed project charter that outlines deliverables, sets firm boundaries, and establishes specific success criteria before any work begins. This practice is non-negotiable; it acts as your project's constitution, preventing scope creep and ensuring every stakeholder shares a unified vision from day one.

Think of NASA’s Apollo 11 mission: its primary objective was unambiguous- "performing a crewed lunar landing and return to Earth." This clarity drove every decision. Similarly, when launching a new software feature, a clear objective isn't just "build a new dashboard"; it's "increase user engagement by 15% within Q3 by launching an intuitive, real-time analytics dashboard." This level of specificity transforms a vague idea into an achievable target, making it a critical project management best practice.
How to Implement This Practice
The first step is centralizing all project documentation. A unified workspace like Zemith is invaluable here, providing a single source of truth where scope documents, work breakdown structures, and stakeholder agreements can be drafted, stored, and accessed by the entire team, ensuring everyone is working from the same playbook.
- Develop a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Deconstruct the total project scope into smaller, more manageable tasks and sub-tasks.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Host workshops to gather input and secure buy-in on the scope document from all essential parties.
- Establish a Change Control Process: Define and communicate the formal process for requesting, evaluating, and approving any changes to the project scope.
- Document Everything: Clearly list all assumptions, constraints, and out-of-scope items to eliminate ambiguity.
2. Implement Effective Communication Plans
A project's success is intrinsically linked to the quality of its communication. Implementing an effective communication plan ensures that the right information reaches the right stakeholders at the right time, preventing misunderstandings and keeping everyone aligned. This proactive approach involves defining communication channels, setting a cadence for updates, and establishing clear protocols for reporting progress and escalating issues. It's the circulatory system of a project, delivering vital information that keeps all parts working in harmony.

Consider Amazon's PR/FAQ document process for new products. Before writing a single line of code, teams draft an internal press release and an FAQ document, forcing them to crystallize the project's purpose and anticipate stakeholder questions. This creates a powerful communication artifact that aligns everyone from engineers to executives. Similarly, a well-executed communication strategy isn't just about sending emails; it's a core component of project management best practices that fosters transparency and trust, directly impacting team morale and project outcomes.
How to Implement This Practice
Instead of fragmented email chains and chat messages, an actionable first step is to create a unified hub for all project-related discussions and updates. A platform like Zemith accomplishes this by centralizing communication and documentation, ensuring everyone has access to the latest information and reducing the risk of decisions being made on outdated data.
- Tailor Communication to Stakeholders: Not everyone needs the same level of detail. Create different report templates and frequencies for team members, executives, and clients.
- Establish Clear Escalation Paths: Document and share the process for raising critical issues, ensuring problems are addressed swiftly by the correct personnel.
- Use Visual Dashboards: Leverage project management tools to provide real-time, at-a-glance status updates on key metrics and milestones.
- Schedule Regular Check-ins: Institute daily stand-ups for the core team and weekly or bi-weekly syncs for broader stakeholder groups to maintain alignment.
3. Risk Management and Mitigation Planning
A key project management best practice is the proactive identification, assessment, and management of potential project risks. Instead of reacting to problems as they arise, this approach involves systematically analyzing what could go wrong and creating robust contingency plans. By anticipating obstacles, you can neutralize threats before they derail your timeline, budget, or quality standards, turning uncertainty into a managed variable.

Consider large-scale construction projects that develop detailed mitigation plans for supply chain disruptions and adverse weather conditions. Similarly, Google’s engineers conduct rigorous risk assessments before rolling out major algorithm updates to prevent negative impacts on search results. This foresight is not about pessimism; it's about building resilience and ensuring project success against all odds. It solidifies your control over the project's destiny, rather than leaving it to chance.
How to Implement This Practice
Effective risk management relies on continuous monitoring and transparent communication. To make this actionable, use a centralized tool like Zemith to create and track a risk register. This allows your team to assign ownership for each risk and link mitigation tasks directly to the project plan, creating a dynamic, accessible system for managing threats.
- Conduct Regular Risk Brainstorming: Hold dedicated sessions with your team and stakeholders to identify potential risks across all project areas.
- Use a Probability-Impact Matrix: Qualitatively assess each risk by plotting its likelihood against its potential impact to prioritize your focus.
- Assign Risk Owners: Designate a specific team member to monitor each identified risk and lead the execution of its response plan.
- Develop Response Plans: For high-priority risks, create clear action plans detailing how the team will avoid, mitigate, transfer, or accept the risk.
4. Agile and Iterative Development Approaches
Adopting agile and iterative methodologies is a transformative project management best practice for navigating complex projects in a dynamic environment. Instead of a single, long-term plan, this approach breaks projects into smaller, manageable increments called sprints. It emphasizes continuous collaboration, customer feedback, and adaptive planning, allowing teams to respond quickly to changes while delivering tangible value throughout the project lifecycle.

Consider Spotify's famous "squad" model. Small, autonomous teams work in rapid cycles to develop and improve features for their streaming platform, enabling constant innovation. Similarly, Salesforce continuously delivers platform updates through an iterative process, ensuring the product evolves based on real-time market demands. This flexibility and focus on incremental delivery are what make Agile a cornerstone of modern project management.
How to Implement This Practice
Implementing Agile requires a cultural shift towards transparency and adaptation, supported by the right tools. A centralized workspace like Zemith promotes this shift by providing integrated tools for sprint planning, backlog management, and visual progress tracking. This ensures everyone, from developers to stakeholders, has real-time visibility into the project's status.
- Invest in Team Training: Equip your team with the knowledge of Agile principles and frameworks like Scrum or Kanban.
- Establish a Clear "Definition of Done": Create specific, agreed-upon criteria for when a task or user story is officially complete to ensure quality.
- Use Burndown Charts: Track progress visually to see if you are on schedule to complete the planned work within a sprint.
- Start with a Pilot Project: Test the agile approach on a smaller, lower-risk project before rolling it out across the entire organization.
5. Resource Planning and Allocation
Effective project management hinges on the strategic allocation of your most valuable assets: your people, budget, and tools. Resource planning is the process of identifying, forecasting, and assigning these resources to tasks over the project’s lifecycle. This practice is essential for preventing team burnout, avoiding budget overruns, and ensuring that you have the right talent and equipment available precisely when needed. It transforms your project plan from a simple to-do list into a feasible, operational roadmap.
Consider how Apple orchestrates its product launches. They meticulously allocate experts from design, engineering, and marketing into cross-functional teams, ensuring every stage has the required skill set without overburdening any single department. This level of coordination is a masterclass in resource allocation. Similarly, in construction, optimizing the deployment of heavy machinery and skilled labor is the difference between a profitable project and a costly delay. This strategic approach is a universal project management best practice that maximizes efficiency and guarantees operational readiness.
How to Implement This Practice
Mastering resource allocation requires complete visibility into team capacity and project demands. An actionable way to achieve this is by using a centralized platform that provides a clear view of schedules and workloads. This proactive visibility, which a unified workspace like Zemith can provide, helps you manage multiple projects without creating bottlenecks or overwhelming your team.
- Utilize Resource Management Software: Adopt a tool that provides a centralized view of everyone's workload, availability, and skills. This makes assigning the right person to the right task significantly easier.
- Plan for Realistic Capacity: Avoid scheduling team members at 100% capacity. A common best practice is to plan for 80% utilization, leaving a buffer for unforeseen tasks, meetings, and administrative work.
- Cross-Train Your Team: Increase your team’s flexibility and reduce dependency on single individuals by encouraging skill-sharing and cross-training.
- Conduct Regular Resource Reviews: Hold weekly or bi-weekly meetings to review resource allocation, identify potential conflicts, and rebalance workloads as project priorities shift.
6. Stakeholder Engagement and Management
Systematic stakeholder engagement is a crucial project management best practice that transforms potential opposition into active support. This involves identifying, analyzing, and actively managing the expectations of any individual or group impacted by your project. By proactively engaging stakeholders, you can mitigate risks, build consensus, and align project outcomes with organizational goals, ensuring a smoother path from kickoff to completion.
Consider a large-scale urban development project. Without continuous engagement with community groups, local government, and business owners, the project would face immediate public backlash and regulatory hurdles. Similarly, in a corporate merger, managing the diverse concerns of employees, investors, and customers is paramount to success. Effective stakeholder management ensures all voices are heard and key relationships are nurtured, directly contributing to the project’s viability and acceptance.
How to Implement This Practice
Successful stakeholder management relies on strategic communication and organized documentation. Using a central workspace like Zemith allows teams to maintain a stakeholder register, track communications, and manage expectations transparently. This creates a single source of truth for all stakeholder-related activities, which is vital for maintaining alignment. For deeper insights, explore various knowledge management strategies to refine your approach.
- Map Stakeholders Early: Create a stakeholder map that charts each group's influence and interest level to prioritize engagement efforts.
- Understand Motivations: Go beyond titles and identify what truly drives each stakeholder, including their concerns, expectations, and success criteria.
- Develop a Communication Plan: Define how, when, and what you will communicate to different stakeholder groups, using multiple channels.
- Address Conflicts Transparently: Tackle disagreements head-on with open and honest dialogue to find mutually agreeable solutions before they escalate.
7. Quality Assurance and Control
Integrating rigorous quality assurance and control is a critical project management best practice that ensures deliverables meet or exceed stakeholder expectations. This involves proactively establishing quality standards and systematically checking work against those benchmarks, rather than reactively fixing errors at the end. It's the difference between building quality into the process and inspecting for it after the fact, ensuring the final product is fit for its purpose and free from defects.
Consider Toyota's world-renowned production system, which empowers any worker to halt the assembly line if a quality issue is detected. This "Jidoka" principle builds quality into every step. In the software world, this translates to implementing automated testing within a CI/CD pipeline, catching bugs long before they reach the user. This approach transforms quality from an afterthought into a continuous, integrated activity, preventing costly rework and safeguarding project success.
How to Implement This Practice
Effective quality management requires embedding checks throughout the project lifecycle. An actionable insight is to centralize your quality documentation and test plans in a tool like Zemith. This ensures the entire team is aligned on the standards and can track performance against them in one place. You can learn more about how to refine your approach with these software testing best practices.
- Define Quality Criteria Upfront: Work with stakeholders to establish clear, measurable quality metrics and acceptance criteria before development begins.
- Implement Peer Reviews: Institute a process for team members to review each other's work at key milestones to catch errors early.
- Use Quality Checklists: Develop and use standardized checklists for tasks to ensure consistency and prevent common mistakes.
- Automate Testing Where Possible: Leverage automation for repetitive testing tasks to increase efficiency, improve accuracy, and provide rapid feedback.
8. Change Management and Control
Establishing a formal process for managing change is essential for protecting a project's integrity while allowing for necessary evolution. Effective change management and control involve a structured approach to submitting, evaluating, approving, and implementing modifications to the project scope, schedule, or budget. This practice isn't about preventing change; it’s about controlling its impact, ensuring every adjustment is carefully considered and documented. This structured approach is a critical project management best practice that prevents chaos and maintains alignment with strategic goals.
Think of NASA's rigorous change control board for space shuttle missions. Every proposed modification, no matter how small, underwent intense scrutiny to assess its impact on safety, schedule, and mission objectives. Similarly, in a large enterprise software implementation, a Change Advisory Board (CAB) ensures that updates don't disrupt business operations. This formal process transforms potential disruptions into managed, value-adding adjustments, ensuring the project remains on a stable, predictable path.
How to Implement This Practice
The key is to establish and communicate your change management process before any requests arise. You can immediately make this actionable by using a platform like Zemith to create a dedicated workflow for logging, tracking, and discussing change requests. This provides a transparent and auditable history for all stakeholders, ensuring nothing slips through the cracks.
- Establish a Formal Change Request Process: Define a clear procedure for how stakeholders can submit a change request, including what information is required.
- Create a Change Control Board (CCB): Assemble a group of key stakeholders responsible for reviewing, evaluating, and approving or rejecting change requests.
- Assess the Impact: For every change request, thoroughly analyze its potential impact on the project's scope, timeline, budget, and resources.
- Communicate All Decisions: Clearly communicate the outcome of all change requests to the entire project team and relevant stakeholders to ensure universal alignment.
9. Performance Monitoring and Reporting
Implementing systematic performance monitoring and reporting is essential for steering a project toward its goals. This practice involves tracking progress against planned objectives using key performance indicators (KPIs), earned value management, and regular status reports. It's the project's real-time feedback loop, transforming raw data into actionable intelligence. This proactive approach allows teams to identify potential issues early, make informed, data-driven decisions, and maintain transparent communication with all stakeholders.
Consider how agile software teams use burndown charts to visualize the rate at which work is being completed and predict the likelihood of finishing on time. This isn't just tracking; it’s a diagnostic tool that highlights bottlenecks or scope changes. Similarly, a construction project manager uses percentage completion reports to ensure the project stays on budget and schedule. This continuous measurement is a core project management best practice because it replaces guesswork with evidence, ensuring accountability and control.
How to Implement This Practice
To effectively monitor and report on performance, you need a centralized system that aggregates data and presents it clearly. A tool like Zemith makes this actionable by providing integrated dashboards that pull data from various project components into a single, easy-to-understand view. This simplifies tracking KPIs and sharing progress with stakeholders without manual effort.
- Define Meaningful KPIs: Select a few key metrics that directly reflect project health and link to objectives, such as Cost Performance Index (CPI) or Schedule Performance Index (SPI).
- Automate Data Collection: Wherever possible, automate the gathering of data to reduce manual effort and minimize human error, ensuring your reports are always based on current information.
- Utilize Visual Dashboards: Use charts, graphs, and other visual aids to communicate project status at a glance, making complex data digestible for all audiences.
- Establish a Reporting Cadence: Set up a consistent schedule for formal progress reports (e.g., weekly or bi-weekly) to keep all stakeholders informed and aligned.
10. Lessons Learned and Continuous Improvement
The most successful projects are not just completed; they serve as learning opportunities to refine future endeavors. Systematically capturing, analyzing, and applying lessons learned is a critical project management best practice that fuels continuous improvement. This process involves conducting post-project reviews or agile retrospectives to identify what went right, what went wrong, and why. It transforms individual experiences into a collective, organizational asset, building long-term project management maturity.
Consider how top consulting firms refine their methodologies after every client engagement or how NASA maintains an extensive lessons learned database from every mission. These organizations don't just finish a project and move on; they invest in understanding the process to avoid repeating mistakes and to replicate successes. This proactive approach to organizational learning is what separates good project teams from great ones, ensuring that each new project starts on a stronger foundation than the last.
How to Implement This Practice
To make this practice actionable, create a centralized knowledge hub for lessons learned. A platform like Zemith provides an ideal repository where teams can document retrospective notes, link them to specific projects, and build a searchable database of best practices. This turns insights from past projects into a tangible asset for future planning.
- Schedule Regular Retrospectives: Don’t wait until the end. Hold lessons-learned sessions after major milestones to capture fresh, relevant insights.
- Create a Safe Environment: Foster a "blameless" culture where team members feel comfortable sharing honest feedback about challenges without fear of reprisal.
- Document and Categorize Insights: Use a consistent template to capture what was learned, its impact, and actionable recommendations for future projects.
- Integrate Learnings into Onboarding: Incorporate key lessons into training materials and project kickoff processes to ensure new initiatives benefit from past experiences.
Project Management Best Practices Comparison
| Item | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Define Clear Project Scope and Objectives | Medium – requires upfront analysis and frequent updates | Moderate – time for documentation and stakeholder involvement | Clear direction, prevents scope creep, aligned expectations | Projects needing defined deliverables and boundaries | Prevents scope creep, enables accurate resource allocation |
| Implement Effective Communication Plans | Medium – coordinating channels and schedules | Moderate to high – ongoing communication effort | Better transparency, faster decisions, stakeholder engagement | Projects with many stakeholders or remote teams | Reduces conflicts, builds trust, facilitates issue ID |
| Risk Management and Mitigation Planning | High – continuous risk analysis and updates | High – workshops, monitoring, and mitigation planning | Reduced failures, proactive problem-solving, budget protection | Projects with high uncertainty or complexity | Minimizes surprises, improves predictability |
| Agile and Iterative Development Approaches | High – cultural change and iterative cycles | High – continuous stakeholder involvement and team collaboration | Faster delivery, better adaptability, continuous value delivery | Dynamic projects needing flexibility and rapid feedback | Increased satisfaction, reduced risk, improved morale |
| Resource Planning and Allocation | High – complex forecasting and optimization | High – tracking tools and expertise | Efficient resource use, avoids bottlenecks, cost control | Multi-project environments or resource-constrained projects | Maximizes ROI, prevents conflicts |
| Stakeholder Engagement and Management | Medium to high – requires ongoing relationship management | Moderate to high – time and skilled facilitation | Increased buy-in, reduced resistance, improved decision-making | Projects with diverse or influential stakeholder groups | Enhances legitimacy, improves requirements accuracy |
| Quality Assurance and Control | Medium to high – specialized processes and continuous checks | Moderate to high – skilled resources and tools | High-quality deliverables, reduced rework and support issues | Projects with strict quality standards or compliance needs | Improves satisfaction, predictable quality outcomes |
| Change Management and Control | Medium – formal procedures and governance | Moderate – administrative effort and discipline | Controlled changes, audit trails, maintains baseline integrity | Projects with evolving requirements or regulatory needs | Prevents scope creep, balances flexibility and control |
| Performance Monitoring and Reporting | Medium to high – setup of KPIs, dashboards, and analysis | Moderate – data collection and reporting systems | Objective tracking, early issue detection, informed decisions | Projects requiring transparency and data-driven management | Improves forecasting, increases stakeholder confidence |
| Lessons Learned and Continuous Improvement | Medium – scheduled sessions and knowledge management | Moderate – time for reviews and documentation | Prevents repeated mistakes, builds knowledge, improves future projects | Organizations focused on maturity and ongoing improvement | Accelerates learning, enhances team skills |
Unify Your Workflow and Master Your Projects
Navigating the complexities of modern projects requires more than just a checklist; it demands a holistic and integrated approach. Throughout this guide, we've explored ten essential project management best practices, moving from foundational principles like defining a clear scope and objectives to advanced strategies such as robust risk mitigation and continuous improvement. We've seen how effective communication plans, proactive stakeholder engagement, and disciplined change control are not isolated tasks but interconnected pillars that support the entire project structure.
The core lesson is that successful project management is a dynamic system, not a static set of rules. Each practice, from agile development to rigorous quality assurance, builds upon the others. When you master these principles, you move from simply managing tasks to orchestrating successful outcomes, ensuring every project delivers tangible value on time and within budget.
From Theory to Integrated Execution
Adopting these project management best practices provides a powerful framework, but their true potential is unlocked only through seamless execution. The biggest obstacle many teams face is workflow fragmentation. Constantly switching between different tools for documentation, communication, research, and analysis creates friction, drains cognitive energy, and leads to costly errors. A project charter lives in one app, stakeholder feedback is scattered across email threads, and performance data is trapped in another spreadsheet.
This is where an integrated AI powerhouse like Zemith becomes a game-changer. It transforms these best practices from abstract concepts into a unified, intelligent, and efficient reality. By centralizing your entire project lifecycle, you can eliminate the context-switching tax that sabotages productivity. Imagine conducting deep market research, generating a comprehensive project charter with the Smart Notepad, and brainstorming on a digital whiteboard, all within a single, interconnected workspace.
Actionable Steps to Elevate Your Practice
To truly embed these project management best practices into your daily operations, focus on integration and continuous refinement.
- Audit Your Current Workflow: Identify where information silos and communication gaps exist. Where do handoffs fail? Where are you losing time to context switching?
- Centralize Your Project Hub: Move away from scattered tools. Adopt a single platform like Zemith where you can manage documents in a shared Library, track progress, and communicate with stakeholders.
- Automate and Augment: Leverage AI-powered tools to handle repetitive tasks. Use them to generate initial drafts of project plans, summarize meeting notes, or conduct competitor analysis, freeing your team to focus on high-impact strategic work.
- Embed Continuous Improvement: Don't wait for a project post-mortem. Use your centralized hub to gather feedback and insights in real-time, making "lessons learned" an ongoing process rather than an afterthought.
By unifying your tools and processes, you create an environment where these best practices can thrive. You empower your team to not just follow a plan but to adapt, innovate, and deliver exceptional results with unparalleled clarity and ease.
Ready to transform your project management from a fragmented process into a unified, AI-powered workflow? Discover how Zemith integrates every best practice into a single, intelligent platform. Explore Zemith today and start mastering your projects with unparalleled efficiency.
Explore Zemith Features
Introducing Zemith
The best tools in one place, so you can quickly leverage the best tools for your needs.
All in One AI Platform
Go beyond AI Chat, with Search, Notes, Image Generation, and more.
Cost Savings
Access latest AI models and tools at a fraction of the cost.
Get Sh*t Done
Speed up your work with productivity, work and creative assistants.
Constant Updates
Receive constant updates with new features and improvements to enhance your experience.
Features
Selection of Leading AI Models
Access multiple advanced AI models in one place - featuring Gemini-2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, GPT 5, and more to tackle any tasks

Speed run your documents
Upload documents to your Zemith library and transform them with AI-powered chat, podcast generation, summaries, and more
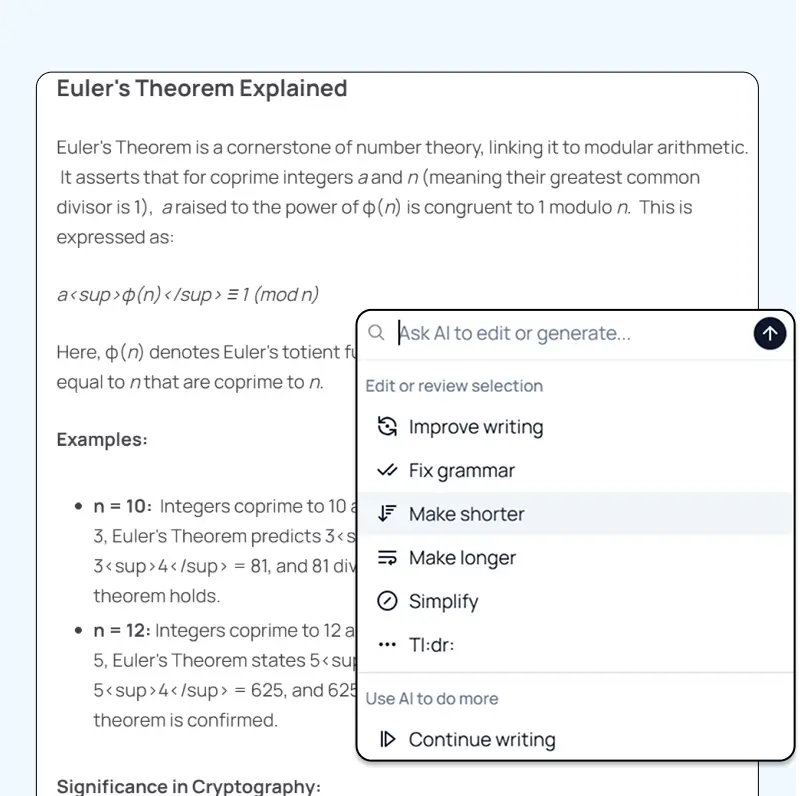
Transform Your Writing Process
Elevate your notes and documents with AI-powered assistance that helps you write faster, better, and with less effort
Unleash Your Visual Creativity
Transform ideas into stunning visuals with powerful AI image generation and editing tools that bring your creative vision to life

Accelerate Your Development Workflow
Boost productivity with an AI coding companion that helps you write, debug, and optimize code across multiple programming languages
Powerful Tools for Everyday Excellence
Streamline your workflow with our collection of specialized AI tools designed to solve common challenges and boost your productivity

Live Mode for Real Time Conversations
Speak naturally, share your screen and chat in realtime with AI
AI in your pocket
Experience the full power of Zemith AI platform wherever you go. Chat with AI, generate content, and boost your productivity from your mobile device.
Deeply Integrated with Top AI Models
Beyond basic AI chat - deeply integrated tools and productivity-focused OS for maximum efficiency
Straightforward, affordable pricing
Save hours of work and research
Affordable plan for power users
Plus
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
Professional
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
What Our Users Say
Great Tool after 2 months usage
simplyzubair
I love the way multiple tools they integrated in one platform. So far it is going in right dorection adding more tools.
Best in Kind!
barefootmedicine
This is another game-change. have used software that kind of offers similar features, but the quality of the data I'm getting back and the sheer speed of the responses is outstanding. I use this app ...
simply awesome
MarianZ
I just tried it - didnt wanna stay with it, because there is so much like that out there. But it convinced me, because: - the discord-channel is very response and fast - the number of models are quite...
A Surprisingly Comprehensive and Engaging Experience
bruno.battocletti
Zemith is not just another app; it's a surprisingly comprehensive platform that feels like a toolbox filled with unexpected delights. From the moment you launch it, you're greeted with a clean and int...
Great for Document Analysis
yerch82
Just works. Simple to use and great for working with documents and make summaries. Money well spend in my opinion.
Great AI site with lots of features and accessible llm's
sumore
what I find most useful in this site is the organization of the features. it's better that all the other site I have so far and even better than chatgpt themselves.
Excellent Tool
AlphaLeaf
Zemith claims to be an all-in-one platform, and after using it, I can confirm that it lives up to that claim. It not only has all the necessary functions, but the UI is also well-designed and very eas...
A well-rounded platform with solid LLMs, extra functionality
SlothMachine
Hey team Zemith! First off: I don't often write these reviews. I should do better, especially with tools that really put their heart and soul into their platform.
This is the best tool I've ever used. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is very fast.
reu0691
This is the best AI tool I've used so far. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is incredibly fast. Just looking at the changelogs, you can see how consistently the developers have ...
