8 Version Control Best Practices for Teams in 2025
Discover 8 essential version control best practices for 2025. Boost productivity with actionable insights on commits, branching, and code reviews.
In modern software development, efficient collaboration and code integrity are non-negotiable. Version control systems like Git are the backbone of this process, yet simply using them isn't enough. Adopting robust version control best practices is what separates high-performing teams from those bogged down in merge conflicts, lost work, and buggy releases. Poor version control hygiene creates technical debt, slows down delivery, and introduces unnecessary risk into every project. It's the silent killer of productivity.
This guide moves beyond the basics to provide a comprehensive list of actionable strategies that will clean up your project's history and significantly boost your team's efficiency. We'll explore everything from writing perfect commit messages and structuring your workflow to implementing rigorous code reviews and protecting your repositories. You will learn specific, practical steps you can implement today to transform your development cycle from chaotic to clear and predictable.
Mastering these practices can be the single most effective change your team makes. While the principles are universal, executing them flawlessly often requires the right tools. Platforms like Zemith can amplify these best practices by providing a structured, secure environment for your repositories, ensuring your team's hard work is always protected and easily managed. Let's dive into the techniques that will elevate your team's performance.
1. Use Meaningful and Descriptive Commit Messages
A commit message is a permanent record of the "what" and "why" behind a change in your project's history. While it’s tempting to write a quick, one-word message like "fix" or "update," this habit creates a cryptic and unhelpful log. Adopting a structured approach to commit messages is one of the most impactful version control best practices, transforming your project history from a confusing mess into a clear, searchable, and valuable document.

The core principle is to provide context. Future developers, including your future self, should be able to understand the purpose of a change just by reading the commit message, without needing to analyze the code diff. This accelerates debugging, simplifies code reviews, and makes generating release notes almost automatic. The Conventional Commits specification, popularized by projects like Google's Angular, provides an excellent, machine-readable standard for this.
Why It's a Best Practice
A well-crafted commit history is essential for long-term project maintainability. It allows anyone to scan git log and quickly grasp the project's evolution. When a bug appears, a descriptive history helps pinpoint the exact change that introduced it. This practice is crucial for team collaboration, enabling asynchronous communication and knowledge sharing.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Follow a Structure: Adopt the Conventional Commits format:
<type>(<scope>): <subject>. Thetypecould befeat(new feature),fix(bug fix),docs,style,refactor, ortest. - Use the Imperative Mood: Write subjects as if giving a command. For example, use "Add user authentication" instead of "Added user authentication" or "Adds user authentication."
- Link to Issues: If your change resolves a ticket from a project management tool (like Jira, Trello, or an internal system), include the ticket ID in the message body or footer (e.g.,
Resolves: TICKET-123). This creates a traceable link between your code and project requirements. - Automate Enforcement: Use tools like
commitlintandhuskyto automatically check commit messages before they are created. For a more intelligent approach, an AI-powered workspace like Zemith can analyze your changes and suggest perfectly formatted, context-aware commit messages, making this best practice effortless.
2. Follow Git Flow or GitHub Flow Branching Strategy
A branching strategy is a set of rules and conventions that a software development team agrees upon for creating, managing, and merging branches. Without a defined model, development can become chaotic, leading to merge conflicts, broken builds, and deployment delays. Adopting a structured branching strategy like Git Flow or GitHub Flow is a fundamental version control best practice that brings order and predictability to the development lifecycle, ensuring code stability and enabling seamless team collaboration.
The choice between these two popular models depends heavily on a project's release cycle. Git Flow, created by Vincent Driessen, is a robust model with dedicated branches for features, releases, and hotfixes, making it ideal for projects with scheduled releases. In contrast, GitHub Flow is a simpler, trunk-based model where main is always deployable, perfect for teams practicing continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD). Netflix, for example, uses a modified GitHub Flow to support rapid and independent microservice deployments.
Why It's a Best Practice
Implementing a clear branching strategy prevents the main or master branch from becoming unstable. It isolates new development work, allowing multiple features to be built in parallel without interfering with each other. This isolation is crucial for quality assurance, as it enables targeted testing on feature branches before code is integrated. A standardized workflow reduces cognitive overhead for developers and simplifies onboarding new team members, as everyone understands the process for contributing code.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Choose the Right Strategy: Select Git Flow for projects with distinct versioned releases (e.g., enterprise software). Opt for the simpler GitHub Flow if your team practices continuous deployment.
- Use Branch Naming Conventions: Enforce a consistent naming scheme to improve clarity. For example, use prefixes like
feature/TICKET-123-user-loginorhotfix/critical-bug-fix. This makes it easy to identify the purpose of a branch at a glance. - Implement Branch Protection: Protect critical branches like
mainanddevelop. Configure rules in your Git provider (like GitHub or GitLab) to require pull request reviews and passing status checks before merging. - Automate Branch Cleanup: Configure your repository to automatically delete branches after their corresponding pull requests are merged. This keeps the repository tidy and prevents a buildup of stale branches.
- Leverage Integrated Workspaces: For teams managing complex workflows, platforms like Zemith can integrate with your repository. This allows you to visualize your branching strategy, link branches directly to tasks, and manage pull requests within a unified workspace that connects code, notes, and planning in one place.
3. Make Small, Atomic Commits
An atomic commit is a self-contained, logical unit of change that accomplishes one specific task. Instead of bundling unrelated updates into a single, massive commit, this best practice advocates for breaking work down into the smallest possible, complete pieces. Each commit should address a single concern, pass all relevant tests, and leave the project in a stable state. This approach transforms a complex project history into a series of clear, understandable, and manageable steps.

The principle, heavily influenced by pioneers like Linus Torvalds for the Linux kernel, is about creating a clean, reversible history. When a single commit introduces a feature, fixes a bug, or refactors a module, it becomes incredibly easy to understand its impact. If a problem arises, you can quickly identify and revert that specific commit using git revert without disrupting other parts of the codebase. This precision is a cornerstone of effective version control best practices.
Why It's a Best Practice
Atomic commits dramatically simplify code reviews, as reviewers can focus on one isolated change at a time. This accelerates the review cycle and leads to more thorough feedback. It also makes debugging far more efficient; commands like git bisect can automatically pinpoint the exact commit that introduced a bug. For project management, this granular history provides a clear audit trail of development progress, aligning code changes with specific tasks or features.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Stage Changes Selectively: Use
git add -p(patch mode) to interactively review and stage specific chunks of code from your modified files. This gives you fine-grained control over what goes into each commit. - Commit Early and Often: Get into the habit of committing frequently as you complete small, logical steps in your local repository. Don't wait until you've finished a large feature to start committing.
- Clean Up Your History: Before pushing your changes or opening a pull request, use an interactive rebase (
git rebase -i) to squash, reword, and reorder your local commits into a clean, atomic sequence. - Ensure Each Commit is Testable: Every single commit in your history should ideally pass the project's test suite. To manage this process, you can use a workspace like Zemith to organize your thought process, break down tasks into atomic units, and draft notes for each step before committing. This ensures each change is well-planned and self-contained.
4. Use .gitignore Files Properly
A .gitignore file is a simple but powerful configuration that tells Git which files or directories to intentionally ignore. Properly managing this file is a foundational version control best practice that prevents clutter, protects sensitive data, and ensures the repository remains focused solely on source code. Without it, your project can quickly become bloated with build artifacts, dependency folders, and system-specific files that have no place in a shared codebase.

The core principle is to keep your repository clean and universal. Your project's Git history should track meaningful changes to the source code, not the temporary byproducts of your local development environment. For example, a Node.js project should track package.json but ignore the massive node_modules folder, as dependencies can be installed by any developer using the manifest file. This keeps the repository small, speeds up operations, and avoids platform-specific conflicts.
Why It's a Best Practice
A well-configured .gitignore file is essential for team collaboration and repository health. It prevents the accidental commit of secrets like API keys or .env files, a common security vulnerability. It also stops machine-specific IDE settings (like .vscode/ or .idea/) from being shared, which can cause friction among team members using different tools. By defining what not to track, you create a more stable and predictable development environment for everyone involved.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Start with Templates: Don't write your
.gitignorefrom scratch. GitHub maintains a comprehensive collection of.gitignoretemplates for hundreds of languages and frameworks. Use the appropriate one as a starting point for your project. - Establish a Global Ignore: For files specific to your personal setup (like macOS
.DS_Storefiles or your preferred editor's settings), use a global.gitignorefile. This keeps your personal preferences out of project-specific repositories. - Add
.gitignoreEarly: Create and commit the.gitignorefile as one of the very first actions in a new repository. Adding ignore rules after files have already been committed requires you to manually remove them from the repository's tracking history. - Audit Before Committing: Before staging all files with
git add ., usegit statusto review the list of untracked files. A smart workspace like Zemith can help by allowing you to document project setup, including.gitignoreconventions, ensuring new team members follow best practices from day one.
5. Implement Code Reviews Before Merging
Code review is a systematic examination of source code by peers, intended to find and fix mistakes overlooked in the initial development phase. Integrating this practice directly into your version control workflow, typically through pull or merge requests, creates a critical quality gate. This ensures that no code is merged into a primary branch, like main or develop, without at least one other team member's approval, safeguarding code quality and fostering shared ownership.
This practice transforms version control from a simple code repository into a collaborative hub for quality assurance. Major technology companies like Google and Microsoft have institutionalized code reviews, building entire platforms and cultures around them. The open-source world, exemplified by projects like React and Linux, relies heavily on community-led reviews to maintain stability and security across thousands of contributors.
Why It's a Best Practice
Mandatory code reviews before merging are one of the most effective version control best practices for improving software quality and mitigating risk. They serve as a powerful defense against bugs, security vulnerabilities, and architectural inconsistencies. This process also facilitates knowledge sharing, helps onboard new developers, and ensures that multiple team members are familiar with any given part of the codebase, reducing dependency on a single individual.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Establish Clear Guidelines: Create a standardized process for reviews. Define what reviewers should look for, such as adherence to coding standards, logic errors, and test coverage. For a detailed guide, you can start with a comprehensive code review checklist on zemith.com.
- Automate First, Review Second: Use automated tools like linters, static analyzers, and CI test runners to catch simple errors before a human review begins. This frees up reviewers to focus on more complex issues like logic and architecture.
- Set Time Expectations: Define a reasonable turnaround time for reviews, such as 24 hours, to avoid blocking development progress. This balances the need for thoroughness with team velocity.
- Keep Pull Requests Small: Encourage small, focused pull requests that address a single concern. Reviewing 200 lines of code is far more effective and less daunting than reviewing 2,000.
- Use AI to Accelerate Reviews: To make reviews more efficient, use a tool like Zemith to understand complex code sections. Its AI assistant can explain confusing logic or summarize changes, helping you provide higher-quality feedback in less time without losing context.
6. Tag Important Versions and Releases
While commit hashes uniquely identify every change, they are not human-readable or stable reference points for significant milestones. This is where tagging comes in. A tag is a pointer to a specific commit, creating a permanent, named snapshot of your project's history. Using tags for releases like v1.0.0 or v2.1.3 is a fundamental version control best practice that provides clarity, stability, and a reliable way to check out or build specific versions of your software.
The core principle is to mark commits that represent important states, such as a new software release. This practice, often combined with Semantic Versioning (SemVer), allows developers, CI/CD pipelines, and users to easily access specific versions without hunting through the commit log. Projects like the Linux kernel, Kubernetes, and Node.js rely heavily on tags to manage their complex release cycles, proving the scalability and necessity of this approach. It transforms a linear commit history into a well-defined project timeline with clear milestones.
Why It's a Best Practice
A well-tagged repository is crucial for reproducible builds and effective release management. It allows anyone to easily fetch a specific production version to investigate a bug or roll back a deployment. When managing dependencies, tags provide the stable reference points needed to ensure that different projects are using a consistent version of a library. For collaborative platforms, tags power "Releases," which can be associated with binaries and release notes, creating a formal record of project progress.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Follow Semantic Versioning: Adopt the SemVer standard (
MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH) to communicate the nature of changes. For example,v2.1.5signals the fifth patch on the second minor version of major release two. - Use Annotated Tags for Releases: Always use annotated tags (
git tag -a v1.0.0 -m "Initial release") for official releases. They are stored as full objects in the Git database and can include a tagger name, email, date, and a message, making them ideal for official records. - Automate Tagging in CI/CD: Integrate tag creation into your automated release pipeline. When a build for production is successful, the pipeline should automatically create and push a corresponding version tag to prevent manual errors.
- Document Releases Centrally: Use a tool like Zemith to manage release notes and documentation associated with each tag. Its integrated knowledge base allows you to link Git tags directly to project milestones, creating a single source of truth for your entire release process.
7. Keep Repositories Focused and Well-Organized
A version control repository should be a self-contained, logical unit of work, not a disorganized collection of files. Keeping repositories focused and well-organized means maintaining a clean, purposeful structure with a logical arrangement of code, documentation, and configuration files. This practice transforms a repository from a potential maze into a welcoming and navigable project space for any contributor.
The core principle is to establish and follow a consistent structure. This structure should be intuitive and, whenever possible, adhere to the established conventions of the language or framework being used. For example, a Java project using Maven has a standard directory layout that any Java developer would immediately recognize, just as a React project bootstrapped with Create React App follows a familiar pattern. This adherence to convention drastically reduces the cognitive load for new team members and streamlines onboarding.
Why It's a Best Practice
A well-organized repository is a cornerstone of effective version control best practices and long-term project health. It ensures that developers can find what they need quickly, understand the project's architecture at a glance, and contribute code that fits neatly into the existing structure. This organization prevents "file sprawl," where related files are scattered across different directories, making maintenance and debugging significantly more difficult. A clean repository is easier to navigate, automate, and scale.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Follow Language Conventions: Adhere to community-accepted project structures. Use the standard Maven layout for Java, follow PEP 8 and setuptools conventions for Python, or use the standard Go project layout. Frameworks like Ruby on Rails and Django enforce this for you.
- Maintain the README: Your
README.mdis the front door to your project. Keep it current with a clear project description, setup and installation instructions, usage examples, and contribution guidelines. - Use Descriptive Naming: Name directories and files clearly and consistently. For example, use
srcfor source code,docsfor documentation,testsfor tests, andconfigfor configuration files. Avoid generic names likeutilsorhelperswhere a more specific name would be better. - Centralize Project Knowledge: Use an integrated workspace like Zemith to create and maintain documentation, architectural diagrams, and contribution guidelines right alongside your code. This ensures your repository's structure is always well-documented and easily accessible to the entire team.
8. Backup and Protect Your Remote Repositories
Your remote repository is the central source of truth for your project, so treating its security and resilience as an afterthought is a significant risk. While services like GitHub or GitLab are highly reliable, they are not immune to outages, data corruption, or sophisticated security breaches. A robust strategy for backing up and protecting your remote repositories is a critical version control best practice that safeguards your most valuable intellectual property from catastrophic loss and unauthorized access.
This practice involves creating redundant copies of your codebase and implementing strict security controls to govern who can access and modify it. It moves beyond relying solely on the cloud provider's safeguards and establishes a multi-layered defense. By implementing these measures, you ensure business continuity, protect sensitive data within your code, and maintain the integrity of your project's history against both accidental and malicious threats.
Why It's a Best Practice
A compromised or lost remote repository can bring development to a halt, leak proprietary algorithms or security keys, and cause irreparable damage to your organization's reputation. Proactive protection is essential for risk management. Strong access controls prevent unauthorized changes, while regular backups ensure that you can restore your project to a known good state in a worst-case scenario. This combination is fundamental for maintaining a secure and efficient development lifecycle. For a deeper look into how security enhances your development processes, you can learn more about improving workflow efficiency and its connection to robust practices.
Actionable Implementation Tips
- Use Multiple Remotes: For critical projects, configure a secondary remote repository on a different service or a self-hosted server. Regularly push updates to both remotes (
git push primaryandgit push secondary) to create a redundant, off-site backup. - Enforce Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Make 2FA mandatory for all contributors across your organization. This is one of the most effective ways to prevent unauthorized access, even if a team member's password is compromised.
- Implement Branch Protection Rules: Protect your
mainanddevelopbranches. Configure rules in your hosting platform (like GitHub or GitLab) to require status checks to pass, mandate code reviews before merging, and restrict who can push directly to these branches. - Regularly Audit Access Permissions: Periodically review who has access to your repositories. Remove permissions for former employees or collaborators who no longer need them to minimize your attack surface.
- Choose a Secure Platform: When selecting development tools, prioritize platforms that offer robust security and backup features. An integrated workspace like Zemith provides a secure environment for your code and project knowledge, centralizing your assets and reducing the risk of data fragmentation and loss.
8 Key Version Control Best Practices Comparison
| Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Use Meaningful and Descriptive Commit Messages | Moderate - requires consistent discipline | Low - mainly developer time | Better project history, easier reviews, changelog automation | Teams emphasizing clear history and collaboration | Improves code review efficiency and debugging |
| Follow Git Flow or GitHub Flow Branching Strategy | High - structured workflows and training | Moderate - tooling and process setup | Clear development structure, stable releases | Medium to large teams with multiple concurrent features | Reduces merge conflicts, supports stable releases |
| Make Small, Atomic Commits | Moderate - requires discipline and focus | Low - developer effort during commits | Easier reviews and debugging, granular rollbacks | Codebases requiring detailed tracking and bug isolation | Simplifies code review and history readability |
| Use .gitignore Files Properly | Low - initial setup and maintenance | Low - minimal ongoing effort | Clean repository, prevents sensitive or unwanted files | All projects to maintain clean repos | Prevents accidental commits, reduces noise |
| Implement Code Reviews Before Merging | Moderate to High - team process enforcement | Moderate - time investment from reviewers | Improved code quality and team knowledge sharing | Teams prioritizing code quality and collaboration | Catches bugs early and enforces standards |
| Tag Important Versions and Releases | Low to Moderate - requires consistent versioning | Low - automated or manual tagging | Stable reference points, better release tracking | Projects with frequent or critical releases | Enables rollbacks and automatic changelogs |
| Keep Repositories Focused and Well-Organized | Moderate - requires agreement and upkeep | Low to Moderate - effort to maintain | Easier navigation and onboarding, better tooling | All codebases requiring maintainability | Enhances professionalism and reduces cognitive load |
| Backup and Protect Your Remote Repositories | High - security and backup systems setup | High - tooling, monitoring, and management | Prevents data loss and unauthorized access | Critical enterprise or sensitive code repositories | Ensures business continuity and compliance |
Supercharge Your Workflow with AI-Powered Practices
Mastering version control is not just about learning commands; it's about adopting a disciplined mindset that transforms collaborative development. Throughout this guide, we've journeyed through the essential pillars of effective version control, from crafting meaningful commit messages and adopting robust branching workflows like Git Flow, to the practical necessity of atomic commits and well-maintained .gitignore files. These aren't just arbitrary rules; they are the bedrock of a stable, transparent, and efficient development cycle.
By implementing rigorous code reviews, tagging releases, and keeping repositories focused, you build a safety net that protects your project’s integrity and accelerates team velocity. These version control best practices are the collective wisdom of developers who have navigated the complexities of large-scale projects. They ensure every change is traceable, every feature is isolated, and every release is a stable, documented milestone. Adopting them means shifting from a chaotic, reactive process to a structured, proactive one where your project’s history becomes a clear, invaluable asset rather than a tangled mess.
Beyond the Basics: Integrating Intelligence into Your Workflow
While these foundational practices are crucial, the modern development landscape offers powerful tools to amplify their impact. The next evolution in productivity lies in leveraging artificial intelligence to streamline and enhance these very tasks. Imagine an intelligent assistant that not only helps you adhere to commit message conventions but also understands the context of your code changes, suggesting clear and concise summaries automatically. This is where the principles of version control meet the power of AI.
The true challenge often lies in consistently applying these best practices amidst tight deadlines and cognitive overload. For instance, when facing a complex legacy branch during a code review, an AI tool can instantly explain convoluted logic, helping you provide more insightful feedback without spending hours deciphering the code. Similarly, when documenting a new feature, an integrated AI can help draft markdown files and organize notes, ensuring your repository stays clean and well-documented. To further enhance efficiency, exploring how to leverage AI automation for SaaS success can provide a broader framework for integrating intelligent systems across all your operational processes, turning manual tasks into automated workflows.
Adopting these version control best practices is the first step. The next is to empower yourself and your team with tools that make adherence effortless. By integrating an AI-powered workspace like Zemith.com, you can transform these principles from abstract goals into concrete, daily habits. Zemith acts as your coding co-pilot, smart notepad, and research assistant, all within a single, unified environment. It helps you draft perfect commit messages, understand complex code during reviews, and organize project knowledge seamlessly. This consolidation eliminates the friction of context switching, allowing you to focus on what truly matters: building great software.
Ready to turn version control best practices into an effortless part of your daily routine? Discover how Zemith integrates a powerful AI assistant with your development workflow, helping you write better commits, review code faster, and keep your projects perfectly organized. Explore Zemith today and unlock a new level of productivity.
Explore Zemith Features
Introducing Zemith
The best tools in one place, so you can quickly leverage the best tools for your needs.
All in One AI Platform
Go beyond AI Chat, with Search, Notes, Image Generation, and more.
Cost Savings
Access latest AI models and tools at a fraction of the cost.
Get Sh*t Done
Speed up your work with productivity, work and creative assistants.
Constant Updates
Receive constant updates with new features and improvements to enhance your experience.
Features
Selection of Leading AI Models
Access multiple advanced AI models in one place - featuring Gemini-2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, GPT 5, and more to tackle any tasks

Speed run your documents
Upload documents to your Zemith library and transform them with AI-powered chat, podcast generation, summaries, and more
Transform Your Writing Process
Elevate your notes and documents with AI-powered assistance that helps you write faster, better, and with less effort
Unleash Your Visual Creativity
Transform ideas into stunning visuals with powerful AI image generation and editing tools that bring your creative vision to life

Accelerate Your Development Workflow
Boost productivity with an AI coding companion that helps you write, debug, and optimize code across multiple programming languages
Powerful Tools for Everyday Excellence
Streamline your workflow with our collection of specialized AI tools designed to solve common challenges and boost your productivity

Live Mode for Real Time Conversations
Speak naturally, share your screen and chat in realtime with AI
AI in your pocket
Experience the full power of Zemith AI platform wherever you go. Chat with AI, generate content, and boost your productivity from your mobile device.
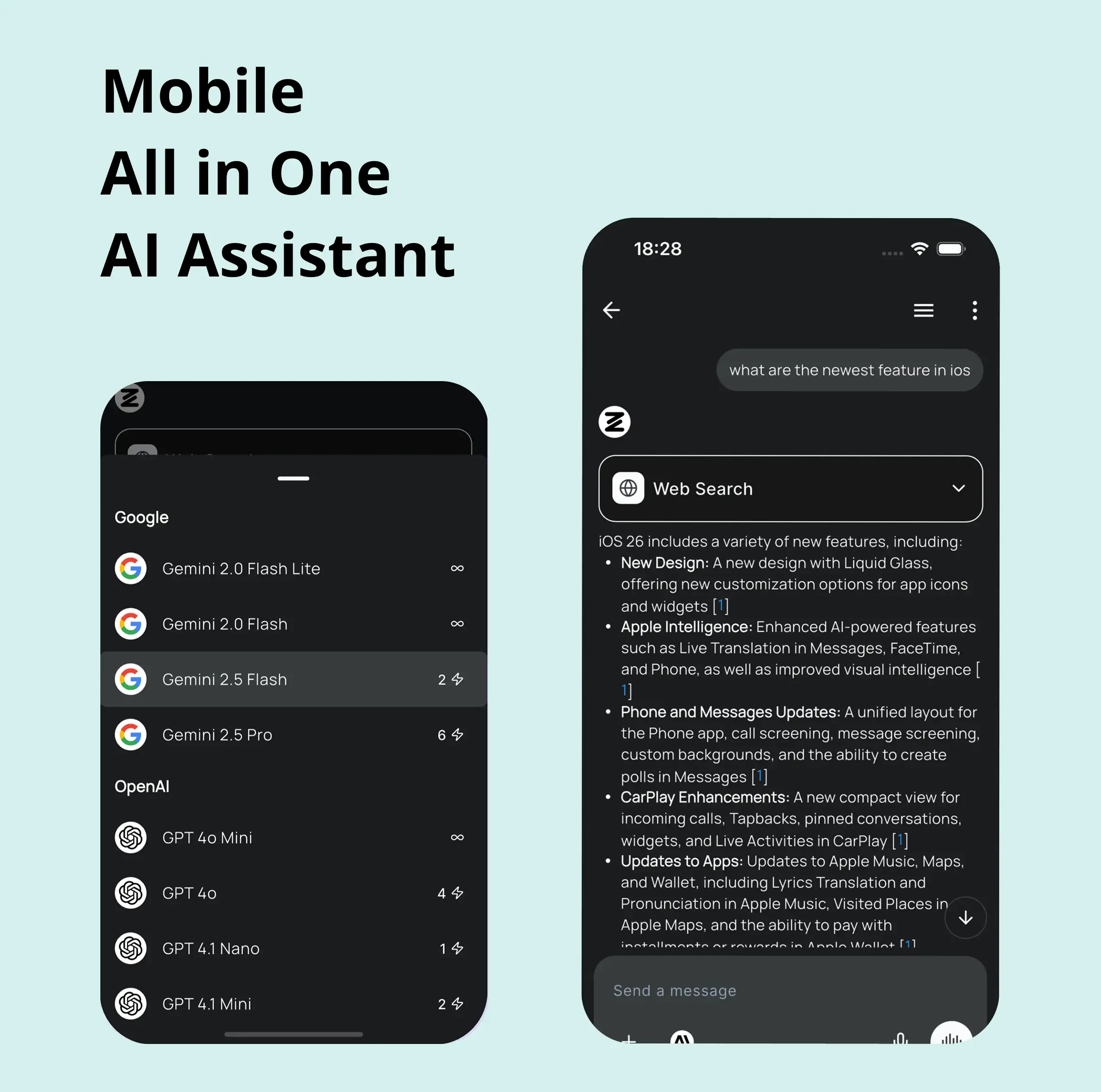
Deeply Integrated with Top AI Models
Beyond basic AI chat - deeply integrated tools and productivity-focused OS for maximum efficiency
Straightforward, affordable pricing
Save hours of work and research
Affordable plan for power users
Plus
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
Professional
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
What Our Users Say
Great Tool after 2 months usage
simplyzubair
I love the way multiple tools they integrated in one platform. So far it is going in right dorection adding more tools.
Best in Kind!
barefootmedicine
This is another game-change. have used software that kind of offers similar features, but the quality of the data I'm getting back and the sheer speed of the responses is outstanding. I use this app ...
simply awesome
MarianZ
I just tried it - didnt wanna stay with it, because there is so much like that out there. But it convinced me, because: - the discord-channel is very response and fast - the number of models are quite...
A Surprisingly Comprehensive and Engaging Experience
bruno.battocletti
Zemith is not just another app; it's a surprisingly comprehensive platform that feels like a toolbox filled with unexpected delights. From the moment you launch it, you're greeted with a clean and int...
Great for Document Analysis
yerch82
Just works. Simple to use and great for working with documents and make summaries. Money well spend in my opinion.
Great AI site with lots of features and accessible llm's
sumore
what I find most useful in this site is the organization of the features. it's better that all the other site I have so far and even better than chatgpt themselves.
Excellent Tool
AlphaLeaf
Zemith claims to be an all-in-one platform, and after using it, I can confirm that it lives up to that claim. It not only has all the necessary functions, but the UI is also well-designed and very eas...
A well-rounded platform with solid LLMs, extra functionality
SlothMachine
Hey team Zemith! First off: I don't often write these reviews. I should do better, especially with tools that really put their heart and soul into their platform.
This is the best tool I've ever used. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is very fast.
reu0691
This is the best AI tool I've used so far. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is incredibly fast. Just looking at the changelogs, you can see how consistently the developers have ...
