8 Essential Document Management Best Practices for 2025
Unlock efficiency with our guide to document management best practices. Learn actionable tips to organize, secure, and streamline your files in 2025.
In a fast-paced work environment, disorganized files are more than just a nuisance; they are a direct threat to productivity, security, and compliance. The time teams lose searching for misplaced reports, the rework caused by conflicting file versions, and the constant risk of data breaches can cripple even the most efficient operations. The solution is not simply more storage but a smarter strategy built on proven organizational principles. Adopting robust document management best practices is the key to transforming your digital clutter into a streamlined, secure, and highly efficient information ecosystem.
This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a comprehensive roundup of the top strategies that deliver tangible results. We will explore eight essential, actionable practices designed to help you regain control over your digital assets, boost team collaboration, and unlock new levels of operational productivity. From establishing consistent naming conventions to implementing secure access controls and disaster recovery plans, each point is crafted to be immediately applicable.
Throughout this listicle, we will also highlight how modern tools can amplify these efforts. For example, platforms like Zemith are revolutionizing this space by leveraging AI to automate tedious organizational tasks, providing intelligent search capabilities, and offering a unified workspace that makes it easier than ever to implement these critical strategies effectively. By the end of this article, you will have a clear, practical roadmap for creating a powerful and scalable document management system that supports your team’s success.
1. Implement a Consistent File Naming Convention
A consistent file naming convention is the bedrock of any successful document management system. It establishes a standardized, predictable structure for naming every file across an organization, eliminating guesswork and dramatically reducing the time spent searching for information. Without this foundational practice, digital archives quickly devolve into a chaotic, unnavigable mess. This is one of the most critical document management best practices for creating order from digital clutter.
By defining a set of rules for file names - incorporating elements like dates, project identifiers, document types, and version numbers - you create a universal language for your data. This ensures that anyone, at any time, can understand a file's content and context at a glance, without needing to open it.
Why It Works and How to Implement It
A standardized naming convention works because it forces uniformity, making documents easily sortable and identifiable. For instance, legal firms often use a ClientName_YYYY-MM-DD_DocumentType_Matter# format. This structure allows them to instantly sort all documents by client, date, or specific legal matter. Similarly, NASA’s stringent naming rules, such as NASA-STD-8719.24_2019-05-30_Safety_Standards_v02.pdf, ensure absolute clarity and version control for critical safety documents.
To fully master your digital workspace, learning how to organize computer files effectively is paramount. This starts with creating a clear file name structure.
This infographic illustrates a simple yet powerful hierarchical structure for building a file name.
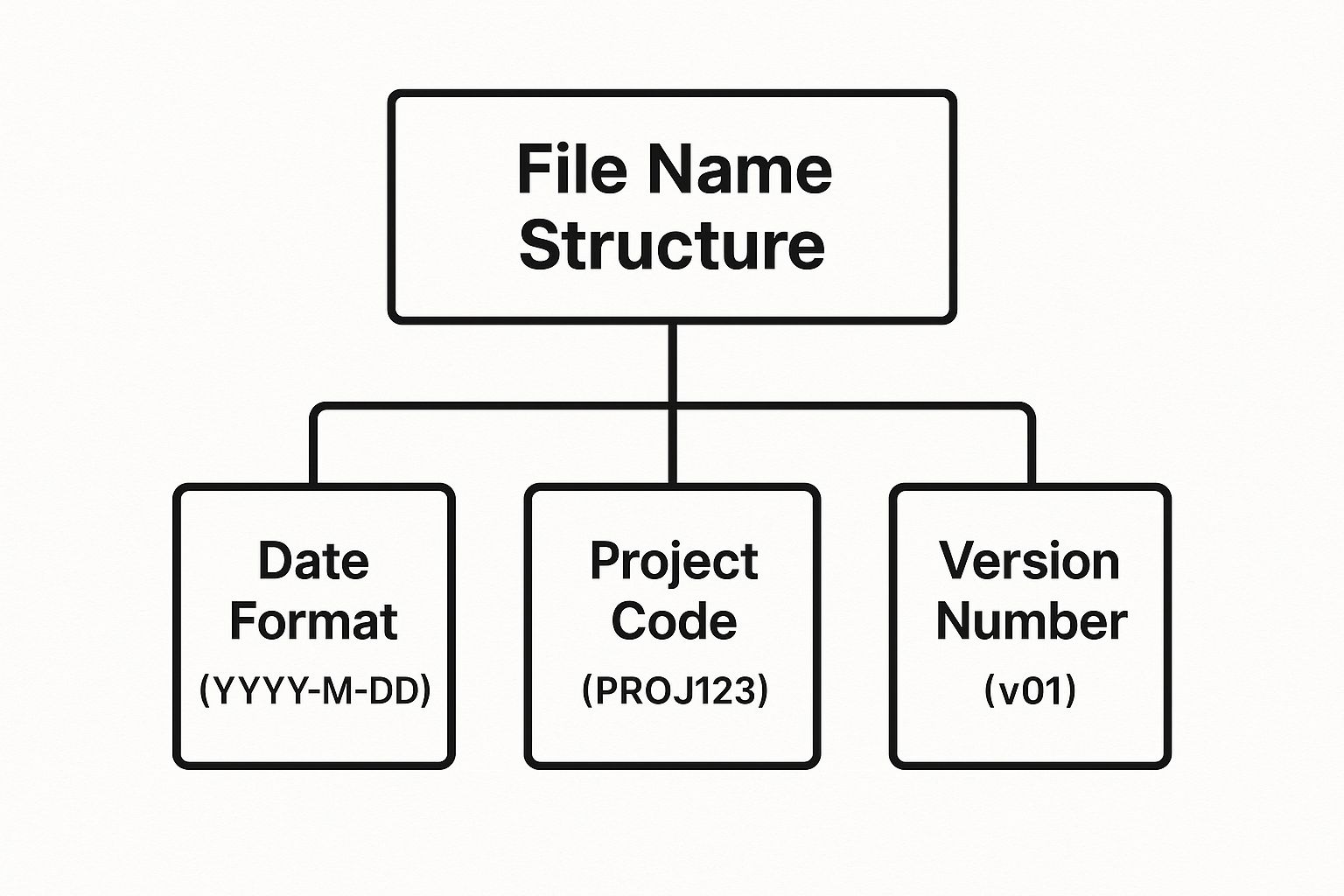
The visualization shows how combining distinct, standardized components creates a logical and descriptive whole. By defining the hierarchy of information in the file name, from the date to the project and version, you build a self-organizing system.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Create a Guide: Document your naming convention in a shared guide. Outline the required elements, their order, and specific formats (e.g.,
YYYY-MM-DDfor dates). - Use Leading Zeros: For numbered sequences, use leading zeros (e.g.,
01,02,09,10). This ensures files sort correctly in all operating systems. - Avoid Special Characters: Steer clear of characters like
!,@,#,$,*,?which can cause errors in different systems and cloud platforms. Use hyphens or underscores instead of spaces. - Actionable Insight: A rule is only effective if followed. Conduct training sessions and use software tools where possible to automate and enforce naming standards. For a more robust solution, an AI-powered platform like Zemith can automatically suggest and apply consistent names based on document content, ensuring your conventions are applied without manual effort.
2. Establish a Logical Folder Structure and Hierarchy
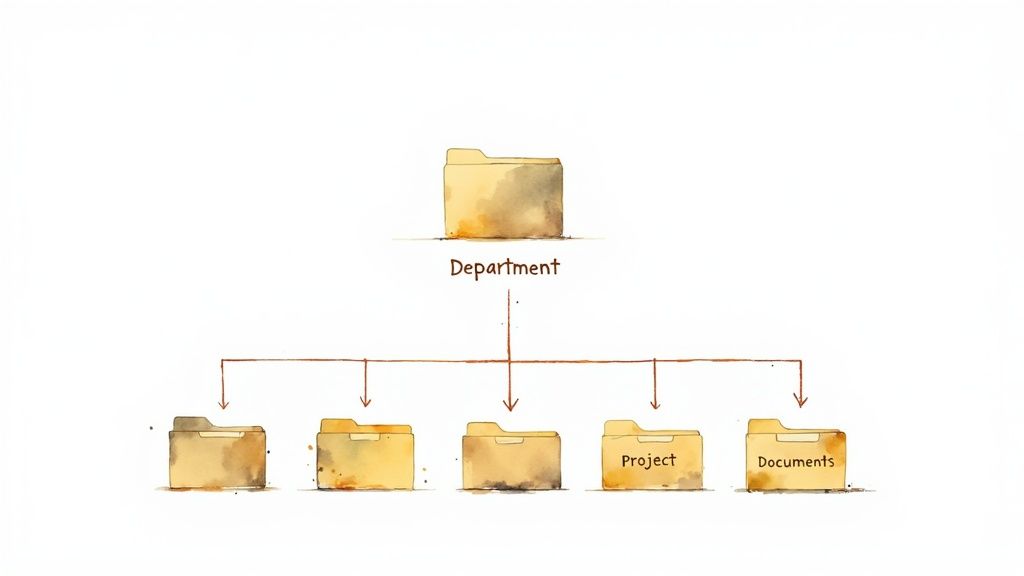
Just as a file naming convention brings order to individual documents, a logical folder structure creates a coherent map for your entire digital archive. This practice involves organizing documents into a clear, hierarchical system of folders and subfolders that intuitively mirrors your business's real-world processes. Without this framework, even well-named files become lost in a flat, sprawling digital landscape. Establishing this hierarchy is a cornerstone of effective document management best practices, ensuring information is not just stored, but is also easily discoverable.
A well-designed structure provides a predictable pathway for users to navigate, allowing them to locate information based on context, such as department, project, or date. It transforms a chaotic collection of files into a logical, browsable library where anyone in the organization can find what they need with minimal effort.
Why It Works and How to Implement It
A logical folder hierarchy works by creating a mental model that aligns with how people naturally categorize information. For example, a global consulting firm like McKinsey & Company often organizes its vast knowledge base using a Client > Project > Work Stream > Document Type structure. This allows consultants to intuitively drill down to find specific deliverables. Similarly, universities might use Academic Year > Department > Course Code > Assignment Type, making it simple for faculty and students to access course materials.
This top-down approach ensures scalability and prevents digital clutter. The goal is to create a system so logical that a new employee could navigate to the correct folder on their first try. When this structure is programmed into a central platform, it becomes even more powerful, guiding users and automating placement.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Keep It Shallow: Limit your folder depth to a maximum of 4-5 levels. Overly nested structures become cumbersome and counterintuitive, defeating the purpose of easy navigation.
- Start Broad, Get Specific: Use broad, stable categories for your top-level folders (e.g.,
Departments,Clients,Projects). Lower-level folders should contain more specific, granular information. - Create Folder Templates: For recurring work like new client onboarding or project kickoffs, create pre-defined folder templates. This ensures consistency and saves time.
- Document and Train: Just like with naming conventions, document your folder structure in a central guide. This reference helps maintain order and onboard new team members.
- Actionable Insight: Schedule periodic reviews to archive old projects and delete redundant folders. For a streamlined approach, intelligent platforms like Zemith can automatically organize files into the correct folder or 'Library' based on content and metadata, enforcing your hierarchy without constant manual intervention.
3. Implement Version Control and Document Lifecycle Management
Effective version control and lifecycle management are essential for maintaining document integrity and clarity. This practice establishes a systematic process for tracking changes, managing different document iterations, and guiding a file from its creation to its eventual archival or deletion. It eliminates confusion over which version is current, prevents conflicting edits, and preserves a complete historical record of a document's evolution. Implementing this is a cornerstone of modern document management best practices, ensuring everyone is working from the correct information.
A robust version control system prevents the common pitfall of having multiple, slightly different copies of the same file (e.g., Report_final, Report_final_v2, Report_final_USE_THIS_ONE). Instead, it creates a single source of truth with a clear, auditable history of all modifications. This systematic approach is critical for collaborative projects, regulatory compliance, and maintaining quality standards.

Why It Works and How to Implement It
Version control works by creating a timeline of changes, allowing users to see who changed what and when. For example, Fortune 500 companies rely on the built-in versioning in Microsoft SharePoint to manage collaborative documents, ensuring that all team members access the latest iteration while retaining the ability to restore previous versions if needed. Similarly, pharmaceutical firms use validated document control systems to comply with strict FDA regulations, where every change to a protocol or report must be tracked and justified. In the tech world, systems like Git, originally built by Linus Torvalds, are used for managing technical documentation, providing unparalleled control over revisions.
Implementing this involves more than just software; it requires a defined process. The document lifecycle-creation, review, approval, distribution, and archival-must be clearly mapped out.
The video above provides a clear overview of how version control works in practice, illustrating its importance in preventing data loss and confusion.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Use Semantic Versioning: Adopt a
Major.Minor.Patchsystem (e.g.,v1.0.0,v1.1.0,v2.0.0). Use major numbers for significant changes, minor for new features that are backward-compatible, and patch for bug fixes or small corrections. - Train on Check-In/Check-Out: Properly train all users on the procedure for "checking out" a document to edit it and "checking it in" when finished. This locks the file and prevents simultaneous, conflicting edits.
- Automate Where Possible: Set up automatic notifications to alert team members when a new version is published. Configure systems to automatically check in documents after a period of inactivity to prevent them from being locked indefinitely.
- Actionable Insight: Establish clear rules for how long different versions of a document should be kept. Platforms like Zemith can automate retention policies and maintain a clear version history, ensuring your system remains clean, compliant, and easy to navigate without manual purges.
4. Define and Enforce Access Controls and Security Permissions
Defining and enforcing access controls is a non-negotiable component of modern document management. This practice involves creating a granular permission system that dictates who can view, edit, share, or delete documents. It’s about ensuring the right information is accessible to the right people at the right time, while shielding sensitive data from unauthorized access. This is one of the most vital document management best practices for safeguarding intellectual property and complying with regulations.
By implementing the principle of least privilege, where users are granted the minimum level of access necessary to perform their job functions, you drastically reduce the risk of data breaches, accidental deletions, and compliance failures. This creates a secure, auditable environment where information flow is controlled and intentional.
Why It Works and How to Implement It
A robust access control system works because it maps security directly to organizational structure and responsibility. This prevents data chaos and enforces accountability. For instance, healthcare organizations use HIPAA-compliant controls to ensure only authorized medical staff can view patient records, protecting privacy. Similarly, government agencies use multi-level security clearances, mirroring standards like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, to restrict access to classified information.
Financial services firms like JPMorgan Chase implement Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) compliant document controls, ensuring that financial data has a strict, auditable chain of custody. These real-world applications demonstrate that structured permissions are essential for operational integrity and risk management. When selecting platforms, it is critical to review their data protection measures. For robust protection, it's essential to understand a platform's commitment to data security, such as their comprehensive legal security policy.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Use Roles, Not Individuals: Assign permissions to roles or groups (e.g., "Marketing Team," "Legal Reviewers") instead of individual users. This simplifies administration, as you only need to add or remove users from a group as their job function changes.
- Audit Permissions Regularly: Schedule quarterly or biannual reviews of all access rights. This helps identify and remove obsolete permissions, ensuring the principle of least privilege is maintained.
- Automate Onboarding/Offboarding: Integrate your document management system with your HR system to automatically grant or revoke access when employees join, change roles, or leave the company. This closes critical security gaps.
- Document Access Procedures: Create a clear, accessible guide that explains how employees can request access to specific documents, who needs to approve it, and the expected timeline.
- Actionable Insight: Embedding security controls directly into your processes is key. A platform like Zemith integrates permissions into project-based 'Libraries', making it simple to manage access for internal teams and external collaborators securely within a unified space. This simplifies the process of controlling who sees what, which is crucial for document workflow automation.
5. Implement Comprehensive Metadata and Tagging Systems
While a smart file name provides context, metadata and tags unlock a far more powerful, multi-dimensional search capability. Metadata is structured information that describes a document - such as author, creation date, or associated project. Tags are more flexible, keyword-style labels. Together, they form a descriptive layer that makes documents findable based on their content and business context, not just their name or location.
Implementing a comprehensive metadata strategy is one of the most transformative document management best practices. It allows you to search, filter, and automate workflows based on specific criteria, turning a static archive into a dynamic, intelligent information hub. This approach moves beyond simple folder hierarchies, enabling you to discover documents through multiple, intersecting search paths.
Why It Works and How to Implement It
Metadata and tagging work by creating a rich, searchable index of your documents. For example, Thomson Reuters leverages AI-powered metadata extraction to automatically categorize legal documents, identifying case numbers, involved parties, and judicial precedents. This allows legal professionals to instantly find all documents related to a specific judge or legal principle, a task that would be impossible with file names alone. Similarly, Adobe's Document Cloud uses AI to suggest relevant tags for PDFs, simplifying categorization for millions of users.
This system creates a web of connections between your files. You can find "all invoices from Q4 2023 for Project Phoenix" or "all marketing brochures approved by Jane Doe" with a simple, filtered search, regardless of where the files are stored. This level of granular control is essential for efficient information retrieval in complex environments.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Use Metadata Templates: Create and enforce standardized metadata templates for common document types (e.g., invoices, contracts, reports). This ensures all necessary information is captured consistently.
- Leverage Controlled Vocabularies: For key metadata fields, use dropdown lists or controlled vocabularies instead of free-text entry. This prevents inconsistencies like "US," "USA," and "United States" from fragmenting your data.
- Automate Where Possible: Reduce manual effort and human error by implementing auto-tagging tools. These systems can analyze document content to suggest or apply relevant tags and metadata automatically.
- Actionable Insight: Educate your team on the importance of tagging, but use technology to do the heavy lifting. An AI-powered platform like Zemith can automatically analyze document content to suggest and apply relevant tags, ensuring every file is enriched with the right information without manual intervention.
6. Establish Document Retention and Archival Policies
A document retention policy is a formal framework that dictates the entire lifecycle of a document, from creation to final deletion. It establishes clear rules on how long specific document types must be kept (retention), when they should be moved to long-term storage (archival), and when they must be securely destroyed. This practice is essential for legal compliance, risk mitigation, and operational efficiency, preventing the costly accumulation of redundant, obsolete, and trivial information.
By systematically managing document lifecycles, organizations avoid the severe legal and financial penalties associated with improper record handling. It also optimizes storage resources and keeps the active system clean and high-performing. Implementing these rules is a core component of effective document management best practices, turning a potential liability into a structured, compliant asset.
Why It Works and How to Implement It
This practice works by replacing guesswork with a defined, legally-vetted process. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act, enacted after the Enron scandal where crucial documents were shredded, mandates strict retention schedules for corporate records. Similarly, GDPR's "right to be forgotten" requires companies to have a system to delete personal data upon request, which is impossible without a retention policy. In highly regulated fields like pharmaceuticals, companies must adhere to FDA rules requiring some records be kept for 25 years or more.
A well-designed retention policy automates these critical decisions, ensuring compliance without constant manual intervention. For instance, a policy might automatically flag all invoices over seven years old for deletion, while archiving project-related documents for ten years before a final review. This systematic approach is a cornerstone of a robust knowledge management system, ensuring information remains valuable and compliant.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Consult Legal Counsel: Work with legal experts to define retention periods that comply with all relevant industry, federal, and state regulations (e.g., SOX, HIPAA, GDPR).
- Implement Graduated Archival: Create a tiered lifecycle for documents: active (frequent use), inactive (infrequent use), archived (long-term cold storage), and deleted. This optimizes storage costs and system speed.
- Actionable Insight: Manual enforcement is prone to error. Use a document management system with built-in tools to automate this process. Platforms like Zemith help enforce these rules by design, allowing you to set policies within specific 'Libraries' to ensure your entire content ecosystem remains compliant.
- Create an Exception Process: Define a clear process for placing legal holds or special extensions on documents that have unique historical, legal, or business value beyond their standard retention period.
- Review and Update Regularly: Laws and business needs change. Review and update your retention policies at least annually to ensure they remain relevant and compliant.
7. Create Regular Backup and Disaster Recovery Procedures
A robust document management system is incomplete without a plan for when things go wrong. Creating regular backup and disaster recovery procedures is the ultimate safety net, safeguarding your organization’s most valuable digital assets from loss due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, human error, or natural disasters. This practice ensures business continuity and the rapid restoration of critical information, preventing catastrophic operational disruptions.
This systematic approach moves beyond simple file copies to a comprehensive strategy. It involves automated backup schedules, secure storage in multiple locations, and a clear, tested plan for restoring data. Implementing this is one of the most vital document management best practices for ensuring long-term data resilience and availability, no matter the circumstances.
Why It Works and How to Implement It
A backup and disaster recovery plan works by creating redundant, accessible copies of your documents, minimizing the impact of any single point of failure. The goal is to make data loss a temporary, recoverable event rather than a permanent disaster. For example, after Hurricane Sandy, financial firms with robust, geographically distributed backups were able to resume operations swiftly, while others faced prolonged outages. Similarly, when shipping giant Maersk was hit by ransomware, its diligent backup practices were critical to its recovery.
The core principle is redundancy. Enterprises often leverage services like Amazon S3’s cross-region replication to automatically maintain copies of their data in different geographic locations, ensuring that even a region-wide outage doesn't result in data loss. For those seeking a deeper understanding, exploring the Best Practices for Secure Data Backup can provide a comprehensive foundation for building a resilient data protection strategy.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Follow the 3-2-1 Rule: Maintain at least three copies of your data, store them on two different types of media, and keep one copy off-site or in the cloud.
- Automate and Monitor: Use software to automate your backup schedules (e.g., daily, weekly) and implement monitoring systems that alert you immediately if a backup fails.
- Test Your Recovery Plan: Regularly conduct mock disaster scenarios to test your recovery procedures. A backup is useless if you can't restore it successfully. Document the steps and train key personnel.
- Actionable Insight: Modern cloud platforms handle much of this for you. For organizations aiming for seamless resilience, adopting a cloud-native platform like Zemith incorporates these protocols into a unified framework, ensuring your data is not only organized but also fully protected by enterprise-grade backup and recovery systems.
8. Provide Comprehensive User Training and Governance
Even the most sophisticated document management system will fail without widespread user adoption and adherence to its rules. Comprehensive training and a solid governance framework are the essential components that translate system design into consistent, real-world practice. This practice ensures that every team member, from new hires to senior leadership, understands not only how to use the system but why its protocols are crucial for organizational efficiency, security, and compliance.
Establishing ongoing training and governance moves your document management from a passive repository to an active, living ecosystem. It creates a culture of accountability where everyone shares responsibility for maintaining data integrity. This is one of the most vital document management best practices for ensuring long-term success and ROI on your technology investment.
Why It Works and How to Implement It
A strong training and governance program works because it eliminates ambiguity and empowers users. It provides clear, role-specific guidance, transforming abstract policies into practical, daily habits. For instance, government agencies often mandate records management training based on the ISO 15489 framework, ensuring all employees understand their legal obligations for handling official records. Similarly, IBM’s extensive digital workplace training ensures its global workforce can collaborate effectively and securely, reinforcing best practices at every level.
These programs build confidence and competence, reducing user error, minimizing support requests, and preventing the creation of rogue data silos. By formalizing the rules and providing the skills to follow them, you create a self-sustaining system of order. To explore this topic in greater depth, you can learn more about how to provide comprehensive user training and governance for your team.
Actionable Tips for Success
- Create Role-Based Training: Tailor training content to specific job functions. A legal assistant needs different skills than a marketing manager. Focus on the features and policies most relevant to their daily tasks.
- Use Interactive Methods: Move beyond static presentations. Use hands-on workshops, real-world scenarios, and quizzes to engage users and improve knowledge retention.
- Establish "Power Users": Identify and train departmental champions or "power users." These individuals can act as the first line of support, provide peer-to-peer guidance, and advocate for best practices within their teams.
- Provide Quick-Reference Guides: Develop simple, one-page cheat sheets or digital guides that outline key procedures like file naming, version control, and access permissions. This gives users an easy resource for quick questions.
- Actionable Insight: A powerful system can reinforce training by automating rules for tagging, classification, and workflow. An intuitive platform like Zemith bridges the gap between training and perfect execution by embedding governance into the user experience, making it easier for users to do the right thing.
8-Key Document Management Practices Comparison
| Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implement a Consistent File Naming Convention | Low to Moderate: Define and train on rules | Low: Primarily time and training | Improved searchability, reduced duplicates | Organizations needing standardized file identification | Enhances findability, supports automation |
| Establish a Logical Folder Structure and Hierarchy | Moderate: Design and maintain folder trees | Moderate: Planning and governance | Intuitive navigation, better collaboration | Businesses organizing large document sets logically | Reduces cognitive load, supports access control |
| Implement Version Control and Document Lifecycle Management | High: Setup automated controls and training | High: Tools, storage, user training | Clear version tracking, reduced editing conflicts | Regulated industries, collaborative environments | Prevents version conflicts, ensures compliance |
| Define and Enforce Access Controls and Security Permissions | High: Complex permission setup and upkeep | Moderate to High: Security systems | Protected sensitive data, compliance adherence | Sensitive or regulated data environments | Enhances security, audit trails, and controlled collaboration |
| Implement Comprehensive Metadata and Tagging Systems | Moderate to High: Metadata schema and tools | Moderate: Tools and governance | Enhanced search, automated workflows | Large document repositories needing advanced search | Improves discoverability, supports analytics |
| Establish Document Retention and Archival Policies | Moderate: Policy creation and enforcement | Moderate: Tools for automation | Regulatory compliance, optimized storage | Regulated industries with strict retention requirements | Reduces liability, controls storage costs |
| Create Regular Backup and Disaster Recovery Procedures | High: Complex backup and recovery planning | High: Infrastructure and testing | Data loss prevention, business continuity | Organizations requiring high data availability | Ensures recovery, protects against cyber and disaster risks |
| Provide Comprehensive User Training and Governance | Moderate to High: Ongoing training programs | Moderate: Training materials and sessions | Consistent best practices, reduced user errors | Any organization adopting or improving document management | Increases adoption, accountability, and system effectiveness |
Supercharge Your Document Strategy with AI
Throughout this guide, we've explored the foundational pillars of effective document management. From establishing consistent file naming conventions and logical folder structures to implementing rigorous version control and security protocols, each practice is a critical component of a well-oiled information ecosystem. Mastering these principles is no longer a luxury for large enterprises; it is an absolute necessity for any individual or team aiming for efficiency, security, and clarity in their daily operations.
The journey from chaotic digital clutter to a streamlined, secure system is built on these core tenets: structure, security, and sustainability. You've learned how a well-defined folder hierarchy prevents information silos, how granular access controls protect sensitive data, and how comprehensive retention policies ensure compliance and reduce risk. These aren't just abstract theories; they are the actionable blueprints for reclaiming control over your most valuable asset: your knowledge.
From Manual Effort to Intelligent Automation
Implementing these document management best practices manually is a significant undertaking. It requires discipline, constant oversight, and a considerable investment of time. While the rewards are substantial, the initial effort can be a major barrier. This is precisely where the next evolution of document management comes into play, transforming a traditionally labor-intensive process into an intelligent, automated workflow.
The true potential of your documents is unlocked when you move beyond simple storage and organization. The future lies in making your documents interactive, queryable, and dynamic. Imagine a system that not only stores your files securely but also understands their content, allowing you to converse with them, extract key insights instantly, and repurpose information with unprecedented speed.
This is the power of integrating AI into your document strategy. An AI-powered platform doesn't just help you adhere to best practices; it supercharges them. For example:
- Metadata and Tagging: Instead of manually tagging every file, AI can analyze content and suggest relevant, consistent tags automatically, ensuring your system remains organized without constant human intervention.
- Search and Retrieval: Traditional search relies on file names and basic metadata. AI-driven search understands context and natural language, allowing you to find a specific chart in a 300-page report by simply asking, "Show me the Q3 revenue projection graph."
- Information Processing: The biggest time sink isn't just finding a document, but processing its contents. AI can generate executive summaries, create study guides, draft email responses based on a report, or even convert dense text into an audio format like a podcast. This fundamentally changes your relationship with your documents, turning static files into active collaborators.
Your Next Steps Toward Mastery
Embracing these concepts is the first step. The next is to translate this knowledge into action. Begin by auditing your current system against the eight practices we've outlined. Identify the most critical pain points, whether it's a lack of version control causing confusion or inconsistent folder structures making files impossible to find.
Start small. Choose one or two practices to implement immediately. Perhaps you can standardize your team's file naming convention this week or define clear access roles for a specific project. The key is to build momentum.
However, for a truly transformative leap in productivity and knowledge management, consider leveraging a platform designed for this new era. A tool like Zemith is built not just for storage but for interaction. By centralizing your documents into organized 'Libraries' and 'Projects', you create a single source of truth. With its Document Assistant, you can instantly chat with any uploaded file, ask complex questions, and get immediate answers. This capability drastically reduces the time spent searching and synthesizing information, freeing you to focus on high-value strategic work. Adopting such a tool is the ultimate expression of mastering document management best practices because it automates the tedious work and amplifies the intellectual value of your information.
Ready to move beyond static folders and make your documents work for you? Discover how Zemith’s AI-powered workspace can automate organization, streamline information retrieval, and transform your files into interactive knowledge partners. Start building your intelligent document ecosystem today by visiting Zemith.
Explore Zemith Features
Introducing Zemith
The best tools in one place, so you can quickly leverage the best tools for your needs.
All in One AI Platform
Go beyond AI Chat, with Search, Notes, Image Generation, and more.
Cost Savings
Access latest AI models and tools at a fraction of the cost.
Get Sh*t Done
Speed up your work with productivity, work and creative assistants.
Constant Updates
Receive constant updates with new features and improvements to enhance your experience.
Features
Selection of Leading AI Models
Access multiple advanced AI models in one place - featuring Gemini-2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, GPT 5, and more to tackle any tasks

Speed run your documents
Upload documents to your Zemith library and transform them with AI-powered chat, podcast generation, summaries, and more
Transform Your Writing Process
Elevate your notes and documents with AI-powered assistance that helps you write faster, better, and with less effort
Unleash Your Visual Creativity
Transform ideas into stunning visuals with powerful AI image generation and editing tools that bring your creative vision to life

Accelerate Your Development Workflow
Boost productivity with an AI coding companion that helps you write, debug, and optimize code across multiple programming languages
Powerful Tools for Everyday Excellence
Streamline your workflow with our collection of specialized AI tools designed to solve common challenges and boost your productivity

Live Mode for Real Time Conversations
Speak naturally, share your screen and chat in realtime with AI
AI in your pocket
Experience the full power of Zemith AI platform wherever you go. Chat with AI, generate content, and boost your productivity from your mobile device.
Deeply Integrated with Top AI Models
Beyond basic AI chat - deeply integrated tools and productivity-focused OS for maximum efficiency
Straightforward, affordable pricing
Save hours of work and research
Affordable plan for power users
Plus
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
Professional
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
What Our Users Say
Great Tool after 2 months usage
simplyzubair
I love the way multiple tools they integrated in one platform. So far it is going in right dorection adding more tools.
Best in Kind!
barefootmedicine
This is another game-change. have used software that kind of offers similar features, but the quality of the data I'm getting back and the sheer speed of the responses is outstanding. I use this app ...
simply awesome
MarianZ
I just tried it - didnt wanna stay with it, because there is so much like that out there. But it convinced me, because: - the discord-channel is very response and fast - the number of models are quite...
A Surprisingly Comprehensive and Engaging Experience
bruno.battocletti
Zemith is not just another app; it's a surprisingly comprehensive platform that feels like a toolbox filled with unexpected delights. From the moment you launch it, you're greeted with a clean and int...
Great for Document Analysis
yerch82
Just works. Simple to use and great for working with documents and make summaries. Money well spend in my opinion.
Great AI site with lots of features and accessible llm's
sumore
what I find most useful in this site is the organization of the features. it's better that all the other site I have so far and even better than chatgpt themselves.
Excellent Tool
AlphaLeaf
Zemith claims to be an all-in-one platform, and after using it, I can confirm that it lives up to that claim. It not only has all the necessary functions, but the UI is also well-designed and very eas...
A well-rounded platform with solid LLMs, extra functionality
SlothMachine
Hey team Zemith! First off: I don't often write these reviews. I should do better, especially with tools that really put their heart and soul into their platform.
This is the best tool I've ever used. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is very fast.
reu0691
This is the best AI tool I've used so far. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is incredibly fast. Just looking at the changelogs, you can see how consistently the developers have ...
