10 Web Scraping Best Practices That Actually Work in 2025
Tired of getting blocked? Master these 10 web scraping best practices for ethical, legal, and efficient data collection. Go from novice to pro today!
So, you want to scrape the web? Welcome to the club! It’s like being a digital Indiana Jones, hunting for treasure (data) in vast, ancient temples (websites). But just like Indy, you can't just barge in and snatch the idol; you'll trigger booby traps (IP bans), angry guardians (legal notices), and maybe even a giant rolling boulder (a server crash). It’s a jungle out there, friend, and without a map, you're toast.
This isn't just another dry-as-a-bone list of "be nice to servers." This is your survival guide, your definitive roadmap to mastering web scraping best practices. We're diving deep into 10 actionable strategies that cover the technical, the legal, and the just-plain-smart. Forget vague advice; we’re talking about real-world implementation details for everything from respecting the digital handshake of robots.txt to navigating the legal minefield of GDPR.
You'll learn how to build scrapers that are not only effective but also ethical and resilient. We'll cover how to avoid getting your IP address thrown into digital jail, manage data responsibly, and keep your code running smoothly even when websites change their layout for the fifth time this month. Think of this as the ultimate checklist for anyone serious about what is the most ethical way to scrape a website.
By the end, you'll have the toolkit to gather the data you need without waking the server gods or attracting unwanted attention from a legal team. Ready to build smarter, more robust scrapers? Let's get started.
1. Respect robots.txt and Site Terms of Service
Before you write a single line of code, your first stop should be the website's rulebooks: the robots.txt file and its Terms of Service (ToS). Think of this as asking for permission before entering someone’s house. Ignoring these is not just bad manners; it's a first-class ticket to getting your IP blocked or earning a nastygram from a lawyer. This initial check is the cornerstone of ethical web scraping best practices.
The robots.txt file is a simple text file at the root of a domain (e.g., domain.com/robots.txt). It tells bots which parts of the site they're welcome to visit. It’s like the bouncer at a club pointing to the V.I.P. section and saying, "Yeah, not for you, pal."

Beyond the Robot: The Human Rules
While robots.txt is a technical guide, the Terms of Service is a legally binding contract. It outlines what you can and cannot do with the site's data. Famously, LinkedIn has legally enforced its ToS against companies that scrape user profiles. It is paramount to always consult and respect a website's guidelines, including their detailed site's terms of service, before kicking off any scraping operations.
Actionable Checklist for Compliance:
- Check
robots.txtFirst: Seriously, do it. Look forUser-agent: *to see the general rules, and check for anyDisallow:directives that apply to your project. - Read the ToS Carefully: Pop open the ToS and use
Ctrl+Fto search for keywords like "scrape," "crawl," or "automated access." This will quickly show you the red flags. - Document Everything: Screenshot the
robots.txtand ToS before you start. If your practices are ever questioned, you'll have proof you did your homework. - Look for an Official API: If a site explicitly forbids scraping, check if they offer an API. This is their preferred method for data access and a much safer route. If you're building out a larger project, a platform like Zemith can help you manage and integrate various data sources, including APIs, all in one place.
2. Implement Respectful Rate Limiting and Throttling
Okay, you've cleared the legal hurdles. Now, don't act like a bull in a china shop. Firing off requests as fast as your machine can handle them is a surefire way to get blocked. Think of it as showing up to a buffet and trying to eat everything in 30 seconds; you'll get kicked out. Rate limiting and throttling are your tools to be a polite, effective, and undetected guest. This is one of the most fundamental web scraping best practices for how to avoid getting blocked when web scraping.
Implementing delays ensures your scraper doesn't overwhelm the target server, which could accidentally cause a denial-of-service (DoS) situation. By distributing your requests over time, you mimic human browsing behavior, reduce server strain, and dramatically lower the chances of your IP being flagged. It’s just good manners.
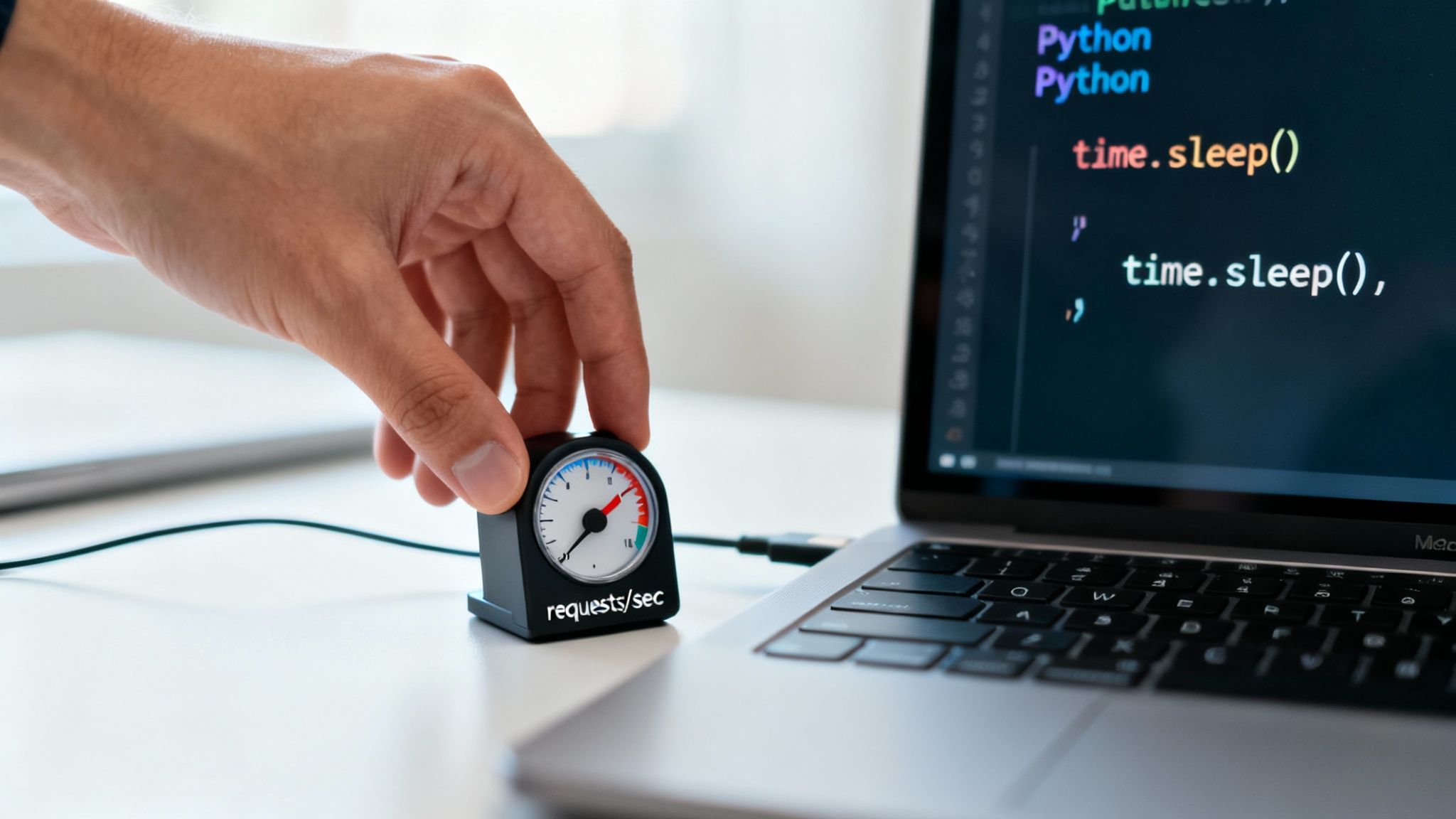

Finding the Right Cadence
The simplest way to start is by adding a static delay between requests. In Python, a simple time.sleep(2) can work wonders. But for the pros, dynamic throttling is where it's at. The Scrapy framework's AutoThrottle extension, for example, is brilliant; it automatically adjusts the crawling speed based on the server's load, slowing down when the server is busy and speeding up when it's not. It’s like a car with adaptive cruise control, but for data.
Actionable Checklist for Rate Limiting:
- Start Conservatively: Begin with a generous delay between requests, like 2-5 seconds. You can always fine-tune it later. Better to be the tortoise than the banned hare.
- Listen to the Server: Monitor HTTP response codes. If you get a
429 Too Many Requestsor503 Service Unavailable, your scraper needs to back off immediately. The server is literally yelling "GIVE ME A BREAK!" - Implement Exponential Backoff: When a request fails, don't just retry instantly. Increase the delay exponentially with each failed attempt (e.g., wait 2s, then 4s, then 8s). This prevents hammering a struggling server.
- Use Dynamic Delays: Instead of a fixed
sleep(3), use a randomized delay likesleep(random.uniform(2, 5)). This makes your scraper's request pattern less robotic and harder to detect. For complex projects where managing proxies and request patterns is key, exploring a robust platform like Zemith can provide the necessary infrastructure to do this at scale.
3. Use Appropriate HTTP Headers and User-Agent Strings
When your scraper sends a request, it introduces itself with HTTP headers. Think of the User-Agent string as your scraper's business card. Showing up with a generic, default, or blank card is the digital equivalent of wearing a fake mustache to a meeting. It’s a dead giveaway that you're an automated bot, and an easy way to get the door slammed in your face.
The User-Agent string tells the server who's asking for the page (e.g., Chrome on Windows, or Google's own crawler). Many websites automatically block requests from common library defaults, like the one from Python's requests library, because they scream "I am a lazy bot!" A well-crafted User-Agent, on the other hand, helps you fly under the radar. For example, Googlebot’s User-Agent is Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Googlebot/2.1; +http://www.google.com/bot.html). It clearly identifies itself and provides a link for more info. Classy.
Beyond the Name Tag: Full HTTP Etiquette
Your User-Agent is just the start. Real web browsers send a whole suite of headers with every request, like Accept-Language, Accept-Encoding, and Referer. A request missing these sticks out like a sore thumb. Mimicking a real browser's header profile makes your scraper appear more like legitimate human traffic. Are we getting better at this? Let's check: are Accept and Referer headers important for web scraping? Yes, absolutely!
Actionable Checklist for Header Management:
- Craft a Custom User-Agent: Never use a library's default. Create a unique string that identifies your bot and, if possible, provides a way to contact you. Example:
'MyAwesomeScraper/1.1 (+http://mycompany.com/info; admin@mycompany.com)'. - Mimic Browser Headers: Use a full set of realistic headers. Open your browser's developer tools, copy the headers it sends, and replicate them in your scraper. Pay attention to
Accept,Accept-Language, andAccept-Encoding. - Use a Referer Header: The
Refererheader tells the server which page you came from. Setting this to a plausible URL (like the previous page in a pagination sequence) makes your scraper’s navigation look much more natural. - Handle Cookies Gracefully: Websites use cookies to maintain sessions. Your scraper should accept and send back cookies just like a browser would to navigate logins or search filters. When you're managing complex scraper states and workflows, the coding assistant in Zemith can help you quickly generate the code snippets you need to handle these details correctly.
4. Handle Data Privacy and GDPR/CCPA Compliance
Once you start collecting data, especially about people, you’re no longer just a developer; you’re a data custodian. This shift comes with serious legal and ethical responsibilities. Regulations like GDPR and CCPA are not just suggestions; they are strict laws with massive penalties. Ignoring them is like juggling chainsaws—it's not a matter of if you'll get hurt, but when.
These laws give people rights over their personal information. Scraping names, emails, user photos, or any other personally identifiable information (PII) immediately places your project under their scrutiny. Famously, Amazon was fined a staggering €746 million for GDPR violations. You probably don't have that kind of cash lying around.

Beyond Scraping: Becoming a Data Steward
Thinking like a data steward means treating information with respect. This involves understanding not just the tech, but also the legal framework. The core principle is "data minimization": only collect what is absolutely necessary. Understanding a website's specific guidelines, such as its Privacy Policy, is essential for responsible data handling and compliance.
Actionable Checklist for Compliance:
- Audit Your Data Needs: Before scraping, ask yourself: "Do I really need this personal data?" If not, don't collect it. Stick to the absolute minimum.
- Anonymize Where Possible: If you can achieve your goal with anonymized or aggregated data, do that. It significantly reduces your compliance burden.
- Secure Your Data: This is not a drill. Encrypt data both in transit (while scraping) and at rest (in your database).
- Plan for Deletion: Don't be a data hoarder. Establish a clear policy for how long you will store PII and create automated schedules to delete it once it's no longer needed.
- Maintain Records: Keep detailed logs of your data processing. This documentation is crucial for proving compliance if regulators come knocking. The research tools inside Zemith are great for documenting your project's compliance strategy right alongside your code and data.
5. Implement Robust Error Handling and Logging
A web scraper that breaks silently is worse than one that never runs at all. Without a proper safety net, your scraper could be pulling incomplete data, getting blocked without you knowing, or just crashing in the middle of the night. Robust error handling and detailed logging transform your fragile script into a resilient, production-ready data pipeline. This is one of the most crucial web scraping best practices for building systems you can actually trust.
Think of logging as your scraper’s black box recorder. It tells you exactly what happened, when, and why. If a request fails, your logs should capture the URL, the HTTP status code, and the error. This record is invaluable for debugging. It’s the difference between knowing "it broke" and knowing "it broke at 3:15 AM on URL X because of a 503 error after 3 retries."
From Failure to Recovery
Error handling is what you do about those logged issues. It’s not just about catching exceptions; it’s about smart recovery. Instead of giving up after one failed request, a good scraper implements retry logic, often with exponential backoff. This gives the target server (or your own connection) a chance to recover. It’s the polite thing to do.
Actionable Checklist for Reliability:
- Log Everything That Matters: Use a standard logging library (like Python's
loggingmodule) to record timestamps, URLs, response codes, and exceptions. Use different levels likeDEBUGfor development andINFOfor production. - Implement Smart Retries: When a request fails (e.g., with a 503 error), don't give up. Retry it a few times with an increasing delay between attempts (exponential backoff).
- Set Up Alerts: Configure your system to send you an alert via email or Slack if something goes wrong. This lets you intervene before bad data pollutes your database.
- Use Circuit Breakers: If a scraper hits a high rate of consecutive errors, a circuit breaker can temporarily halt all activity to prevent getting banned. For a deeper dive, the coding assistant in Zemith can help you draft a robust error-handling class for your specific Python project in seconds.
6. Respect Authentication and Session Management
Scraping public data is one thing, but navigating past a login screen is a whole different ballgame. Properly handling authentication is both a technical necessity and a critical ethical requirement. This practice is about respecting digital boundaries. Ignoring it is a surefire way to get more than just your IP blocked; it can lead to serious legal consequences for unauthorized access.
Many websites protect valuable content behind an authentication wall. Attempting to programmatically bypass these logins without explicit, written permission from the account owner and the website operator is a massive violation of trust. This is a core principle in ethical web scraping best practices that separates legitimate data gathering from unauthorized intrusion. Is it legal to scrape a website after logging in? Only with explicit permission!
The Key to the Digital Kingdom
When you do have permission, managing the session becomes paramount. This involves storing and reusing cookies or session tokens provided by the server after a successful login. Poor session management can lead to your scraper being logged out repeatedly, triggering security alerts, or failing to access the data.
Actionable Checklist for Authenticated Scraping:
- Get Explicit Permission: Never scrape content behind a login wall without clear, written consent from the website owner and the account holder. Full stop.
- Secure Credentials: Do not hardcode usernames or passwords in your script. Use environment variables or a secure vault service to manage sensitive credentials safely.
- Respect Paywalls: Subscriber-only content is for subscribers. Scraping it en masse, even with valid credentials, can be a breach of the terms of service, especially if you plan to redistribute it.
- Maintain Session Security: Always use HTTPS. Understand how the site handles session tokens and timeouts, and build your scraper to respect those mechanisms.
7. Use Proxies and Distributed Scraping Responsibly
Proxies act as intermediaries, routing your requests through different IP addresses. This is powerful for tasks like accessing geo-restricted content, but it's also easily abused. Using proxies responsibly is a core tenet of ethical web scraping best practices. It’s about leveraging a tool for legitimate purposes, not for playing digital cat-and-mouse to bypass a website's defenses.
Distributed scraping and proxies are essential for large-scale projects, like an e-commerce aggregator checking product prices in the US, UK, and Japan simultaneously. The key is that the intent isn't malicious. Misusing them to hammer a server after an IP ban is a fast way to escalate a simple block into a much more serious confrontation.
Navigating the Gray Areas of Anonymity
The primary function of a proxy is to mask your origin, but the "why" behind it matters. Are you trying to see a German version of a website from your desk in Canada? Legitimate. Are you rapidly rotating hundreds of IPs to circumvent rate limits you were given for a reason? That's heading into problematic territory. It mimics a denial-of-service attack and puts unnecessary strain on servers.
Actionable Checklist for Responsible Proxy Use:
- Define Your Justification: Before using a proxy, document why you need it. Is it for geo-targeting, load balancing, or failover? Have a clear, ethical reason.
- Avoid Aggressive Rotation: Don't cycle through thousands of IPs on a single domain in a short period. This is highly suspicious. Instead, assign specific proxies to specific targets for longer sessions.
- Choose Ethical Providers: Vet your proxy provider. Ensure they source their IP addresses ethically. Not all proxy services are created equal.
- Use Residential Proxies Sparingly: Residential proxies are powerful but ethically complex. Reserve them for only the most critical and legitimate use cases. A good system, like one you could architect with guidance from Zemith, helps you manage these resources effectively and document their use.
8. Monitor for Changes and Maintain Scraper Robustness
A web scraper that works perfectly today might completely break tomorrow. This isn't a sign of bad code; it's a fundamental reality. Websites are constantly evolving. Treating your scraper as a "set it and forget it" tool is a recipe for disaster. Robust maintenance is a core web scraping best practice that separates successful projects from those that quickly become obsolete.
Think of your scraper like a high-performance car. It needs regular check-ups. A simple redesign of a product page could shift the location of the price element, causing your scraper to return null values or, even worse, grab the wrong data. Proactive monitoring prevents data corruption and downtime.
Staying Ahead of the Breakage
The key is to build a system that alerts you to problems before they cascade. This involves more than just watching for crashes. A scraper can "succeed" in running but fail in its mission by returning empty or incorrect data. Implementing automated checks that validate the output is crucial. For example, if your financial scraper suddenly reports that every stock price is $0.00, your monitoring system should immediately flag this anomaly.
Actionable Checklist for Robustness:
- Implement Automated Validation: Write tests that run after each scrape to check for expected data patterns. Are prices within a realistic range? Are dates in the correct format? Flag any jobs that return a high percentage of null values.
- Set Up Smart Alerts: Configure alerts for critical failures: spikes in HTTP error codes (like 404s or 503s), a sudden drop in data volume, or schema validation failures.
- Use Version Control Religiously: Track every change to your scraper's code and selectors using Git. When something breaks, having a clear history makes debugging a thousand times easier. You can dive deeper into effective strategies by exploring best practices for version control on zemith.com.
- Perform Regular Spot-Checks: Don't rely solely on automation. Once a week, manually inspect the data from a few target pages to ensure the quality is still top-notch. It's the best way to catch subtle issues automation might miss.
9. Cache and Store Data Responsibly and Legally
Successfully extracting data is only half the battle; how you cache, store, and manage it carries significant technical and legal weight. Responsible data handling is a core tenet of ethical web scraping best practices. Think of it as being a good digital librarian: you don't just hoard books, you organize, secure, and eventually archive them properly.
The goal is to move from a "collect everything" mindset to a "collect what's necessary" strategy. This involves implementing clear policies for what data you keep, for how long, and how you secure it. For instance, a price monitoring service doesn’t need to store every historical price point forever.
From Scraping to Storing: The Ethical Data Lifecycle
Proper data storage isn't just about avoiding lawsuits; it's about building a sustainable and efficient data pipeline. When you only store essential information, your databases are faster, your backups are smaller, and your analysis is more focused. Applying solid database design principles is a crucial step in this process.
Actionable Checklist for Responsible Storage:
- Practice Data Minimization: Before saving anything, ask yourself: "Do I absolutely need this field?" If the answer is no, don't store it. This reduces costs and legal exposure.
- Implement Retention Policies: Establish automated deletion schedules. For example, job board scrapers should delete postings once they are no longer active on the source site.
- Encrypt Sensitive Data: Always encrypt data both in transit (while scraping) and at rest (in your database). This is non-negotiable, especially if you handle any PII.
- Secure Your Backups: Don't let your guard down with backups. Ensure they are also encrypted and stored in a secure, access-controlled location.
- Never Republish Without Permission: Unless the site’s ToS explicitly allows it, do not resell or republish scraped content as your own. This is a fast track to a cease and desist letter.
- Document Your Policies: Keep a clear record of your data handling policies. This documentation is invaluable for demonstrating compliance.
10. Test for and Avoid Legal Liability
Navigating the web scraping world can feel like walking through a legal minefield. The landscape is dotted with landmark court cases and evolving laws like the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA). Ignoring this is a high-stakes gamble. Understanding and mitigating potential legal risks is a foundational pillar of sustainable web scraping best practices.
The legal status of scraping often hinges on nuances. The landmark hiQ Labs vs. LinkedIn case affirmed that scraping publicly accessible data does not violate the CFAA. However, cases like Associated Press vs. Meltwater show that simply republishing scraped content can lead to copyright infringement liability. The key takeaway: how you access data and what you do with it both matter.
Beyond the Scraper: Your Legal Due Diligence
Proactively managing legal risk involves more than just crossing your fingers. It requires a documented, thoughtful approach. This isn't just about avoiding lawsuits; it's about building a project on a solid, defensible foundation. It ensures your hard work isn't undone by an entirely preventable legal challenge.
Actionable Checklist for Legal Compliance:
- Consult a Professional: For any large-scale or commercial scraping project, consult with an attorney specializing in internet law. This is a critical investment.
- Document Your "Fair Use": If relying on fair use, document your analysis. Consider the purpose (e.g., non-commercial, transformative), the nature of the work, the amount used, and the effect on the original market.
- Avoid Direct Competition: A major red flag is using scraped data to create a product that directly competes with the target website's core business model.
- Transform, Don't Republish: Focus on transforming the data into something new and valuable, like analytics or research. Avoid simply copying and pasting content. A well-designed internal tool, like those you can build within a platform like Zemith, can help process and transform this data effectively.
- Establish a Review Process: Create a formal process where legal or compliance stakeholders review scraping projects before they are deployed to identify potential risks early.
Web Scraping: 10 Best-Practices Comparison
| Practice | Implementation 🔄 | Resources ⚡ | Expected outcomes ⭐📊 | Ideal use cases 💡 | Key advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Respect robots.txt and Site Terms of Service | Low 🔄 — parse robots.txt; review ToS | Low ⚡ — minimal compute; legal review time | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — lowers legal/banning risk | Startups; public-data scraping; compliance-first projects | Avoids legal action; preserves access; ethical |
| Implement Respectful Rate Limiting and Throttling | Medium 🔄 — delays, backoff, queuing | Low ⚡ (CPU) but increases runtime | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — reduces server strain and bans | Large crawls; continuous scraping; polite bots | Prevents overload; sustainable long-term access |
| Use Appropriate HTTP Headers and User-Agent Strings | Low 🔄 — set descriptive headers; include contact | Low ⚡ — negligible overhead | ⭐⭐⭐ — improves transparency; can reduce blocks | Bots that must be contactable; API-like crawlers | Builds trust; enables contact; may avoid blocks |
| Handle Data Privacy and GDPR/CCPA Compliance | High 🔄 — DPIA, consent, retention policies | High ⚡ — legal, engineering, secure storage | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ — minimizes fines; builds trust | Any project collecting personal data; commercial services | Legal defensibility; customer trust; avoids fines |
| Implement Robust Error Handling and Logging | Medium 🔄 — retries, structured logs, alerts | Medium ⚡ — log storage + monitoring costs | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — faster debugging; higher reliability | Production scrapers; regulated data collection | Root-cause analysis; audit trails; proactive alerts |
| Respect Authentication and Session Management | High 🔄 — secure tokens, cookie handling | Medium-High ⚡ — credential management infra | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — prevents unauthorized access | Any site with logins or paywalls (only with permission) | Protects accounts; reduces liability; ethical access |
| Use Proxies and Distributed Scraping Responsibly | Medium-High 🔄 — rotation strategies, orchestration | High ⚡ — proxy costs; orchestration complexity | ⭐⭐ — improves reach but increases scrutiny/risk | Geo-specific testing; redundancy (with clear permission) | Geo access; load distribution; redundancy (use ethically) |
| Monitor for Changes and Maintain Scraper Robustness | Medium-High 🔄 — CI, tests, change detection | Medium ⚡ — CI/CD, alerts, maintenance effort | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — fewer outages; better data quality | Long-term pipelines; sites with frequent redesigns | Early detection; reduced downtime; consistent quality |
| Cache and Store Data Responsibly and Legally | Medium 🔄 — retention policies, encryption | Medium-High ⚡ — secure storage, backups | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — reduces breach/compliance risk | Any persisted scraped data; GDPR/CCPA environments | Limits liability; protects sensitive data; compliance |
| Test for and Avoid Legal Liability | High 🔄 — legal reviews, ToS analysis, docs | High ⚡ — counsel fees; time for assessments | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ — strong legal defensibility | High-risk commercial projects; large-scale scraping | Prevents lawsuits; documents due diligence; risk-aware decisions |
Go Forth and Scrape Responsibly
You made it! You've navigated the technical pitfalls, the legal mazes, and the ethical tightropes of web scraping. From respecting robots.txt like it's a sacred text to managing proxies without looking like a botnet herder, we've covered a ton of ground. Think of this as your web scraping graduation ceremony—the diploma is a folder full of clean, ethically sourced data.
Remember, great power (to collect data) comes with great responsibility (to not be a jerk about it). These web scraping best practices aren't just rules to slow you down; they are the foundation of sustainable, reliable data collection. Following them means your scrapers are less likely to break, your IP is less likely to get banned, and you're far less likely to get a sternly worded letter from a lawyer.
Your Cheat Sheet for Ethical Scraping
Let's boil it all down. If you walk away with anything, let it be these core principles:
- Be a Good Guest: This is the golden rule. Announce yourself with a clear
User-Agent, respectrobots.txtand Terms of Service, and don't hammer the server. A gentle, throttled approach is always better than a brute-force data smash-and-grab. - Plan for Failure: The web is chaotic. Websites change, servers go down, and anti-bot measures get smarter. Your code needs to be resilient. Robust error handling, comprehensive logging, and proactive monitoring aren't "nice-to-haves"; they are essential.
- Think Legally and Ethically: Always ask: "Should I be scraping this?" Just because you can extract data doesn't always mean you should. Be extra careful with personal information, copyrighted content, and data behind a login wall.
- Stay Human (or at Least Pretend To): Vary your request patterns, use appropriate headers, and rotate through high-quality proxies. The goal isn't deception, but to mimic human browsing patterns, which places a lighter load on the target server.
From Best Practices to Best-in-Class Workflow
Mastering these concepts transforms web scraping from a risky gamble into a powerful, predictable tool. It's the difference between building a rickety raft and engineering a state-of-the-art research vessel. A well-built scraper is a valuable asset that can provide a continuous stream of high-quality data for years.
But let's be real, even with the best practices, managing the entire workflow—from research to writing code to analyzing data—can feel like juggling chainsaws. You're constantly switching contexts: from researching targets, to debugging Python scripts, to wrangling data in a spreadsheet, and then trying to summarize your findings. It's a fragmented process that drains time and energy.
That's where a unified workspace can be a game-changer. Imagine conducting your research, writing and debugging your scraper code with an AI assistant that understands your goals, and then analyzing your collected data, all in one place. This is the future of efficient data work.
Take these principles, build something amazing, and remember to always scrape with purpose and respect. The web is a vast, incredible resource. With the right approach, you can unlock its secrets without leaving a trail of broken servers in your wake. Happy scraping!
Ready to streamline your entire research and data collection process? Zemith provides an integrated environment with Deep Research and Coding Assistant tools to help you manage everything from discovery to data analysis in one seamless workspace. Stop juggling tabs and start building your next data project more efficiently at Zemith.
*Explore Zemith Features
Introducing Zemith
The best tools in one place, so you can quickly leverage the best tools for your needs.
All in One AI Platform
Go beyond AI Chat, with Search, Notes, Image Generation, and more.
Cost Savings
Access latest AI models and tools at a fraction of the cost.
Get Sh*t Done
Speed up your work with productivity, work and creative assistants.
Constant Updates
Receive constant updates with new features and improvements to enhance your experience.
Features
Selection of Leading AI Models
Access multiple advanced AI models in one place - featuring Gemini-2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, GPT 5, and more to tackle any tasks

Speed run your documents
Upload documents to your Zemith library and transform them with AI-powered chat, podcast generation, summaries, and more
Transform Your Writing Process
Elevate your notes and documents with AI-powered assistance that helps you write faster, better, and with less effort
Unleash Your Visual Creativity
Transform ideas into stunning visuals with powerful AI image generation and editing tools that bring your creative vision to life

Accelerate Your Development Workflow
Boost productivity with an AI coding companion that helps you write, debug, and optimize code across multiple programming languages
Powerful Tools for Everyday Excellence
Streamline your workflow with our collection of specialized AI tools designed to solve common challenges and boost your productivity

Live Mode for Real Time Conversations
Speak naturally, share your screen and chat in realtime with AI
AI in your pocket
Experience the full power of Zemith AI platform wherever you go. Chat with AI, generate content, and boost your productivity from your mobile device.
Deeply Integrated with Top AI Models
Beyond basic AI chat - deeply integrated tools and productivity-focused OS for maximum efficiency
Straightforward, affordable pricing
Save hours of work and research
Affordable plan for power users
Plus
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
Professional
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
What Our Users Say
Great Tool after 2 months usage
simplyzubair
I love the way multiple tools they integrated in one platform. So far it is going in right dorection adding more tools.
Best in Kind!
barefootmedicine
This is another game-change. have used software that kind of offers similar features, but the quality of the data I'm getting back and the sheer speed of the responses is outstanding. I use this app ...
simply awesome
MarianZ
I just tried it - didnt wanna stay with it, because there is so much like that out there. But it convinced me, because: - the discord-channel is very response and fast - the number of models are quite...
A Surprisingly Comprehensive and Engaging Experience
bruno.battocletti
Zemith is not just another app; it's a surprisingly comprehensive platform that feels like a toolbox filled with unexpected delights. From the moment you launch it, you're greeted with a clean and int...
Great for Document Analysis
yerch82
Just works. Simple to use and great for working with documents and make summaries. Money well spend in my opinion.
Great AI site with lots of features and accessible llm's
sumore
what I find most useful in this site is the organization of the features. it's better that all the other site I have so far and even better than chatgpt themselves.
Excellent Tool
AlphaLeaf
Zemith claims to be an all-in-one platform, and after using it, I can confirm that it lives up to that claim. It not only has all the necessary functions, but the UI is also well-designed and very eas...
A well-rounded platform with solid LLMs, extra functionality
SlothMachine
Hey team Zemith! First off: I don't often write these reviews. I should do better, especially with tools that really put their heart and soul into their platform.
This is the best tool I've ever used. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is very fast.
reu0691
This is the best AI tool I've used so far. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is incredibly fast. Just looking at the changelogs, you can see how consistently the developers have ...
