Normalized vs Denormalized Data The Ultimate Database Design Showdown
Struggling with normalized vs denormalized data? This guide breaks down the trade-offs with real-world examples to help you optimize your database.
The core difference between normalized vs denormalized data boils down to a simple trade-off: normalization prioritizes data integrity by stamping out redundancy, which is perfect for transactional systems like an e-commerce checkout. On the other hand, denormalization deliberately introduces redundancy to make queries run faster—a lifesaver for analytics and reporting.
The Great Database Design Showdown
Welcome to the main event in the world of database design! In one corner, you have the disciplined champion of data integrity: Normalized Data. In the other, the powerhouse built for pure read speed: Denormalized Data.
Think of it this way: normalization is like a meticulously organized toolbox where every screw has its own labeled drawer. Denormalization is more like a workbench where you’ve laid out all your most-used tools for quick and easy access. So, are you a neat freak or a speed demon?
This isn't just a technical squabble; it's a strategic decision that directly impacts your application's performance. Choosing the wrong model is like trying to race a cargo ship—it’s incredibly reliable, but you’re not going to win any sprints. Let's break down this rivalry and show you why picking the right approach is one of the most important calls you'll make.

Key Differences at a Glance
Before we get into the nitty-gritty, let's start with a high-level look at the battlefield. This table cuts right to the chase, outlining the fundamental trade-offs you'll be making with each model.
| Characteristic | Normalized Data | Denormalized Data |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Minimize data redundancy and ensure consistency | Maximize read speed and simplify queries |
| Data Structure | Data is split across multiple, related tables | Data is combined into fewer, larger tables |
| Best For | Write-heavy applications (e.g., OLTP systems) | Read-heavy applications (e.g., OLAP, analytics) |
| Data Integrity | High, enforced through relational rules | Lower, requires application-level logic to maintain |
| Query Speed | Can be slower for complex reads due to joins | Typically much faster due to fewer or no joins |
| Storage Space | More efficient, as it avoids storing duplicate data | Less efficient, requires more space for redundant data |
This table gives you a snapshot, but remember that the right choice always depends on what you're trying to build.
Grasping how to structure and optimize data is a cornerstone skill for many technical careers. If you're exploring this path, learning how to become a data analyst can give you a great roadmap. Nailing fundamentals like these is non-negotiable.
As you start mapping out your data models, things can get complex fast. Juggling schemas, relationships, and design choices is a lot to handle. This is where a tool like Zemith's AI document assistant can be a game-changer, helping you organize all that documentation into a clear, queryable knowledge base from day one.
Understanding Normalization: The Art of Tidy Data
Let's start with normalization. Think of it as the Marie Kondo method for organizing a database. It's all about one core principle: keeping your data ridiculously clean and consistent. Imagine trying to manage a chaotic closet where socks, shirts, and shoes are all tossed into one big pile. It's a mess. Normalization is the act of giving each item its own dedicated drawer or shelf.
In database terms, this means breaking down large, clunky tables into smaller, more focused ones and then linking them together. The primary goal here is to stamp out data redundancy. You don't want the same piece of information repeated all over the place.

This approach is the gold standard for data integrity, and for good reason. When a customer updates their shipping address, you only have to change it in one spot—the Customers table. Without normalization, that same address could be duplicated across hundreds of old order records. That's a recipe for inconsistent data and a whole lot of shipping disasters. For developers building transaction-heavy apps where accuracy is non-negotiable, this is a dream come true.
The Rules of Tidiness: The Normal Forms
So, how do you achieve this state of data nirvana? We follow a set of rules called "normal forms." They sound a bit academic, but they're just progressive steps to make your data cleaner. Honestly, you'll mostly just need to worry about the first three.
Let's walk through it with a simple e-commerce example. Imagine you started with a single, messy spreadsheet for all your orders.
1. First Normal Form (1NF)
- The Rule: Each cell must hold a single, atomic value, and there should be no repeating groups.
- The Problem: Your "ProductsOrdered" column is crammed with a list like "T-Shirt, Hoodie, Socks." That single cell is doing way too much work.
- The Fix: You break it up, giving each product its own row. An order from one customer might now span three rows, but every cell is clean and holds just one piece of information.
2. Second Normal Form (2NF)
- The Rule: You have to be in 1NF, and all non-key columns must depend on the entire primary key.
- The Problem: In your new table, customer details (name, address) are repeated for every single item they ordered. The customer's address depends on the customer ID, not the specific product they bought in that order.
- The Fix: You solve this by pulling customer information into its own
Customerstable and product details into aProductstable. TheOrderstable now just uses IDs to link everything together.
3. Third Normal Form (3NF)
- The Rule: You must be in 2NF, and non-key columns can't depend on other non-key columns.
- The Problem: Maybe your
Orderstable has the customer's "LoyaltyStatus," which is actually determined by their "TotalSpent." The loyalty status depends on their spending history, not on this specific order ID. That's called a transitive dependency, and it's a big no-no. - The Fix: You move "LoyaltyStatus" and "TotalSpent" into the
Customerstable, where they logically belong. TheOrderstable doesn't need to know about that stuff.
There's a saying among database old-timers that perfectly sums up the goal of 3NF: "Every non-key attribute must provide a fact about the key, the whole key, and nothing but the key, so help me Codd."
Why This Tidy Structure Matters
By following these forms, you build a database that is incredibly robust. Making changes is straightforward, data anomalies become a rarity, and you can actually trust the information you're storing. This kind of careful organization is a core principle of effective research data management, ensuring that your information stays reliable over the long haul.
Of course, when you're dealing with complex schemas, this process can feel overwhelming. That’s where a tool like Zemith's AI coding assistant becomes a lifesaver. It can help you quickly generate SQL schemas for different normal forms and even prototype the queries you'd need to join them back together, letting you see the structure in action without all the manual grunt work.
Denormalization: Breaking the Rules for Raw Speed
Alright, let's talk about the other side of the coin. If normalization is about creating a perfectly organized, tidy database, then denormalization is about strategically making a mess to go incredibly fast.
Think of it this way: to get a complete sales report from a normalized database, your query has to act like a detective. It runs from the Customers table to the Orders table, then over to Products and OrderDetails, collecting clues and piecing them together. These "joins" are powerful, but they take time and computational horsepower, especially when you're dealing with massive datasets.
Denormalization says, "Forget the detective work." It's the express lane for your data. The whole point is to intentionally duplicate data to make your read-heavy operations, like analytics and reporting, absolutely fly. For a business intelligence dashboard that needs to load in milliseconds, this isn't just a nice feature—it's everything.
Trading Purity for Blazing Performance
The concept behind denormalization is actually quite simple. Instead of forcing the database to perform the same complex joins over and over again every time someone runs a report, you do the work upfront. You create wider, "flatter" tables that already contain all the information you need.
Let's go back to our e-commerce store. Instead of four separate, pristine tables, we could create a single sales_report table specifically for analytics.
Here’s what that might look like:
| OrderID | OrderDate | CustomerName | CustomerEmail | ProductName | Category | Price | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | 2023-10-26 | Jane Doe | jane@email.com | "AI T-Shirt" | "Apparel" | 25.00 | 2 |
| 102 | 2023-10-26 | John Smith | john@email.com | "Code Mug" | "Accessories" | 15.00 | 1 |
See what happened? The CustomerName and ProductName are right there in the same row. No more joins needed. If someone wants to see all apparel sales in October, the database just has to scan this one table. It’s a direct, straight-line query.
By pulling related data into a single place, denormalization slashes the computational work needed for read operations. You’re essentially doing the join work once when the data is written to save time on potentially millions of future queries.
This is a massive advantage for systems that serve up dashboards to lots of users at once. The performance boost isn't trivial, either. Industry benchmarks often show that denormalized structures can deliver 10-15x performance improvements for complex analytical queries. When you combine that with column-oriented storage, those gains can jump by another 3-5x. If you want to dive deeper, you can explore some of the numbers in this detailed technical breakdown.
Prototyping Your Need for Speed
Of course, this speed isn't free. The trade-offs are real—you're using more storage space, and you introduce the headache of keeping all that redundant data in sync. Deciding what and when to denormalize is a critical architectural decision. It’s especially relevant in modern systems; for example, many microservices architecture patterns intentionally duplicate data between services to keep them independent and fast.
This is where a little help from modern tooling can make a world of difference. Manually refactoring schemas and rewriting queries just to test a denormalized approach is a slog. But with an AI tool like Zemith's coding assistant, you can quickly prototype these heavy-duty analytical queries. You can have it generate the SQL for a denormalized view or a new summary table and get an immediate sense of the performance impact—all without getting bogged down writing the code yourself. It's like having a crystal ball for your database performance.
Head-to-Head: A Nuanced Comparison
Alright, let's get down to brass tacks. It's time to put normalization and denormalization in the ring to see how they stack up on the metrics that actually matter. We're moving past the textbook definitions and digging into the real-world trade-offs you'll face when picking a side.
This isn't just a theoretical exercise; it's a decision that will ripple through your application's entire lifecycle. Think of it like choosing between a precision screwdriver and a sledgehammer. Both have their place, but you really don't want to get them mixed up.
Data Integrity: The Consistency Crown
When it comes to keeping your data clean and trustworthy, normalization is the undisputed champion. Honestly, it’s the whole reason the concept was invented in the first place. By breaking data into distinct, related tables, you establish a single source of truth for every piece of information.
This structure is an absolute godsend for data consistency. A normalized model slashes redundancy by ensuring data isn't duplicated all over the place, which directly boosts integrity because an update only has to happen in one spot. This approach can cut the risk of inconsistent data by 40-60% in many real-world applications—a massive win for reliability. If you want to get into the nitty-gritty, you can learn more about normalized versus denormalized structures on Netdata.cloud.
Denormalization, on the other hand, lives in a state of controlled chaos. It deliberately duplicates data. This means one simple update—like a customer changing their address—sends you on a scavenger hunt to find and change every single copy. Miss just one, and you've instantly created conflicting records.
The Bottom Line: For any application where data accuracy is non-negotiable (think banking, e-commerce, or healthcare systems), normalization is your steadfast ally. Denormalization demands careful, upfront planning and solid processes to keep its redundant data in sync.
Query Performance: The Speed Demon
Now, let’s talk speed. If normalization is the careful librarian, meticulously organizing every book, denormalization is the getaway driver. Its entire purpose is to make your read queries ridiculously fast by getting rid of those complex, resource-intensive joins.
Think about an analytics dashboard trying to pull data from five different tables in a normalized schema. The database has to work hard, joining them on the fly every single time the query runs. This can become a serious bottleneck. A denormalized table, however, has all that data pre-joined and ready to go. It’s like having the answers to the test before you even walk in the room.
The following infographic breaks down the key benefits that make denormalization a beast for read-heavy workloads, focusing on speed, simpler reporting, and that ever-present trade-off of redundancy.
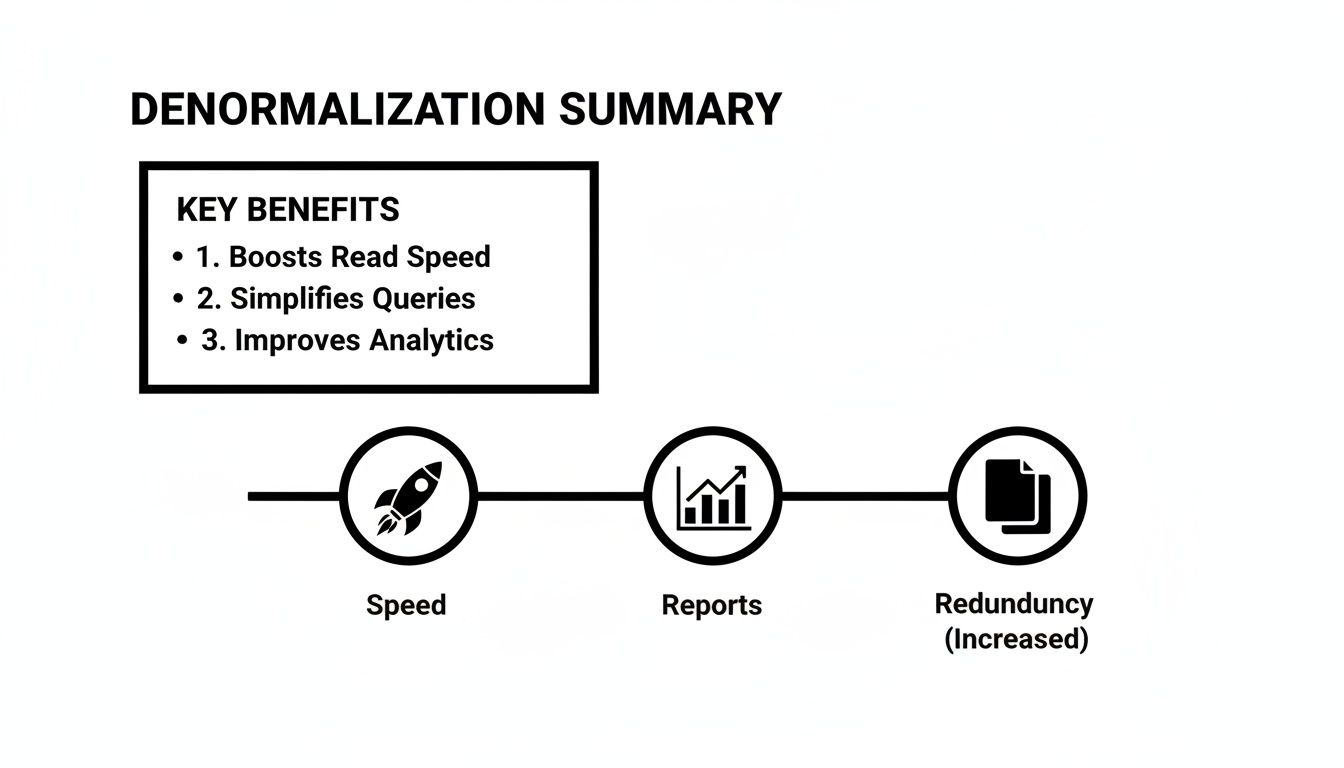
As you can see, denormalization is all about combining data to speed things up and make reporting easier, but it comes at the cost of having to manage that extra, redundant information.
Storage and Maintenance: The Hidden Costs
Back in the day, the storage argument was straightforward: normalization saves space. But with storage being so cheap now, and with powerful compression algorithms, that argument doesn't hold as much weight. The real cost today is in complexity and ongoing maintenance.
A normalized schema is usually much easier to modify and extend. Need to add a new attribute for your customers? Just add a new column to the Customers table. Done.
In a denormalized world, that same simple change might force you to update multiple tables, tweak data pipelines, and rewrite validation rules. It’s a much bigger, more coordinated effort. It's also worth remembering that how your data is structured deeply impacts how you expose it to other services; our article on API design best practices is a great read on that topic.
However, normalization has its own hidden headaches. Managing cascading updates and deletes in a deeply nested schema can become a maintenance nightmare. Sometimes, the pure simplicity of a denormalized query is well worth the extra planning on the maintenance front.
Ultimately, the battle between normalized vs denormalized data is a classic case of "it depends." You have to carefully weigh the integrity needs of your write operations against the performance demands of your read operations. If you're struggling to document these trade-offs for your team, Zemith's AI Document Assistant can help you create a clear, centralized knowledge base of your architectural decisions, keeping everyone aligned.
When to Choose Your Champion: OLTP vs. OLAP
So, how do you actually pick a side in the great debate between the neat, disciplined world of normalization and the pure, unadulterated speed of denormalization? It’s not about finding a universally “better” model. It’s about picking the right tool for the job. The entire conversation really boils down to two key concepts you’ll hear thrown around constantly: OLTP and OLAP.
Let's frame it this way: are you building the system that takes orders in a chaotic, busy restaurant kitchen, or are you building the software that generates the end-of-year financial report? One needs to handle a constant barrage of tiny, fast-paced updates with zero mistakes. The other needs to sift through a mountain of old data to spot trends. These are fundamentally different problems that demand different solutions.

OLTP Systems: The Heartbeat of Your Application
Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) systems are the engines that power the day-to-day world. They are the operational core of just about every application you use.
Think about things like:
- The checkout process on an e-commerce site.
- A money transfer in your banking app.
- Booking a flight or a hotel room online.
- Updating inventory levels in a warehouse management system.
These systems are built to handle a huge volume of small, rapid-fire transactions—mostly writes, updates, and deletes. For OLTP, data integrity is everything. You simply cannot have errors. Charging a customer twice or losing their order isn't just a bug; it's a disaster.
This is exactly why OLTP systems almost universally rely on a normalized data model. By ensuring every piece of information has one single, authoritative home, normalization makes these high-stakes transactions both safe and consistent.
OLAP Systems: The Brains of the Operation
On the other side of the coin, you have Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) systems. These are the big-picture thinkers. Their job isn’t to manage individual transactions but to comb through vast amounts of historical data to uncover trends, patterns, and valuable business insights.
We're talking about systems like:
- A company's quarterly sales dashboard.
- A report analyzing marketing campaign performance.
- A market analysis tool that forecasts future demand.
OLAP is all about running complex queries across massive datasets. Analysts need to slice, dice, and aggregate data on the fly to make smart decisions, and waiting minutes for a report to load just won't cut it. This is where denormalization truly shines. By pre-joining related data into wider, flatter tables, it delivers the blazing-fast read speeds that analytics absolutely require. For a deep dive into how critical this is, exploring banking data analytics strategies really highlights the need for speed in analytical workloads.
The core difference is simple: OLTP systems are optimized for writing data with perfect accuracy. OLAP systems are optimized for reading and analyzing that data at lightning speed.
Choosing your model really comes down to identifying your primary workload. Are you building the cash register or the accountant's ledger? The answer to that question will guide your entire database design. And once you have those insights, presenting them effectively is the next step; understanding data visualization best practices is crucial.
Trying to figure out the right mix between these two approaches can get complicated. If you're mapping out a hybrid model or just need to clearly explain your reasoning to the team, Zemith's AI document assistant can be a huge help. It's great for quickly generating clear architectural diagrams and written explanations, making sure everyone understands the "why" behind your OLTP vs. OLAP decisions.
Your Practical Decision-Making Checklist
Alright, you've seen the theory and heard the arguments. Now it's time to make a decision. Choosing between a normalized and a denormalized database isn't just a minor technicality—it’s a foundational choice that will shape how your application scales and performs.
To help you cut through the noise, here's a practical checklist to guide the conversation with your team. Think of it as a final sanity check before you commit to a path. It’s less about finding one "right" answer and more about finding the best fit for your specific needs.
Ask These Core Questions First
Before you even start whiteboarding schemas, get your team in a room and hash out these fundamental questions. A little brutal honesty here can save you from a world of refactoring pain later on.
What’s our read-to-write ratio? Will your app be hammered with constant updates, inserts, and deletes—like an e-commerce inventory system? Or will it mostly serve up data to be viewed, like a BI dashboard? A high write volume almost always points toward normalization, while a system heavy on reads will benefit from denormalization.
How catastrophic would data inconsistency be? If a customer's payment details are out of sync across two tables, you've got a serious problem. But if one metric on an internal dashboard is temporarily off, it’s probably not a crisis. The higher the cost of an anomaly, the more you need the safety of a normalized structure.
What are our team’s skills and resources? Let's be real. A denormalized model looks simple on the surface but requires more discipline and robust data pipelines to keep all that redundant data in sync. Does your team have the expertise and bandwidth to manage that complexity? Sometimes, the straightforward maintenance of a normalized database is the smarter long-term move.
The Hybrid Approach: You Don't Have to Pick a Side
Remember, this isn't always an either/or fight. Many of the most resilient systems out there cleverly refuse to choose just one, opting for a hybrid approach instead.
A common and powerful pattern is to use a normalized OLTP database for live, transactional data, then feed that data into a separate, denormalized data warehouse for all your analytics and reporting (OLAP).
This strategy truly gives you the best of both worlds. You get rock-solid data integrity for your core application and blazing-fast queries for your business analysts. It’s all about consistency where it counts and speed where you need it.
Making this call requires solid data, not just gut feelings. This is a perfect spot to lean on Zemith’s research features. Instead of just guessing, you can quickly pull up industry case studies and performance benchmarks relevant to your exact use case. It provides the evidence you need to design an architecture with confidence, making sure you’re building a scalable system based on proven patterns, not just the latest trend.
Frequently Asked Questions
Let's dive into a few questions I hear all the time when I'm in the weeds of database design. These are the quick answers to the stuff that usually trips people up.
Can I Use Both Normalization And Denormalization In The Same Application?
You absolutely can. In fact, it's pretty much standard practice for any large-scale system. You get the best of both worlds with a hybrid approach.
Your core application, the one handling all the live transactions, will almost always run on a highly normalized database like PostgreSQL. Here, data integrity is non-negotiable. Then, for analytics, you'd typically stream that data over to a separate, denormalized data warehouse—think BigQuery or Snowflake—where read speed is all that matters.
Is Denormalization Just Bad Design?
Nope, and that's a common myth. Let me be clear: accidental, messy data redundancy is definitely a sign of bad design. But denormalization is a deliberate, strategic decision to introduce controlled redundancy.
You're intentionally breaking a few normalization rules, but you're doing it with a very specific goal in mind: a massive boost in read performance. You trade a bit of storage and consistency for lightning-fast queries.
Think of it like a pro chef's workstation during a dinner rush. It might look chaotic to an outsider, but every ingredient is placed exactly where it needs to be for maximum speed. That’s denormalization.
Which Normal Form Is The Most Common In Practice?
For the vast majority of transactional databases, the Third Normal Form (3NF) is the sweet spot. It strikes a perfect balance. You get rid of the most harmful data anomalies without making your schema a nightmare to manage.
Sure, higher forms like BCNF and 4NF exist, but pushing for them often creates a tangled web of tables and complex joins that just isn't worth the trouble. Sticking to 3NF keeps things clean and efficient for real-world applications without sending your developers into a tailspin.
Navigating these architectural decisions can feel like a high-stakes chess match. When your team needs to document the "why" behind your choices, generate migration scripts, or prototype queries for both models, Zemith provides an all-in-one AI workspace to get the job done faster. Stop juggling tools and start building smarter at https://www.zemith.com.
Explore Zemith Features
Introducing Zemith
The best tools in one place, so you can quickly leverage the best tools for your needs.
All in One AI Platform
Go beyond AI Chat, with Search, Notes, Image Generation, and more.
Cost Savings
Access latest AI models and tools at a fraction of the cost.
Get Sh*t Done
Speed up your work with productivity, work and creative assistants.
Constant Updates
Receive constant updates with new features and improvements to enhance your experience.
Features
Selection of Leading AI Models
Access multiple advanced AI models in one place - featuring Gemini-2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, GPT 5, and more to tackle any tasks

Speed run your documents
Upload documents to your Zemith library and transform them with AI-powered chat, podcast generation, summaries, and more
Transform Your Writing Process
Elevate your notes and documents with AI-powered assistance that helps you write faster, better, and with less effort
Unleash Your Visual Creativity
Transform ideas into stunning visuals with powerful AI image generation and editing tools that bring your creative vision to life

Accelerate Your Development Workflow
Boost productivity with an AI coding companion that helps you write, debug, and optimize code across multiple programming languages
Powerful Tools for Everyday Excellence
Streamline your workflow with our collection of specialized AI tools designed to solve common challenges and boost your productivity

Live Mode for Real Time Conversations
Speak naturally, share your screen and chat in realtime with AI
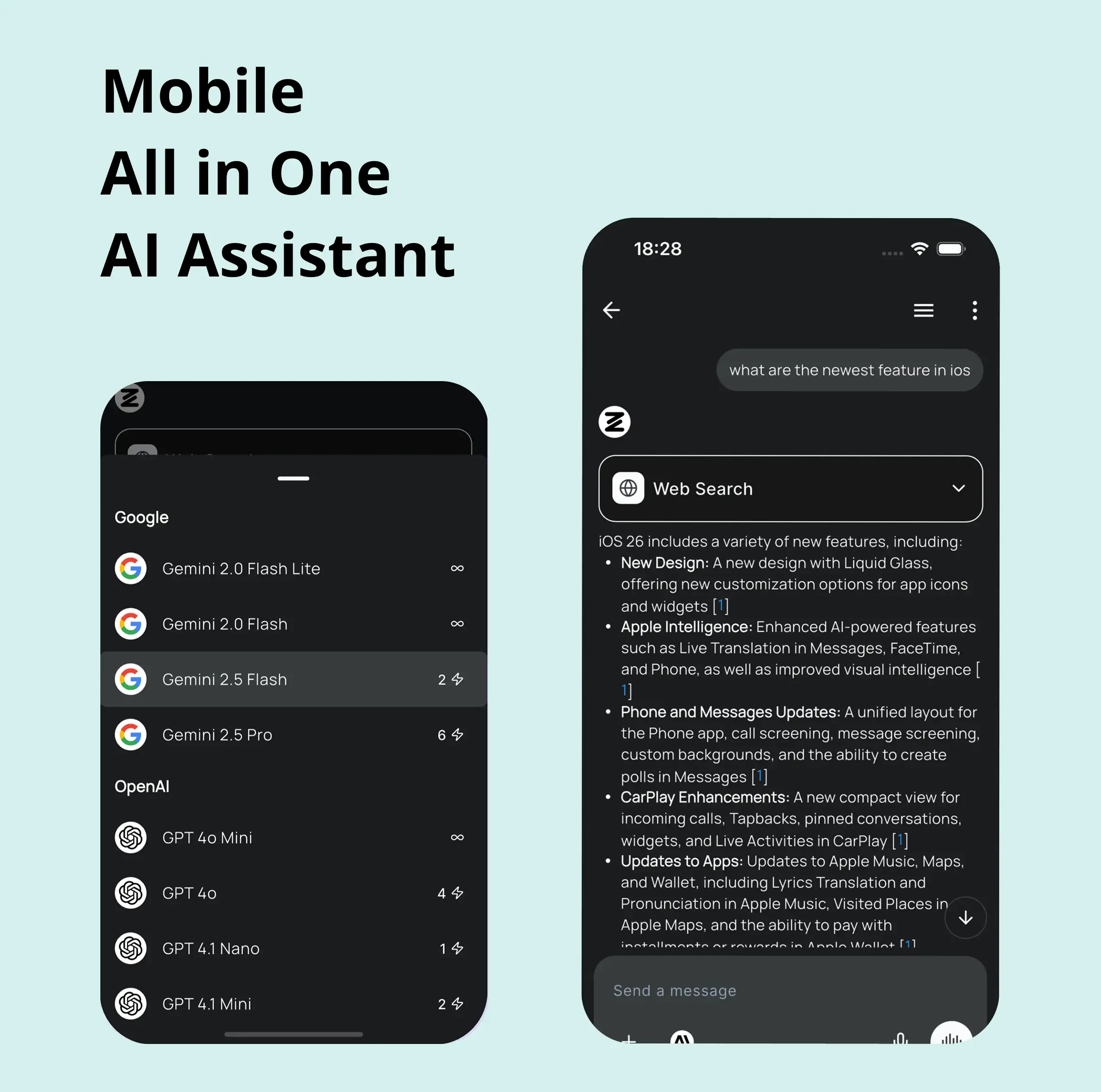
AI in your pocket
Experience the full power of Zemith AI platform wherever you go. Chat with AI, generate content, and boost your productivity from your mobile device.
Deeply Integrated with Top AI Models
Beyond basic AI chat - deeply integrated tools and productivity-focused OS for maximum efficiency
Straightforward, affordable pricing
Save hours of work and research
Affordable plan for power users
Plus
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
Professional
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
What Our Users Say
Great Tool after 2 months usage
simplyzubair
I love the way multiple tools they integrated in one platform. So far it is going in right dorection adding more tools.
Best in Kind!
barefootmedicine
This is another game-change. have used software that kind of offers similar features, but the quality of the data I'm getting back and the sheer speed of the responses is outstanding. I use this app ...
simply awesome
MarianZ
I just tried it - didnt wanna stay with it, because there is so much like that out there. But it convinced me, because: - the discord-channel is very response and fast - the number of models are quite...
A Surprisingly Comprehensive and Engaging Experience
bruno.battocletti
Zemith is not just another app; it's a surprisingly comprehensive platform that feels like a toolbox filled with unexpected delights. From the moment you launch it, you're greeted with a clean and int...
Great for Document Analysis
yerch82
Just works. Simple to use and great for working with documents and make summaries. Money well spend in my opinion.
Great AI site with lots of features and accessible llm's
sumore
what I find most useful in this site is the organization of the features. it's better that all the other site I have so far and even better than chatgpt themselves.
Excellent Tool
AlphaLeaf
Zemith claims to be an all-in-one platform, and after using it, I can confirm that it lives up to that claim. It not only has all the necessary functions, but the UI is also well-designed and very eas...
A well-rounded platform with solid LLMs, extra functionality
SlothMachine
Hey team Zemith! First off: I don't often write these reviews. I should do better, especially with tools that really put their heart and soul into their platform.
This is the best tool I've ever used. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is very fast.
reu0691
This is the best AI tool I've used so far. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is incredibly fast. Just looking at the changelogs, you can see how consistently the developers have ...
