10 Critical Reading Strategies That Actually Work (2026 Guide)
Tired of forgetting what you read? Master these 10 actionable critical reading strategies to boost comprehension, retention, and analytical skills. Start now!
Let's be real. You've spent hours reading a dense report, a technical manual, or a textbook, only to have your brain go completely blank an hour later. It feels like pouring water into a leaky bucket, right? The problem isn't your brain; it's your strategy. Most of us were taught to read, but not how to think while we read. That's where critical reading strategies come in.
This isn't about reading slower; it's about reading smarter. It’s the difference between letting words wash over you and actively wrestling with the ideas they represent. Critical reading is a hands-on, active process where you question, analyze, and evaluate the text instead of just passively accepting it. Think of it as being a detective, not just a spectator. By engaging with material this way, you'll be able to dismantle arguments, connect disparate ideas, and retain information like a pro. Before diving into specific techniques, it's essential to grasp the fundamentals of how to improve reading comprehension skills.
In this guide, we're breaking down 10 powerhouse techniques that will transform you from a passive consumer of information into an analytical powerhouse. We'll cover everything from classic academic methods like SQ3R to practical tactics like chunking and visual organization. We'll give you actionable steps, real-world scenarios, and even show you how AI tools like Zemith can give you some serious superpowers along the way. Ready to upgrade your reading OS?
1. Active Reading and Annotation
Active reading is the difference between letting words wash over you and actually having a conversation with the text. Instead of just passively consuming content, you actively engage with it by highlighting, underlining, and scribbling notes in the margins. This critical reading strategy transforms you from a spectator into an active participant, making the information stickier and much easier to recall later. Think of it as leaving breadcrumbs for your future self, so you can easily retrace your thoughts.

This method is a game-changer for anyone who needs to deeply understand and retain complex information. Academic researchers use it to deconstruct dense papers, law students annotate case studies to pinpoint legal precedents, and software developers mark up technical documentation to quickly find crucial functions. It’s all about creating a personalized map of the material that matters most to you.
How to Implement Active Annotation
Getting started is simple, but a little structure goes a long way.
- Develop a System: Don't just color everything that looks interesting. Create a consistent color-coding key before you start. For example: yellow for core concepts, blue for supporting data, and pink for confusing points you need to revisit.
- Do a Quick Skim First: Read a section or chapter once without making any marks. This gives you the lay of the land. On your second pass, you'll have a much better idea of what's actually important enough to annotate.
- Keep Notes Brief: Your marginal notes should be concise. Think questions ("Why did the author conclude this?"), summaries ("So, the main point is X."), or connections ("This links to that theory from last week.").
Pro-Tip: For digital documents, leverage AI to supercharge your annotation process. Zemith's Document Assistant can instantly highlight key passages and generate summaries from your selected text, saving you tons of time. You can even use it to create flashcards from your notes, turning your annotations into an active study tool. This practice fits perfectly with some of the best note-taking strategies available today.
2. SQ3R Method (Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review)
If active annotation is a conversation with the text, the SQ3R method is your strategic game plan for that conversation. Developed by Francis P. Robinson, this five-step process (Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review) is a structured framework that prevents you from just diving in blind. It’s one of the most powerful critical reading strategies for systematically extracting and retaining information, ensuring you don’t get to the end of a chapter and think, "Wait, what did I just read?"
This methodical approach is a lifesaver in high-stakes learning environments. Students use it to deconstruct dense textbooks for exams, researchers apply it to systematically analyze academic papers, and marketing professionals use it to break down competitor research reports. The goal is to build a mental framework first, making it easier for new information to find its place.
How to Implement the SQ3R Method
This isn't just about reading; it's about processing information in distinct, manageable phases.
- Survey: Before reading, get the lay of the land. Skim headings, subheadings, introductions, and conclusions. Look at charts or bolded terms. This initial survey creates a mental outline.
- Question: Turn those headings into questions. If a section is titled "Agile Development Cycles," ask yourself, "What are the key phases of an agile cycle?" This primes your brain to look for specific answers.
- Read & Recite: Now, read the section with the goal of answering your questions. After each part, stop and recite the key points aloud or summarize them in your own words. Don't just reread; actively recall the information.
- Review: Once you've finished, go back over your notes and the text's key sections. This final pass solidifies the information in your long-term memory.
Pro-Tip: Make the "Review" phase ridiculously easy with AI. Use Zemith's Quiz Generator to instantly create a set of practice questions from your document or notes. This automates the review process and helps you actively test your recall, which is a key technique if you want to learn how to improve your memory retention.
3. Skimming and Scanning Techniques
In a world drowning in data, skimming and scanning aren't just reading shortcuts; they're essential survival skills. These two complementary critical reading strategies help you manage information overload by treating your time as a precious resource. Skimming gives you a high-level overview of a text in seconds, while scanning is your searchlight for pinpointing specific facts or keywords. It's the difference between seeing the whole forest and instantly finding the one specific tree you need.
These techniques are the secret weapon of efficient professionals everywhere. Researchers rapidly survey dozens of academic papers to find the few that are truly relevant. Software developers scan dense API documentation to locate a single function they need to implement. Marketers fly through competitor reports, plucking out key metrics without getting bogged down in the fluff. By adjusting your reading speed to match your goal, you can process huge volumes of text without burning out.
How to Implement Skimming and Scanning
Mastering these skills is about being intentional with your reading. You're not reading for pleasure; you're on a mission.
- Skim First, Read Later: Before committing to a deep read, skim the material. Read the introduction, conclusion, headings, and the first sentence of each paragraph. This quick preview tells you if the text is worth your time and gives you a mental framework if you decide to dive in.
- Identify Scan Targets: For scanning, know exactly what you're looking for before you start. Visualize the keyword or phrase. Let your eyes glide over the page, ignoring everything else until your target word jumps out.
- Practice with a Timer: Challenge yourself to skim a news article in 60 seconds or find a specific name in a report in 30. Using a timer turns this into a focused exercise and trains your brain to process text faster.
Pro-Tip: Before you even start skimming a lengthy document, let an AI give you the cheat codes. Use Zemith’s AI features to generate an instant summary of the entire text. This gives you the core ideas immediately, helping you decide which sections deserve a closer look and which keywords you should scan for. It's like having a personal research assistant that pre-reads everything for you.
4. Contextual Reading and Background Research
Reading a text without its context is like watching a movie on mute; you get the visuals but miss the whole story. Contextual reading involves understanding a piece of writing within its broader environment, including its historical, cultural, or industry-specific background. This critical reading strategy pushes you to investigate the author, the publication date, and the source's credibility before you even accept the first sentence as fact. It's the ultimate defense against taking information at face value.
This method is indispensable for anyone whose job relies on information accuracy. Journalists use it to verify sources before publishing a story, researchers examine publication bias to ensure their work is balanced, and software developers explore the philosophical origins of design patterns to apply them correctly. You're not just reading words; you're uncovering the "why" behind them.
How to Implement Contextual Reading
Putting on your detective hat is easier than it sounds. A little prep work can completely change your understanding of a text.
- Investigate the Author and Source: Who wrote this and where was it published? A quick search on the author's credentials, affiliations, and publication history can reveal potential biases or agendas. Check the publication's reputation and editorial standards.
- Time-Travel a Little: When was the piece written? A 1990s article on AI will have a vastly different perspective than one written yesterday. Understanding the historical context prevents you from misinterpreting outdated information as current truth.
- Look for Dissenting Voices: Actively seek out conflicting viewpoints. If an article makes a bold claim, find another credible source that challenges it. This helps you map out the full landscape of the conversation, not just one curated path.
Pro-Tip: Before diving into a dense document, use an AI tool to build a "context file." With Zemith’s Smart Notepad, you can quickly compile notes on the author, publication, and key background concepts. Its real-time web search feature helps you fact-check claims and pull in related data without ever leaving your workspace, ensuring your reading is always informed. This is a foundational step in any serious research project, like when you learn how to conduct a literature review.
5. Inferential Reading and Close Reading
If active reading is having a conversation with a text, then inferential reading and close reading are like playing detective. This is where you go beyond what’s explicitly stated on the page to uncover what’s implied, assumed, or even intentionally hidden. You're not just consuming information; you're analyzing the author's choices, detecting biases, and drawing logical conclusions based on textual evidence. This is one of the most powerful critical reading strategies for deconstructing complex arguments.

This advanced skill is essential across many fields. Literary scholars use it to analyze symbolism in novels, while fact-checkers use it to spot misleading statistics or cherry-picked data. For developers, it means reviewing code comments and documentation for hidden assumptions that could break a system. It’s all about putting on your Sherlock Holmes hat and looking for clues in language, structure, and subtext.
How to Implement Close and Inferential Reading
This strategy takes patience, but it pays off with a much deeper understanding.
- Focus on Word Choice: Ask yourself, "Why did the author use this specific word and not another?" The difference between saying a policy is "satisfactory" versus "adequate" can reveal a subtle bias or underlying tone.
- Look for What’s Missing: Sometimes the most telling part of an argument is what isn't said. Is there a counter-argument that the author conveniently ignores? Is a key piece of data absent? These omissions are often deliberate and revealing.
- Analyze Sentence Structure: Are sentences long and complex, or short and punchy? The structure can influence how you interpret the information and can be a tool to persuade, confuse, or clarify.
Pro-Tip: When you're stuck on a dense passage, use an AI tool to help you see it from a new angle. With Zemith's Document Assistant, you can ask it to generate alternative interpretations or identify underlying assumptions in the text. This practice is a fantastic way to sharpen your analytical abilities and improve your critical thinking skills by comparing your own inferences against an AI-generated analysis.
6. Comparative and Analytical Reading
Reading one source gives you a single perspective. Reading several sources on the same topic is where true understanding begins. This is the core of comparative and analytical reading: instead of taking one author's word as gospel, you become a detective, piecing together a more complete picture from multiple viewpoints. This critical reading strategy pushes you to identify similarities, contradictions, and hidden patterns across different texts.
This method is the bedrock of rigorous research and smart decision-making. Researchers use it to compare methodologies across academic papers, marketers analyze competitor strategies to find market gaps, and policy analysts evaluate data from multiple sources to form balanced recommendations. It’s about synthesizing information, not just summarizing it, allowing you to form a sophisticated and evidence-based judgment.
How to Implement Comparative and Analytical Reading
Juggling multiple sources can feel like herding cats, but a structured approach makes it manageable.
- Create a Comparison Matrix: Don't try to hold everything in your head. Use a simple table or matrix to track key elements across sources. Columns could include: Author's Main Argument, Key Evidence, Methodology, and Stated Biases. This makes spotting patterns and contradictions much easier.
- Summarize First, Compare Second: Before you start comparing, make sure you understand each source on its own. Create a concise summary of each text, focusing on its core thesis and supporting points. This prevents you from getting lost in the details later.
- Look for Consensus and Outliers: As you compare, note where the authors agree. This consensus often points to a well-established fact. Pay even closer attention to the outliers. Why does one source disagree with all the others? This is often where the most interesting insights are found.
Pro-Tip: Streamline your multi-source analysis with Zemith's Projects. You can create a dedicated Project for your topic, upload all relevant documents, and use the Document Assistant to generate an initial summary for each one. Then, use Zemith's Smart Notepad to build your comparison matrix side-by-side with your sources, creating a powerful hub for your analytical work.
7. Reciprocal Teaching and Questioning Strategies
Reciprocal teaching turns reading from a solo mission into a collaborative brain-building exercise. This strategy involves a structured dialogue about a text, rotating through four key roles: predicting, clarifying, questioning, and summarizing. It's a powerful way to deconstruct complex information as a group, ensuring everyone is on the same page and actively building meaning together rather than just passively reading.
This method shines in any collaborative environment. Study groups use it to tackle dense textbook chapters, research teams apply it to analyze academic papers, and even software development teams can use it to collectively understand technical documentation for a new API. By making thinking visible through conversation, you uncover insights you might have missed on your own. It's one of the most effective group-based critical reading strategies out there.
How to Implement Reciprocal Teaching
To get started, assign one of the four roles to each person for a specific section of the text.
- Predict: Before reading, have one person predict what the text will be about based on the title, headings, and any prior knowledge. This sets a purpose for reading.
- Clarify: During or after reading, the clarifier points out confusing parts, unfamiliar vocabulary, or complex ideas. The group then works together to clear things up.
- Question: The questioner’s job is to ask thought-provoking questions about the text. These should go beyond simple recall and dig into the "why" and "how" of the author's arguments.
- Summarize: Finally, the summarizer concisely restates the main ideas and key points from the section, ensuring the group has a shared understanding before moving on.
Pro-Tip: You can supercharge these questioning strategies with AI. Use Zemith’s Document Assistant to generate a list of potential discussion questions from any document instantly. Then, bring your group into a Zemith AI Live Mode session to have a dynamic, AI-facilitated conversation about the text, ensuring your discussion stays on track and digs deep into the core concepts. This tech-driven approach makes collaboration more focused and productive.
8. Chunking and Segmentation Method
Ever tried to eat an entire pizza in one bite? Probably not, and you shouldn't try it with a dense document either. The chunking and segmentation method is the intellectual equivalent of slicing that pizza. Instead of tackling a massive text all at once, you break it into smaller, manageable segments. This approach systematically reduces cognitive overload, making it one of the most effective critical reading strategies for digesting complex material without getting mental indigestion.
This strategy is a lifesaver for anyone facing a wall of text. Developers use it to master lengthy API documentation by focusing on one endpoint at a time, while academic researchers process dense scholarly articles section by section to isolate key findings. It’s all about creating natural stopping points to process, summarize, and integrate information before you get overwhelmed and your brain starts to buffer.
How to Implement the Chunking Method
Chunking is simple in theory, but a little structure makes it powerful in practice.
- Use Existing Structure: Most well-written documents are already organized for you. Use headings, subheadings, and even long paragraphs as your natural chunk boundaries.
- Summarize Before You Move On: At the end of each chunk, stop and write a one or two-sentence summary. This forces you to confirm you've actually understood the material before proceeding to the next segment.
- Set Time-Based Chunks: For less structured texts, try a time-based approach. Use the Pomodoro Technique: read and process for 25 minutes, then take a 5-minute break to summarize and recharge.
Pro-Tip: Don't guess where a text's natural breaks are. Use Zemith’s Document Assistant to analyze the document structure and suggest logical segments. You can then use the Smart Notepad to create a progress tracker, jotting down your summary for each chunk as you complete it, turning a daunting task into a series of small, satisfying wins. This is a great way to stay organized when applying critical reading skills.
9. Visual and Graphic Organizer Reading
Some brains just think better in pictures, and that's where this critical reading strategy shines. Visual and Graphic Organizer Reading is all about translating linear text into spatial, non-linear diagrams. Instead of just reading words in a line, you actively map out the relationships between ideas using tools like mind maps, flowcharts, or concept diagrams. This process forces you to identify the core structure of a text, see hidden connections, and understand complex hierarchies at a glance.
This method is a lifeline when you're dealing with dense, interconnected information. Software developers use it to map out system architecture from technical documentation, making sense of how different components interact. Marketers visualize the customer journey from research reports, and researchers create concept maps to synthesize findings from dozens of academic papers. It turns an overwhelming wall of text into a clear, navigable visual story.
How to Implement Visual Reading
Ready to turn your reading into art? Here’s how to get started without getting tangled up.
- Start Simple: Don't try to build a massive, all-encompassing chart from the get-go. Begin with a central idea and branch out with main topics. You can always add more detail and complexity later as you read deeper.
- Color-Code Your Concepts: Assign specific colors to different categories of information. For instance, use green for key arguments, orange for supporting evidence, and red for counterarguments or questions. This makes your map instantly scannable.
- Use Different Organizers for Different Texts: A flowchart is perfect for understanding a process described in a user manual. A mind map is great for brainstorming connections in a creative brief. A Venn diagram can help you compare and contrast theories in a research paper. Match the tool to the task.
Pro-Tip: Digital tools can make this process dynamic and collaborative. Zemith's Whiteboard is perfect for creating and sharing visual organizers. You can easily drag and drop concepts, connect ideas, and refine your map as your understanding evolves. For more ways to organize your thoughts visually, check out these powerful mind mapping techniques.
10. Metacognitive Monitoring and Self-Assessment
Metacognitive monitoring is essentially thinking about your own thinking while you read. It's the inner voice that stops you mid-paragraph and asks, "Wait, do I actually get this?" Instead of passively absorbing words, you’re actively checking your comprehension, identifying when it fails, and deciding what to do about it. This is one of the most powerful critical reading strategies because it turns you into a self-sufficient, adaptable learner.
This strategy is crucial for anyone tackling dense or unfamiliar material. A developer reading new API documentation will pause to recognize when a concept isn't clicking and research it further. A researcher uses it to notice when an author's argument conflicts with their existing knowledge, prompting a deeper investigation. It’s all about creating a feedback loop between the text and your brain, ensuring you're not just reading, but truly understanding.
How to Implement Metacognitive Monitoring
Building this self-awareness takes practice, but these steps make it much more manageable.
- Schedule Check-Ins: Don't wait until the end of a chapter to realize you're lost. Pause after every section or every few paragraphs and ask yourself, "What was the main point of that?" or "Can I explain this to someone else?"
- Keep a 'Confusion Log': When you hit a roadblock, don't just skip it. Jot down the confusing point or question in a dedicated notebook. This externalizes the problem, making it easier to solve later without breaking your reading flow.
- Test Yourself Honestly: Don't just assume you've learned something. To effectively monitor your comprehension and consolidate learning, consider active recall techniques like the 'Blurt' method, where you write down everything you remember after reading. This reveals what actually stuck.
Pro-Tip: Make self-assessment an integrated part of your workflow with AI. Use Zemith’s Smart Notepad to create a dedicated 'Confusion Log' you can easily reference. After reading, use the Quiz Generator to create a pop quiz from the text, giving you instant, unbiased feedback on what you truly understood versus what you just skimmed over.
Critical Reading: 10-Strategy Comparison
| Method | Complexity 🔄 | Resources & Tools 💡 | Speed / Efficiency ⚡ | Expected Outcomes ⭐📊 | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active Reading and Annotation | 🔄 Moderate — active, iterative | 💡 Moderate — highlighters, notes, digital annotation tools (e.g., Zemith) | ⚡ Low — time-intensive per text | ⭐ High — better retention & quick review | Researchers, students, knowledge workers |
| SQ3R (Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review) | 🔄 High — structured five-step process | 💡 Low–Moderate — note taking, time blocks, quiz tools (Zemith) | ⚡ Low — slower but thorough | ⭐⭐ Very high — improved comprehension & long-term retention | Students preparing for exams, systematic reviewers |
| Skimming and Scanning | 🔄 Low — skill-based, practice required | 💡 Low — timers, summaries, keyword lists, AI summaries | ⚡ Very high — fast triage of large volumes | ⭐ Moderate — good for overview, may miss nuance | News review, initial literature triage, quick lookups |
| Contextual Reading & Background Research | 🔄 High — multi-source investigation | 💡 High — web search, fact-checking, multiple sources (Zemith Deep Research) | ⚡ Low — slow due to research | ⭐ High — critical evaluation and source reliability | Journalists, content creators, researchers assessing credibility |
| Inferential / Close Reading | 🔄 Very high — detailed, iterative analysis | 💡 Moderate — annotations, comparative notes, AI help for interpretations | ⚡ Very low — extremely time-consuming | ⭐⭐ Very high — deep insight into subtext, bias, assumptions | Literary scholars, critical analysts, methodologists |
| Comparative & Analytical Reading | 🔄 High — multi-source synthesis | 💡 High — multiple documents, comparison matrices, Projects (Zemith) | ⚡ Low — time-intensive synthesis | ⭐⭐ Very high — comprehensive understanding, bias detection | Researchers, policy analysts, competitive intelligence |
| Reciprocal Teaching & Questioning | 🔄 High — collaborative facilitation needed | 💡 Moderate — group, facilitator, quiz/whiteboard tools (Zemith) | ⚡ Low — slower due to discussion | ⭐ High — improved comprehension and metacognition | Classrooms, study groups, team research sessions |
| Chunking & Segmentation | 🔄 Low–Moderate — divide-and-conquer approach | 💡 Low — headings, timers, summarization tools (Zemith) | ⚡ Moderate — maintains pace, reduces overload | ⭐ High — improved manageability and retention | Long technical docs, dense textbooks, API docs |
| Visual & Graphic Organizer Reading | 🔄 Moderate — requires design choices | 💡 Moderate–High — whiteboards, mind‑map tools, visual templates (Zemith Whiteboard) | ⚡ Moderate — upfront time to build visuals | ⭐ High — strong retention and clarity of relationships | Visual learners, architecture mapping, presentations |
| Metacognitive Monitoring & Self‑Assessment | 🔄 High — continuous self-regulation | 💡 Low–Moderate — logs, self-quizzes, Smart Notepad (Zemith) | ⚡ Low — slows reading but increases accuracy | ⭐ High — reduces illusion of understanding, targeted remediation | Independent learners, complex material, skill development |
Your Turn: Go from Reader to Super-Reader
We've just unpacked a treasure chest of ten powerful critical reading strategies, from the foundational Active Reading and Annotation to the analytical power of Comparative Reading and the self-awareness of Metacognitive Monitoring. It’s a lot to take in, but here's the secret: you don't need to become a master of all ten overnight. You just need to start.
The journey from passive reader to active, critical thinker isn't about memorizing acronyms or forcing yourself through a rigid process. It's about building an adaptable toolkit. Think of these strategies as different lenses. You wouldn't use a microscope to look at the stars, and you wouldn't use a telescope to examine a cell. Similarly, you'll choose your critical reading strategy based on your goal.
The Mix-and-Match Approach to Critical Reading
The real magic happens when you start combining these techniques and tailoring them to your specific needs. Here’s a quick recap of how these strategies fit different scenarios:
For Deep Learning & Retention: Pair the SQ3R Method with Reciprocal Teaching. Create your initial questions (Q in SQ3R), and then deepen them with the four questioning roles of Reciprocal Teaching (questioning, clarifying, summarizing, predicting) as you read. This combo is unbeatable for academic study or mastering a complex new subject.
For Rapid Research & Analysis: Start with Skimming and Scanning to triage a large volume of articles. Once you’ve identified the most relevant documents, switch to Comparative Reading to synthesize insights, identify patterns, and spot contradictions across sources. This is a game-changer for researchers and market analysts.
For Technical Documentation & Dense Manuals: The Chunking and Segmentation Method is your best friend here. Break down those intimidating walls of text into manageable sections. Then, use Visual Organizers like flowcharts or diagrams to map out processes and relationships, turning abstract instructions into a concrete visual guide. Software developers and engineers, this one's for you.
For Creative & Persuasive Content: When analyzing a marketing campaign, a novel, or a political speech, Inferential Reading is key. Dig beneath the surface to understand the author's intent, tone, and unstated assumptions. Combine this with Contextual Reading to understand the cultural, historical, or social forces that shaped the text. This gives you a 360-degree view of the message.
Making It a Habit, Not a Chore
The most important takeaway is this: critical reading is a skill, and like any skill, it improves with consistent practice. It's a mental muscle. You wouldn't expect to go to the gym once and be a bodybuilder. Likewise, applying one of these strategies just once won't instantly make you a super-reader.
So, start small. Pick one strategy that resonates with you and apply it to the next article, report, or chapter you read. Maybe it’s just grabbing a highlighter and actively annotating. Or perhaps it’s taking five minutes to "Survey" a document before diving in. Celebrate that small win. The goal is to build momentum until these practices become second nature.
Ultimately, mastering these critical reading strategies is about more than just getting through your reading list faster. It's about reclaiming your focus in a world saturated with information. It’s about transforming from a passive consumer of content into an active, discerning creator of knowledge. You gain the power to question assumptions, connect disparate ideas, and build a truly deep understanding of any topic you choose. That's not just a study skill; it's a life skill.
Ready to put these strategies on steroids? While you focus on the deep thinking, let Zemith handle the heavy lifting of summarizing dense documents, generating flashcards for review, and organizing your insights. Supercharge your critical reading workflow by trying Zemith today and see how smart automation can unlock your full intellectual potential.
Explore Zemith Features
Introducing Zemith
The best tools in one place, so you can quickly leverage the best tools for your needs.
All in One AI Platform
Go beyond AI Chat, with Search, Notes, Image Generation, and more.
Cost Savings
Access latest AI models and tools at a fraction of the cost.
Get Sh*t Done
Speed up your work with productivity, work and creative assistants.
Constant Updates
Receive constant updates with new features and improvements to enhance your experience.
Features
Selection of Leading AI Models
Access multiple advanced AI models in one place - featuring Gemini-2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, GPT 5, and more to tackle any tasks

Speed run your documents
Upload documents to your Zemith library and transform them with AI-powered chat, podcast generation, summaries, and more
Transform Your Writing Process
Elevate your notes and documents with AI-powered assistance that helps you write faster, better, and with less effort
Unleash Your Visual Creativity
Transform ideas into stunning visuals with powerful AI image generation and editing tools that bring your creative vision to life

Accelerate Your Development Workflow
Boost productivity with an AI coding companion that helps you write, debug, and optimize code across multiple programming languages
Powerful Tools for Everyday Excellence
Streamline your workflow with our collection of specialized AI tools designed to solve common challenges and boost your productivity

Live Mode for Real Time Conversations
Speak naturally, share your screen and chat in realtime with AI
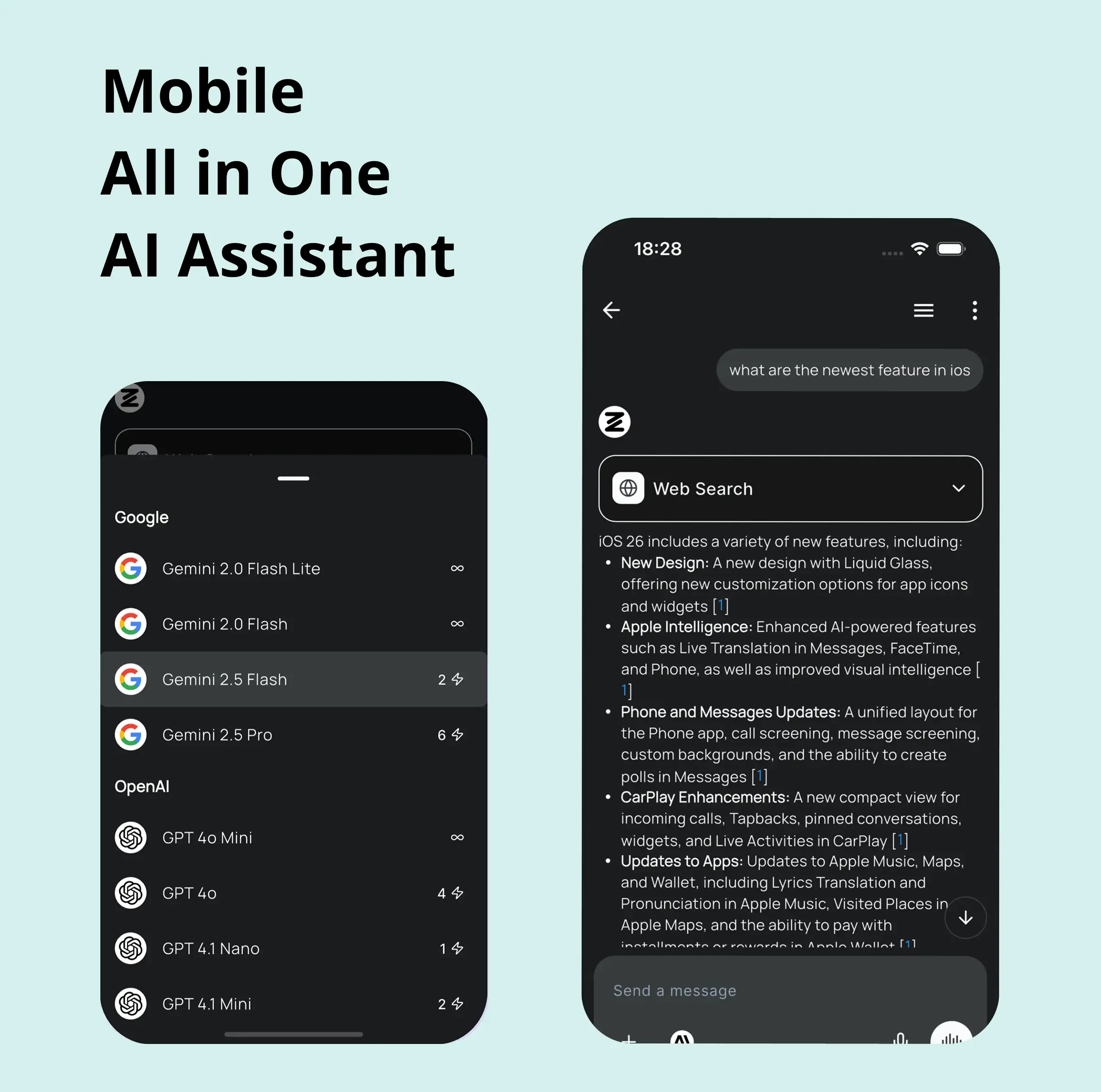
AI in your pocket
Experience the full power of Zemith AI platform wherever you go. Chat with AI, generate content, and boost your productivity from your mobile device.
Deeply Integrated with Top AI Models
Beyond basic AI chat - deeply integrated tools and productivity-focused OS for maximum efficiency
Straightforward, affordable pricing
Save hours of work and research
Affordable plan for power users
Plus
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
Professional
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
What Our Users Say
Great Tool after 2 months usage
simplyzubair
I love the way multiple tools they integrated in one platform. So far it is going in right dorection adding more tools.
Best in Kind!
barefootmedicine
This is another game-change. have used software that kind of offers similar features, but the quality of the data I'm getting back and the sheer speed of the responses is outstanding. I use this app ...
simply awesome
MarianZ
I just tried it - didnt wanna stay with it, because there is so much like that out there. But it convinced me, because: - the discord-channel is very response and fast - the number of models are quite...
A Surprisingly Comprehensive and Engaging Experience
bruno.battocletti
Zemith is not just another app; it's a surprisingly comprehensive platform that feels like a toolbox filled with unexpected delights. From the moment you launch it, you're greeted with a clean and int...
Great for Document Analysis
yerch82
Just works. Simple to use and great for working with documents and make summaries. Money well spend in my opinion.
Great AI site with lots of features and accessible llm's
sumore
what I find most useful in this site is the organization of the features. it's better that all the other site I have so far and even better than chatgpt themselves.
Excellent Tool
AlphaLeaf
Zemith claims to be an all-in-one platform, and after using it, I can confirm that it lives up to that claim. It not only has all the necessary functions, but the UI is also well-designed and very eas...
A well-rounded platform with solid LLMs, extra functionality
SlothMachine
Hey team Zemith! First off: I don't often write these reviews. I should do better, especially with tools that really put their heart and soul into their platform.
This is the best tool I've ever used. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is very fast.
reu0691
This is the best AI tool I've used so far. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is incredibly fast. Just looking at the changelogs, you can see how consistently the developers have ...
